Legislative history offers crucial insights into the intent and purpose behind laws, helping to clarify ambiguous legal provisions and guide judicial interpretation. Understanding the context, debates, and amendments during the legislative process enhances your ability to analyze statutes accurately. Explore the rest of the article to discover how legislative history can impact legal research and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
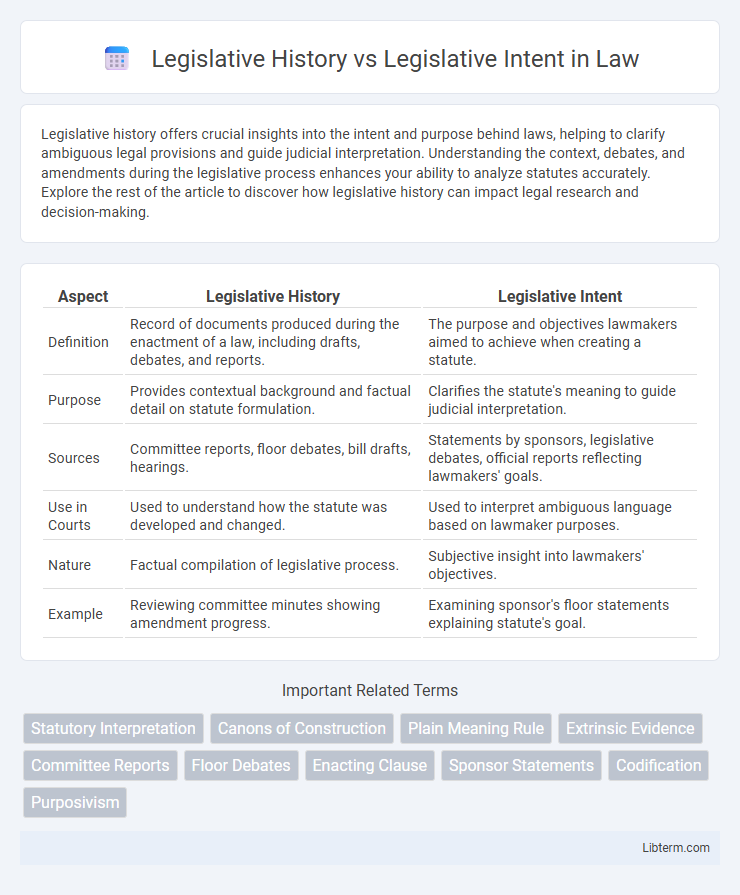
| Aspect | Legislative History | Legislative Intent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Record of documents produced during the enactment of a law, including drafts, debates, and reports. | The purpose and objectives lawmakers aimed to achieve when creating a statute. |
| Purpose | Provides contextual background and factual detail on statute formulation. | Clarifies the statute's meaning to guide judicial interpretation. |
| Sources | Committee reports, floor debates, bill drafts, hearings. | Statements by sponsors, legislative debates, official reports reflecting lawmakers' goals. |
| Use in Courts | Used to understand how the statute was developed and changed. | Used to interpret ambiguous language based on lawmaker purposes. |
| Nature | Factual compilation of legislative process. | Subjective insight into lawmakers' objectives. |
| Example | Reviewing committee minutes showing amendment progress. | Examining sponsor's floor statements explaining statute's goal. |
Introduction to Legislative History and Legislative Intent
Legislative history refers to the official records and documents generated during the creation, consideration, and passage of a law, including drafts, committee reports, hearings, and floor debates. Legislative intent focuses on understanding the purpose and objectives that lawmakers aimed to achieve through the statute. Examining legislative history provides context and aids in interpreting legislative intent to clarify ambiguous statutory language.
Defining Legislative History
Legislative history refers to the collection of documents produced during the creation of a statute, including committee reports, floor debates, drafts, and hearing transcripts, which courts examine to interpret ambiguous laws. Defining legislative history involves identifying these materials as evidence that reflects how lawmakers debated, shaped, and anticipated the application of a statute. Unlike legislative intent, which seeks the purpose or objective lawmakers aimed to achieve, legislative history provides the contextual background essential for understanding the statute's meaning.
Understanding Legislative Intent
Understanding legislative intent involves analyzing the purpose and objectives lawmakers aimed to achieve when drafting a statute, providing critical insight into ambiguous or complex legal provisions. This analysis relies on sources such as committee reports, floor debates, sponsor statements, and earlier drafts to clarify possible interpretations and ensure that judicial decisions align with the law's intended goals. Distinguishing legislative intent from legislative history is essential because intent focuses on the underlying objectives, while legislative history encompasses all documents and records produced during the lawmaking process.
Key Differences Between Legislative History and Legislative Intent
Legislative history comprises the official records and documents produced during the lawmaking process, such as committee reports, debates, and drafts, providing a comprehensive context for statutory interpretation. Legislative intent refers specifically to the lawmakers' purpose and goals behind enacting a statute, focusing on their desired outcomes and policy objectives. The key difference lies in legislative history being a broad collection of materials, while legislative intent zeroes in on the lawmakers' actual rationale and aims guiding the legislation.
Importance of Legislative History in Legal Interpretation
Legislative history provides a comprehensive record of the statutes' development, including committee reports, drafts, and floor debates, offering crucial insight into the lawmakers' objectives. Courts rely on legislative history to clarify ambiguities in statutory language by understanding the broader context and policy considerations behind a law's enactment. This practice enhances precise legal interpretation, ensuring that judicial decisions align with the substantive goals intended by the legislature.
Role of Legislative Intent in Judicial Decisions
Legislative intent plays a crucial role in judicial decisions by guiding courts in interpreting ambiguous statutory language to reflect the purpose behind the legislation. Judges analyze legislative history, such as committee reports and floor debates, to uncover the lawmakers' objectives and ensure rulings align with the statute's intended goals. This approach helps maintain legal consistency and upholds the democratic values embedded in the legislative process.
Methods for Determining Legislative History
Methods for determining legislative history include analyzing committee reports, floor debates, and sponsor statements to uncover the context and purpose behind a law's enactment. Courts and legal scholars prioritize official documents such as bill drafts, amendments, and legislative journals to trace the evolution of the statute. Examining these sources helps clarify legislative intent by revealing lawmakers' objectives and the statute's intended application.
Tools for Uncovering Legislative Intent
Legislative history encompasses the collection of documents such as committee reports, congressional debates, and bill drafts that provide insight into the context and development of legislation. Tools for uncovering legislative intent include examining committee hearings, floor debates, sponsor statements, and legislative amendments to interpret lawmakers' purpose behind a statute. Legal professionals rely on these historical materials to clarify ambiguous statutory language and ensure judicial decisions align with the legislature's original objectives.
Challenges in Distinguishing History from Intent
Distinguishing legislative history from legislative intent presents challenges due to the ambiguity and inconsistency of source materials such as committee reports, floor debates, and sponsor statements. Legislative history reflects the chronological development of legislation, but it often contains conflicting perspectives that complicate identifying a unified legislative intent. Courts and legal scholars must navigate these discrepancies to determine the true purpose behind statutory provisions, creating interpretive difficulties in applying the law.
Practical Implications for Legal Practitioners
Understanding legislative history involves analyzing committee reports, debates, and drafts to clarify ambiguous statutes, while legislative intent focuses on the purpose lawmakers aimed to achieve. Legal practitioners rely on legislative history to interpret complex or vague provisions, helping courts ascertain context and application, whereas legislative intent guides advocacy strategies to align arguments with statutory goals. Mastery of both concepts enables effective statutory construction, influencing case outcomes and ensuring compliance with legislative objectives.
Legislative History Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com