Partnerships foster collaboration, combining strengths and resources to achieve shared goals efficiently. Strong partnerships enhance innovation, increase market reach, and build trust among stakeholders. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your business can benefit from strategic partnerships.
Table of Comparison
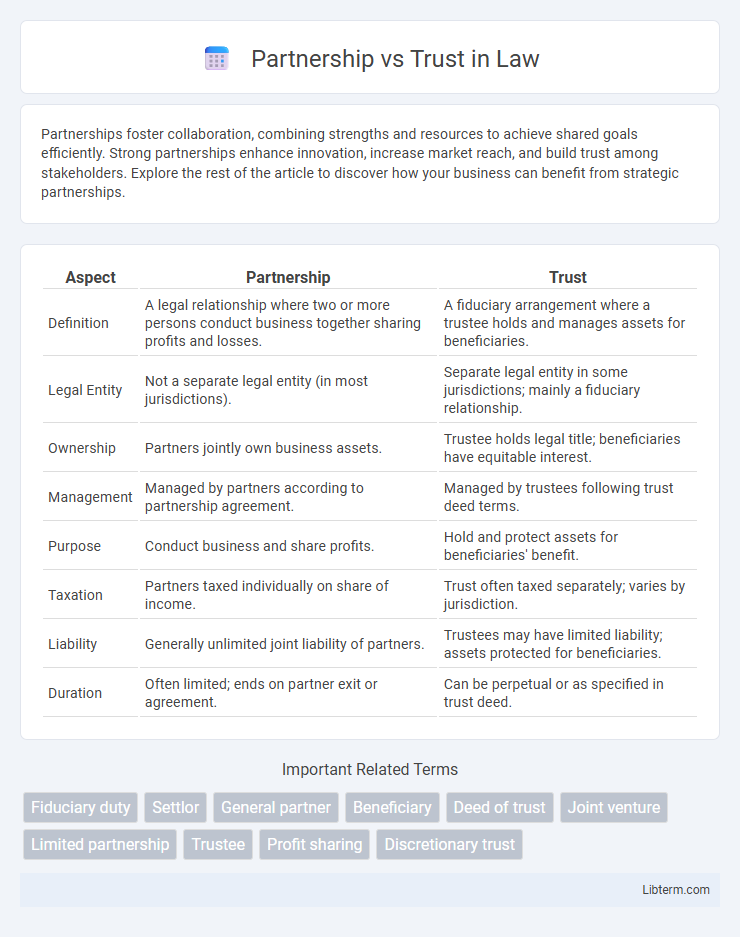
| Aspect | Partnership | Trust |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A legal relationship where two or more persons conduct business together sharing profits and losses. | A fiduciary arrangement where a trustee holds and manages assets for beneficiaries. |
| Legal Entity | Not a separate legal entity (in most jurisdictions). | Separate legal entity in some jurisdictions; mainly a fiduciary relationship. |
| Ownership | Partners jointly own business assets. | Trustee holds legal title; beneficiaries have equitable interest. |
| Management | Managed by partners according to partnership agreement. | Managed by trustees following trust deed terms. |
| Purpose | Conduct business and share profits. | Hold and protect assets for beneficiaries' benefit. |
| Taxation | Partners taxed individually on share of income. | Trust often taxed separately; varies by jurisdiction. |
| Liability | Generally unlimited joint liability of partners. | Trustees may have limited liability; assets protected for beneficiaries. |
| Duration | Often limited; ends on partner exit or agreement. | Can be perpetual or as specified in trust deed. |
Introduction to Partnerships and Trusts
Partnerships and trusts are distinct legal entities primarily used for business and estate planning purposes, each offering unique structures and benefits. Partnerships involve two or more individuals sharing profits, losses, and management responsibilities, governed by a partnership agreement and subject to pass-through taxation. Trusts, established by a grantor, hold and manage assets for beneficiaries under the control of a trustee, providing asset protection, tax advantages, and flexible estate planning options.
