Chronology organizes events in sequential order, allowing a clear understanding of historical timelines and cause-effect relationships. This method helps you analyze developments accurately by placing events in their proper context. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mastering chronology can enhance your comprehension of history and storytelling.
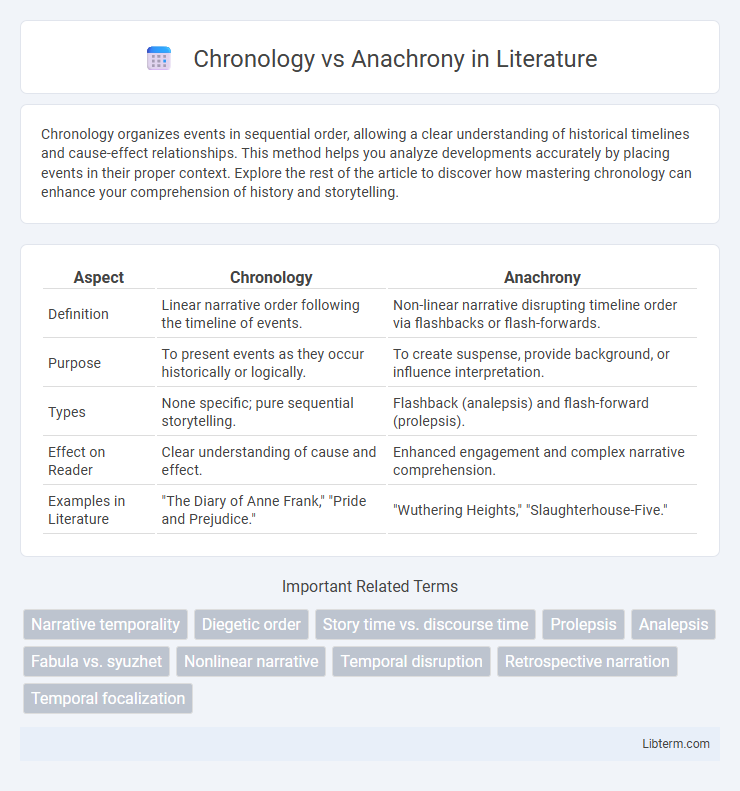
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Chronology | Anachrony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Linear narrative order following the timeline of events. | Non-linear narrative disrupting timeline order via flashbacks or flash-forwards. |
| Purpose | To present events as they occur historically or logically. | To create suspense, provide background, or influence interpretation. |
| Types | None specific; pure sequential storytelling. | Flashback (analepsis) and flash-forward (prolepsis). |
| Effect on Reader | Clear understanding of cause and effect. | Enhanced engagement and complex narrative comprehension. |
| Examples in Literature | "The Diary of Anne Frank," "Pride and Prejudice." | "Wuthering Heights," "Slaughterhouse-Five." |
Introduction to Chronology and Anachrony
Chronology organizes events in their natural, linear order, allowing for clear temporal understanding and historical accuracy. Anachrony disrupts this sequence by presenting events out of their chronological context, often used in literature and film to enhance narrative complexity. Understanding the distinction between chronology and anachrony is essential for analyzing how time is manipulated to influence storytelling and interpretation.
Defining Chronology in Narrative Structures
Chronology in narrative structures refers to the linear sequencing of events as they occur in time, maintaining a clear cause-and-effect progression that enhances comprehension and coherence. It ensures that stories unfold in a straightforward temporal order, aligning with the natural human perception of time and memory. This linear timeline contrasts with anachrony, where narrative elements are intentionally rearranged to create suspense, foreshadowing, or thematic emphasis.
Understanding Anachrony: Types and Examples
Anachrony refers to the manipulation of narrative time, disrupting the chronological order of events to create effects such as suspense or deeper understanding. Types of anachrony include analepsis, or flashbacks, which reveal past events, and prolepsis, or flash-forwards, hinting at future occurrences. Notable examples of anachrony appear in literature like "Wuthering Heights," where the narrative frequently shifts through different timelines to enhance character development and thematic depth.
Key Differences Between Chronology and Anachrony
Chronology refers to the linear, sequential arrangement of events in the order they occurred, providing a clear temporal framework. Anachrony disrupts this sequence by presenting events out of their natural chronological order through techniques such as flashbacks (analepsis) or flash-forwards (prolepsis). The key difference lies in chronology's straightforward timeline, while anachrony manipulates time to create complex narrative structures, enhancing thematic depth or suspense.
The Role of Chronology in Storytelling
Chronology plays a crucial role in storytelling by providing a clear and logical sequence of events that enhances audience comprehension and emotional engagement. Maintaining chronological order helps establish causality, allowing readers or viewers to follow character development and plot progression naturally. Disrupting this sequence through anachrony can create suspense or highlight themes but relies on the foundational clarity that chronological storytelling provides.
Advantages of Using Anachrony in Narratives
Anachrony in narratives allows for complex storytelling by disrupting linear time, enabling flashbacks and flash-forwards that enrich character development and plot depth. This temporal flexibility enhances suspense and reveals information strategically, engaging readers more effectively than strict chronology. By defying chronological order, anachrony fosters a multidimensional understanding of events and themes, making narratives more intellectually stimulating and emotionally resonant.
Chronology vs Anachrony: Impact on Reader Engagement
Chronology presents events in their natural temporal order, facilitating seamless comprehension and enhancing narrative clarity. Anachrony, through techniques like flashbacks or flash-forwards, disrupts this sequence to create suspense, deepen character development, and provoke critical thinking. Reader engagement intensifies as the interplay between chronological progression and anachronistic shifts challenges perception and sustains interest.
Famous Literary Works Employing Anachrony
Famous literary works employing anachrony, such as James Joyce's *Ulysses* and Virginia Woolf's *To the Lighthouse*, disrupt traditional chronology by using flashbacks and nonlinear narratives to explore memory and consciousness. Marcel Proust's *In Search of Lost Time* masterfully blends past and present, illustrating how anachrony enhances thematic depth and character development. These techniques challenge readers' perception of time, creating a complex temporal experience central to modernist literature.
Challenges in Balancing Chronology and Anachrony
Balancing chronology and anachrony in narrative structures presents challenges such as maintaining coherence while incorporating non-linear elements that enhance thematic depth. Writers must carefully manage temporal shifts to prevent reader confusion and ensure that flashbacks or foreshadowing contribute meaningfully to character development and plot progression. Effective use of these techniques requires a nuanced understanding of time manipulation to enrich storytelling without disrupting narrative flow.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Structure for Your Story
Selecting between chronology and anachrony hinges on the narrative's purpose and emotional impact. Chronology preserves a straightforward timeline, aiding clarity and gradual character development, while anachrony enhances intrigue and thematic depth through temporal shifts. Effective storytelling often blends both structures to balance coherence with engaging complexity.
Chronology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com