Judicial misconduct undermines the integrity of the legal system, leading to biased decisions and eroding public trust in courts. Common forms include corruption, bias, and abuse of authority, affecting the fairness and impartiality of judicial proceedings. Explore the rest of the article to understand how judicial misconduct impacts justice and what measures protect your rights.
Table of Comparison
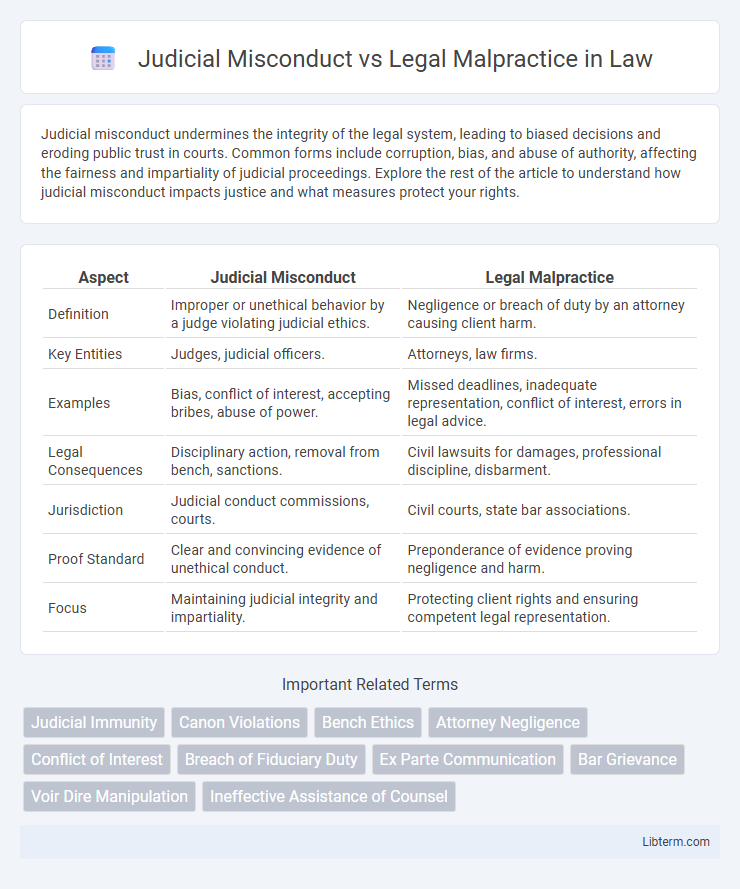
| Aspect | Judicial Misconduct | Legal Malpractice |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Improper or unethical behavior by a judge violating judicial ethics. | Negligence or breach of duty by an attorney causing client harm. |
| Key Entities | Judges, judicial officers. | Attorneys, law firms. |
| Examples | Bias, conflict of interest, accepting bribes, abuse of power. | Missed deadlines, inadequate representation, conflict of interest, errors in legal advice. |
| Legal Consequences | Disciplinary action, removal from bench, sanctions. | Civil lawsuits for damages, professional discipline, disbarment. |
| Jurisdiction | Judicial conduct commissions, courts. | Civil courts, state bar associations. |
| Proof Standard | Clear and convincing evidence of unethical conduct. | Preponderance of evidence proving negligence and harm. |
| Focus | Maintaining judicial integrity and impartiality. | Protecting client rights and ensuring competent legal representation. |
Definition of Judicial Misconduct
Judicial misconduct refers to inappropriate or unethical behavior by a judge that violates judicial codes of conduct, such as bias, conflicts of interest, or abuse of authority during court proceedings. It undermines the integrity of the judiciary and can result in disciplinary actions or removal from the bench. Legal malpractice, in contrast, involves negligence or breach of duty by an attorney in providing legal services to a client.
Understanding Legal Malpractice
Legal malpractice occurs when an attorney fails to perform their duties competently, resulting in harm to the client, often due to negligence, breach of fiduciary duty, or inadequate representation. Judicial misconduct involves judges violating ethical standards, such as bias or abuse of power, but does not directly harm clients through legal service errors. Understanding legal malpractice requires recognizing the attorney's professional obligations and the necessity for clients to prove a direct link between the lawyer's negligence and the damages incurred.