Defining Partnerships: Key Features
Partnerships are defined by the collaboration of two or more individuals or entities who share profits, losses, and management responsibilities according to a partnership agreement. Key features include joint ownership of assets, mutual agency where each partner can bind the business, and shared liability for the business's debts and obligations. This structure contrasts with trusts, which involve a trustee managing assets on behalf of beneficiaries without the partners' direct control or mutual agency.
Defining Trusts: Core Concepts
Trusts are legal arrangements where a trustee holds and manages assets on behalf of beneficiaries, distinct from partnerships that involve shared ownership and business operations among partners. The core concept of a trust involves the separation of legal and beneficial ownership, ensuring that the trustee administers the trust property following the settlor's instructions for the beneficiaries' benefit. Unlike partnerships, trusts do not require active participation in business decisions, focusing instead on asset protection, estate planning, and fiduciary duty.
Legal Structure Differences
Partnerships are formed by two or more individuals who share ownership, profits, and liabilities according to a partnership agreement, whereas trusts involve a legal arrangement where a trustee holds and manages assets for beneficiaries under a trust deed. Partnerships operate as separate legal entities or sometimes as aggregates depending on jurisdiction, exposing partners to joint and several liabilities, while trusts are not separate legal entities, and trustees bear fiduciary duties with limited liability subject to the terms of the trust. The regulatory framework for partnerships often includes registration and tax filings specific to partners, in contrast to trusts that follow trust law principles and often enjoy tax benefits depending on the trust type and governing jurisdiction.
Taxation Implications: Partnership vs Trust
Partnerships are generally taxed on the individual partners' share of income, with profits passed through to partners who report them on personal tax returns, avoiding entity-level taxation. Trusts face different tax rules, where income retained within the trust is taxed at higher rates, while distributions to beneficiaries are taxed at their individual rates. Understanding these differences is critical for tax planning, as partnerships offer more straightforward pass-through taxation, whereas trusts provide flexibility in income distribution but can incur higher tax rates if income is accumulated.
Management and Control Comparison
In a partnership, management and control are typically shared among partners according to the partnership agreement, allowing each partner an active role in decision-making and daily operations. Trusts are managed by designated trustees who have fiduciary duties to administer the trust assets strictly according to the trust document, limiting beneficiaries' involvement in management. The centralized control within trusts provides a clear hierarchy and legal accountability, whereas partnerships rely on collective authority and mutual consent among partners.
Liability and Risk Considerations
In a partnership, partners share unlimited personal liability for business debts and obligations, exposing their personal assets to risk in case of legal claims or financial losses. Trusts, however, separate personal liability from the trust's assets, offering protection by ensuring trustee liability is limited to the trust property unless personal misconduct occurs. Understanding these differences is critical for managing risk exposure and making informed decisions about business structure and asset protection strategies.
Flexibility and Succession Planning
Partnerships offer greater flexibility in decision-making and operational changes, allowing partners to customize roles and profit sharing according to mutual agreements. Trusts provide structured succession planning by legally designating beneficiaries and trustees, ensuring smooth asset management and distribution over time. While partnerships require renegotiation or dissolution for succession changes, trusts enable seamless transfer of control without interrupting asset governance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Structure
Partnerships offer flexibility in management and profit-sharing, with the advantage of easy formation and combined resources, but they face unlimited liability risks and potential conflicts among partners. Trusts provide asset protection and tax benefits, ensuring control over distribution and protecting beneficiaries, yet they involve complex setup processes and ongoing regulatory compliance. Choosing between these structures depends on priorities like liability protection, tax implications, control, and administrative requirements.
How to Choose: Partnership or Trust?
Choosing between a partnership and a trust depends on factors such as liability, management control, tax implications, and the intended purpose of asset management or business operation. Partnerships offer shared management and direct income flow to partners but come with personal liability risks, while trusts provide asset protection and centralized control, often benefiting estate planning and succession. Evaluating the need for flexibility, asset protection, and tax efficiency helps determine the appropriate structure for specific financial and legal goals.
Partnership Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com