Slang enriches everyday communication by adding color and personality to language, reflecting cultural trends and social groups. Understanding slang enhances your ability to connect with others and grasp the nuances of informal speech. Explore the rest of this article to discover the origins, types, and impact of slang in modern communication.
Table of Comparison
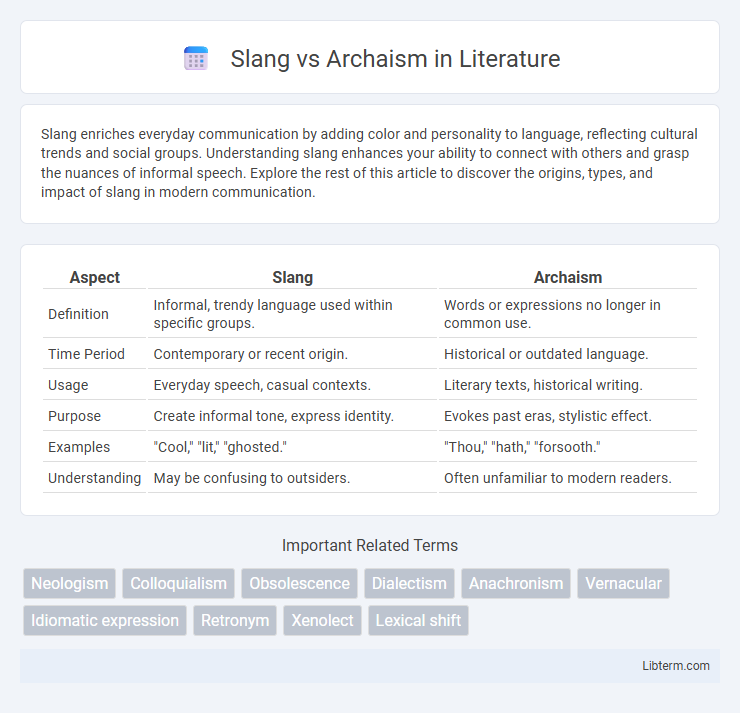
| Aspect | Slang | Archaism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal, trendy language used within specific groups. | Words or expressions no longer in common use. |
| Time Period | Contemporary or recent origin. | Historical or outdated language. |
| Usage | Everyday speech, casual contexts. | Literary texts, historical writing. |
| Purpose | Create informal tone, express identity. | Evokes past eras, stylistic effect. |
| Examples | "Cool," "lit," "ghosted." | "Thou," "hath," "forsooth." |
| Understanding | May be confusing to outsiders. | Often unfamiliar to modern readers. |
Understanding Slang and Archaism
Slang consists of informal, often transient words or phrases used within specific social groups to convey unique cultural meanings or identities. Archaisms are outdated words or expressions that have fallen out of regular use but persist in historical texts or formal contexts to evoke tradition or antiquity. Understanding slang requires recognizing its dynamic and evolving nature, while grasping archaisms involves appreciating their historical significance and fixed place in linguistic heritage.
Definitions: What Are Slang and Archaism?
Slang consists of informal, often ephemeral words or expressions used within specific social groups to convey contemporary ideas or emotions. Archaism refers to words, phrases, or linguistic forms that have fallen out of everyday use but remain in historical texts or poetic contexts. Both serve distinct linguistic purposes: slang breathes life into current language, while archaism preserves linguistic heritage.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Slang originates from informal, often subcultural groups and evolves rapidly through colloquial use, reflecting contemporary societal trends and linguistic innovation. Archaisms stem from older language stages, preserved in literature or historical texts, and gradually fall out of everyday use as language modernizes. The divergence lies in slang's dynamic, adaptive nature versus archaisms' static, historical retention within language evolution.
Usage in Modern Language
Slang consists of informal words and expressions widely used in everyday conversation, evolving rapidly to reflect contemporary culture and social groups. Archaisms are words or phrases that have fallen out of everyday use, often preserved in literature, historical texts, or formal contexts to evoke a sense of antiquity. Modern language favors slang for casual communication while archaisms appear primarily in specialized or artistic contexts, highlighting shifts in linguistic relevance over time.
Social and Cultural Influences
Slang reflects contemporary social trends and cultural identities, evolving rapidly within specific communities to establish group belonging and express current attitudes. Archaisms preserve historical language forms, often evoking past cultural contexts and traditional social values, but are rarely used in everyday speech. The dynamic interplay between slang and archaism highlights how language adapts to shifting social landscapes, reinforcing modern identities or connecting speakers to cultural heritage.
Impact on Communication
Slang introduces dynamic, context-specific vocabulary that fosters group identity and immediacy but can obscure meaning for outsiders, impacting clarity and inclusivity in communication. Archaisms, often perceived as outdated, evoke tradition and formality, potentially enhancing tone but risking confusion due to unfamiliarity in modern discourse. Balancing slang and archaism affects understanding and engagement by shaping the perceived modernity and accessibility of language.
Examples of Slang and Archaism
Slang terms like "lit" (exciting) and "ghosting" (suddenly ignoring someone) are commonly used in modern informal English to convey contemporary social phenomena. Archaisms such as "thou" (you) and "hither" (to this place) appear in historical texts and older literature, reflecting linguistic forms that have fallen out of everyday use. These examples illustrate how slang evolves rapidly to express current culture, whereas archaisms preserve the language of past eras.
Acceptance and Controversies
Slang often gains rapid acceptance within informal social groups but faces resistance from formal institutions due to perceived lack of professionalism and clarity. Archaisms, by contrast, are typically viewed as outdated and sometimes pretentious, leading to their decline in everyday use but occasional revival in literature or historical contexts. Controversies surrounding slang center on issues of language purity and social status, whereas archaisms spark debates about cultural preservation versus linguistic evolution.
Role in Literature and Media
Slang enriches literature and media by capturing contemporary cultural expressions and lending authenticity to dialogue, reflecting evolving social identities and trends. Archaism, conversely, evokes a sense of historical depth and formality, often used to create atmosphere, establish period settings, or convey timeless themes. Both linguistic styles serve distinct narrative functions, with slang energizing realism and archaisms enhancing stylistic elegance or historical resonance.
Future Trends and Linguistic Adaptation
Slang continues to evolve rapidly, driven by digital communication platforms and youth culture, reflecting dynamic linguistic adaptation in real-time. Archaisms, while largely obsolete in everyday speech, experience selective revival in literature, media, and branding to evoke nostalgia or authenticity. Future trends suggest an increasing interplay where emerging slang may become archaisms, showcasing the cyclical nature of language change influenced by social and technological factors.
Slang Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com