Provision ensures the necessary resources or arrangements are available to meet specific needs or requirements efficiently. Proper provision plays a critical role in project success, disaster management, and everyday planning by preventing shortages and delays. Discover how optimizing provision strategies can improve your outcomes in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
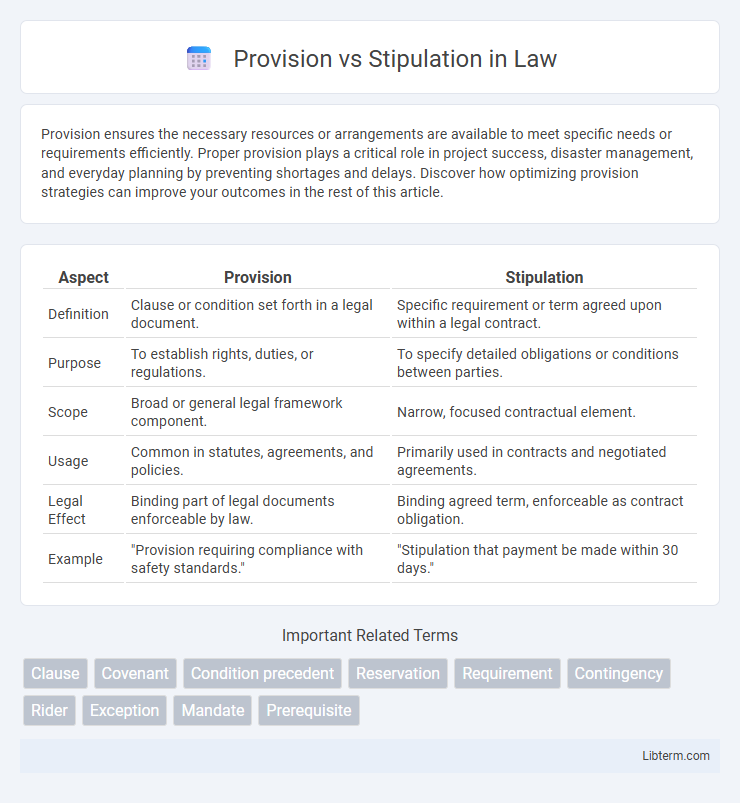
| Aspect | Provision | Stipulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clause or condition set forth in a legal document. | Specific requirement or term agreed upon within a legal contract. |
| Purpose | To establish rights, duties, or regulations. | To specify detailed obligations or conditions between parties. |
| Scope | Broad or general legal framework component. | Narrow, focused contractual element. |
| Usage | Common in statutes, agreements, and policies. | Primarily used in contracts and negotiated agreements. |
| Legal Effect | Binding part of legal documents enforceable by law. | Binding agreed term, enforceable as contract obligation. |
| Example | "Provision requiring compliance with safety standards." | "Stipulation that payment be made within 30 days." |
Understanding Provision and Stipulation: Definitions
Provision refers to a specific clause or condition within a legal document, contract, or agreement that outlines obligations, rights, or requirements for the parties involved. Stipulation is a formal agreement or condition mutually agreed upon by parties in a legal context, often specifying particular terms or facts to be accepted without dispute. Understanding the distinction between provision as a codified clause and stipulation as an agreed condition is essential for accurately interpreting legal texts and contracts.
Key Differences Between Provision and Stipulation
A provision is a broad clause within a contract that outlines rights, obligations, or conditions, whereas a stipulation refers to a specific requirement or condition agreed upon by the parties involved. Provisions typically set the overall framework of the agreement, while stipulations detail particular terms that must be met or actions to be taken. Understanding the distinction helps clarify contract interpretation and compliance, as provisions guide the general structure and stipulations govern precise commitments.
Legal Context: How Provisions and Stipulations Are Applied
Legal provisions are specific clauses within contracts or statutes that define rights, duties, or conditions, establishing enforceable rules between parties. Stipulations serve as agreed-upon terms or conditions negotiated and accepted during legal proceedings or contract formation to resolve particular issues or clarify obligations. Both provisions and stipulations function to structure legal agreements, yet provisions are formalized elements of law or contracts, while stipulations often represent negotiated or procedural agreements within the legal process.
Types of Provisions and Stipulations in Contracts
Contracts contain various types of provisions and stipulations that define rights and obligations. Provisions include essential clauses such as payment terms, confidentiality agreements, and termination conditions, while stipulations often specify conditions or requirements that parties must meet, like quality standards or delivery schedules. Understanding these distinct elements ensures clearer contract interpretation and effective enforcement.
Drafting Effective Provisions and Stipulations
Drafting effective provisions and stipulations requires clear, precise language that eliminates ambiguity to ensure enforceability in legal agreements. Provisions serve as the fundamental clauses outlining rights and obligations, while stipulations specify conditions or requirements tied to performance or compliance. Utilizing semantic clarity and context-specific terminology enhances interpretability and reduces potential disputes during contract execution.
Common Examples in Legal Agreements
Provisions in legal agreements often include payment terms, confidentiality clauses, and termination conditions, setting the framework for parties' rights and obligations. Stipulations specify detailed requirements such as deadlines for performance, quality standards, or documentation needed to fulfill contractual duties. Common examples include non-disclosure provisions safeguarding sensitive information and stipulations outlining delivery schedules or penalties for breach.
The Role of Provisions in Risk Management
Provisions play a critical role in risk management by allowing organizations to set aside financial resources for anticipated liabilities or uncertain future expenses, ensuring financial stability and compliance with accounting standards. These recognized obligations help businesses prepare for potential risks such as legal disputes, warranty claims, or restructuring costs, reducing the impact on cash flow and profitability. Stipulations, by contrast, are specific contractual requirements that define rights and duties, whereas provisions are accounting measures that quantify and manage risks embedded in these agreements.
Enforceability of Provisions vs. Stipulations
Provisions and stipulations differ mainly in enforceability, where provisions are enforceable contractual terms explicitly outlined to govern the rights and duties of parties. Stipulations generally refer to agreed-upon conditions or requirements within a contract but may lack the same level of binding authority unless clearly integrated and intended as enforceable obligations. Courts typically uphold provisions as legally binding clauses, whereas stipulations require explicit mutual consent and clarity to be deemed enforceable.
Impact on Parties: Rights and Obligations
A provision in a contract outlines specific rights and obligations that parties must adhere to, directly shaping their legal responsibilities and entitlements. A stipulation often sets conditions or requirements that affect how parties execute or enforce the contract, influencing compliance and performance expectations. The impact of provisions and stipulations is pivotal in defining the scope of duties, potential liabilities, and remedies available to the parties involved.
Tips for Choosing Between Provisions and Stipulations
Choosing between provisions and stipulations hinges on the legal document's purpose and desired clarity; provisions are broad clauses outlining general rights or duties, while stipulations are specific conditions agreed upon by parties. Prioritize provisions when establishing ongoing obligations or core contract frameworks, ensuring comprehensive coverage of responsibilities. Opt for stipulations to detail precise terms, deadlines, or contingencies to minimize ambiguity and enhance enforceability in disputes.
Provision Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com