Key Differences Between Judicial Misconduct and Legal Malpractice
Judicial misconduct involves improper or unethical behavior by judges, such as bias, corruption, or abuse of judicial power, which undermines the integrity of the judicial system. Legal malpractice refers to negligence or misconduct by attorneys, including errors, omissions, or breach of fiduciary duty, that causes harm to a client. The key difference lies in the roles and responsibilities: judicial misconduct pertains to judges violating judicial ethics, while legal malpractice concerns attorneys failing to provide competent legal services.
Common Examples of Judicial Misconduct
Common examples of judicial misconduct include bias or prejudice affecting impartiality, accepting bribes or engaging in corruption, and improperly influencing the outcome of a case. Other instances involve conflicts of interest, inappropriate communication with parties outside the courtroom, and failure to follow legal procedures or ethical standards. These actions undermine the integrity of the judicial system and can lead to appeals or disciplinary action against judges.
Common Examples of Legal Malpractice
Common examples of legal malpractice include missing critical deadlines, failure to properly investigate cases, inadequate client communication, and conflicts of interest affecting representation quality. Judicial misconduct, distinct from legal malpractice, involves inappropriate behavior by judges such as bias, abuse of power, or ethical violations during court proceedings. Legal malpractice claims specifically address attorney negligence that causes harm to clients, whereas judicial misconduct pertains to violations of judicial ethics and impartiality.
Legal Consequences for Judicial Misconduct
Judicial misconduct involves violations of ethical standards or abuse of judicial power, resulting in disciplinary actions such as censure, suspension, or removal from the bench. Legal consequences for judicial misconduct can include formal judicial discipline, forfeiture of judicial office, and potential criminal charges depending on the severity of the actions. Unlike legal malpractice, which leads to civil liability and damages claims against attorneys, judicial misconduct primarily triggers administrative and criminal penalties aimed at preserving the integrity of the judiciary.
Legal Ramifications of Legal Malpractice
Legal malpractice occurs when an attorney fails to competently perform their legal duties, resulting in harm to the client and potential financial losses. The legal ramifications include civil lawsuits for negligence, breach of contract, or breach of fiduciary duty, often leading to compensatory damages awarded to the injured party. Courts may impose sanctions on the attorney, and malpractice claims can also damage professional reputations and lead to disciplinary actions by state bar associations.
Reporting and Investigating Judicial Misconduct
Reporting judicial misconduct involves filing complaints with judicial conduct commissions or ethics boards responsible for overseeing judges' behavior and ensuring accountability. Investigations into judicial misconduct are typically conducted by specialized committees that evaluate evidence, conduct hearings, and recommend disciplinary actions such as censure, suspension, or removal from the bench. Unlike legal malpractice claims, which are pursued through civil litigation against attorneys for professional negligence, judicial misconduct cases emphasize maintaining judicial integrity and public trust through administrative and regulatory procedures.
Filing a Legal Malpractice Claim
Filing a legal malpractice claim requires proving that an attorney breached the standard of care, directly causing financial harm to the client, whereas judicial misconduct involves unethical or illegal actions by a judge, such as bias or corruption. Legal malpractice claims focus on attorney negligence during case handling, with evidence including missed deadlines or inadequate representation. Judicial misconduct complaints are typically addressed through judicial review boards, while malpractice claims proceed through civil litigation.
Preventing Judicial Misconduct and Legal Malpractice
Preventing judicial misconduct involves enforcing strict ethical codes and continuous judicial training to uphold impartiality and integrity in the legal system. Legal malpractice can be avoided by ensuring thorough client communication, diligent case management, and adherence to professional standards by attorneys. Both judicial and legal professionals benefit from transparent accountability mechanisms to maintain public trust and reduce instances of abuse or negligence.
Judicial Misconduct Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com