A participial phrase functions as an adjective to provide additional information about a noun or pronoun in a sentence, often beginning with a present or past participle. Understanding how to correctly identify and use participial phrases can enhance the clarity and detail of your writing. Explore the rest of this article to master the use of participial phrases in various contexts.
Table of Comparison
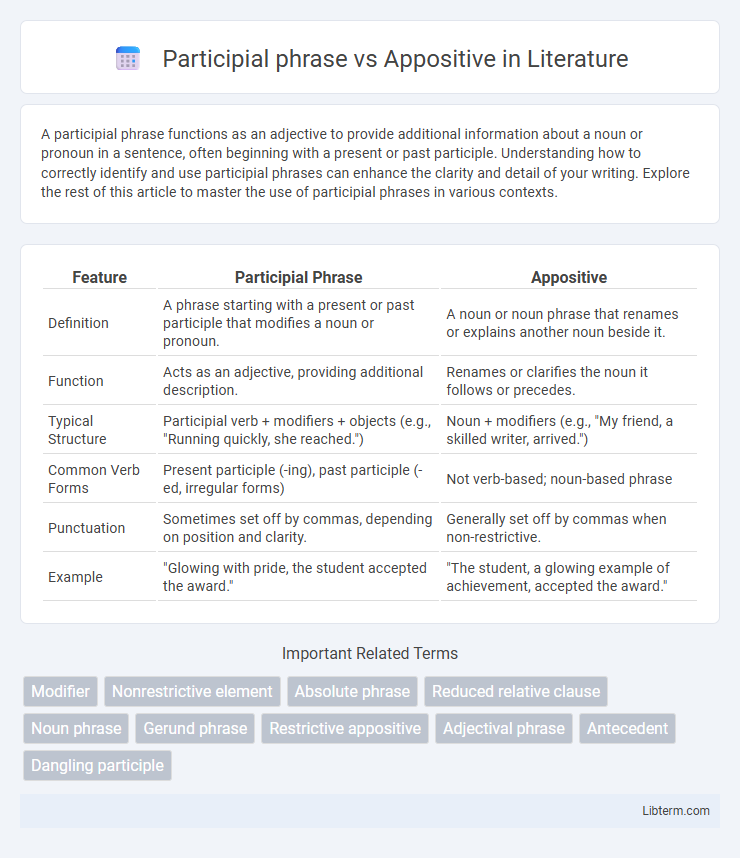
| Feature | Participial Phrase | Appositive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A phrase starting with a present or past participle that modifies a noun or pronoun. | A noun or noun phrase that renames or explains another noun beside it. |
| Function | Acts as an adjective, providing additional description. | Renames or clarifies the noun it follows or precedes. |
| Typical Structure | Participial verb + modifiers + objects (e.g., "Running quickly, she reached.") | Noun + modifiers (e.g., "My friend, a skilled writer, arrived.") |
| Common Verb Forms | Present participle (-ing), past participle (-ed, irregular forms) | Not verb-based; noun-based phrase |
| Punctuation | Sometimes set off by commas, depending on position and clarity. | Generally set off by commas when non-restrictive. |
| Example | "Glowing with pride, the student accepted the award." | "The student, a glowing example of achievement, accepted the award." |
Introduction to Participial Phrases and Appositives
Participial phrases function as modifiers consisting of a present or past participle and its complements, providing descriptive detail about a noun or pronoun. Appositives are noun phrases that rename or clarify another noun, offering specific information or identification directly adjacent to the noun they modify. Recognizing the distinct roles of participial phrases and appositives enhances sentence clarity and precision in writing.
Definition of Participial Phrases
Participial phrases consist of a present or past participle along with its modifiers and function as adjectives, describing nouns or pronouns in a sentence. These phrases provide additional information about the subject or object, often indicating actions or conditions related to the noun. Unlike appositives, which rename or clarify a noun, participial phrases emphasize descriptive or active qualities.
Definition of Appositive Phrases
Appositive phrases are noun phrases that rename or clarify a preceding noun, providing additional information without changing the sentence's core meaning. They often follow the noun they describe and are set off by commas, enhancing sentence detail and clarity. Unlike participial phrases, appositive phrases function solely as noun modifiers rather than verb modifiers.
Key Differences Between Participial and Appositive Phrases
Participial phrases function as adjectives modifying nouns or pronouns and typically begin with present or past participles like "running" or "broken," providing descriptive action or state. Appositive phrases rename or clarify a noun or pronoun directly and usually consist of a noun or noun phrase placed next to another noun for identification or explanation. The key difference lies in their grammatical roles: participial phrases describe actions or conditions related to a noun, while appositive phrases provide additional naming or identification information about the noun.
Structure and Placement in Sentences
Participial phrases begin with present or past participles and function as adjectives, typically placed directly before or after the noun they modify to provide descriptive detail. Appositives are noun phrases that rename or explain another noun, usually positioned immediately after the noun for clarification or emphasis. The key structural difference lies in participial phrases modifying verbs or nouns with action or state, while appositives serve as noun modifiers providing additional identification or explanation.
Common Errors and How to Avoid Them
Common errors in using participial phrases include misplacing them, which can cause confusion about the noun they describe. To avoid this, position the participial phrase immediately before or after the noun it modifies for clear and concise meaning. Appositive mistakes often involve punctuating essential and non-essential appositives incorrectly; using commas around non-essential appositives and omitting them for essential ones ensures proper sentence structure.
Examples of Participial Phrases
Participial phrases begin with present or past participles and function as adjectives, such as "Running swiftly, the athlete won the race" or "Burned by the fire, the house remained uninhabitable." These phrases provide descriptive details about nouns and often include accompanying modifiers or objects. Unlike appositives, which rename nouns (e.g., "My friend, a skilled musician"), participial phrases emphasize action or condition related to the noun.
Examples of Appositive Phrases
Appositive phrases rename or clarify a noun, providing essential or non-essential information for better understanding, such as in "My brother, a skilled guitarist, plays in a band" and "The city of Paris, the capital of France, is famous for its landmarks." These phrases often appear between commas and help add detail without creating separate sentences. Unlike participial phrases that act as adjectives, appositives directly identify or explain the noun they follow, enhancing sentence precision and clarity.
When to Use Participial vs Appositive Phrases
Use participial phrases to modify nouns or pronouns by providing descriptive action details, often clarifying how something is done or its state. Employ appositive phrases to rename or provide essential or non-essential information about a noun, offering concise definitions or explanations. Choose participial phrases for dynamic, verb-based descriptions and appositives for static, noun-based clarifications.
Practice Exercises and Quiz
Practice exercises and quizzes targeting participial phrases and appositives enhance understanding of their distinct grammatical roles. Participial phrase exercises focus on identifying modifiers that describe nouns or pronouns, often formed from verbs ending in -ing or -ed. Appositive quizzes test the ability to recognize noun phrases that rename or provide additional information about a preceding noun, reinforcing sentence clarity and structure mastery.
Participial phrase Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com