Prognostication involves predicting future outcomes based on current data and historical trends, essential in fields like medicine, finance, and meteorology. Accurate prognostication helps you make informed decisions by anticipating potential scenarios and risks. Explore the rest of this article to understand effective prognostication techniques and their practical applications.
Table of Comparison
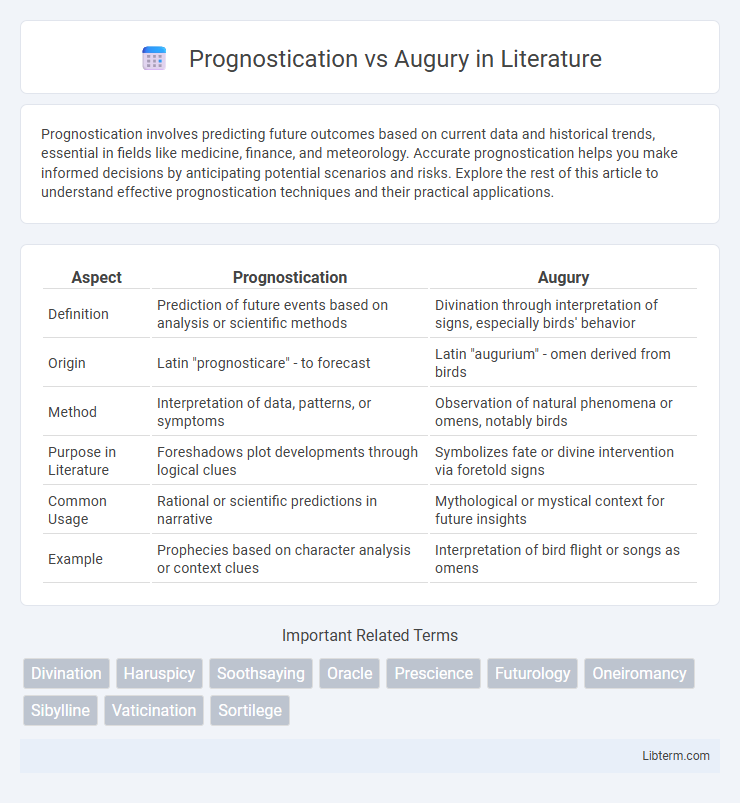
| Aspect | Prognostication | Augury |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prediction of future events based on analysis or scientific methods | Divination through interpretation of signs, especially birds' behavior |
| Origin | Latin "prognosticare" - to forecast | Latin "augurium" - omen derived from birds |
| Method | Interpretation of data, patterns, or symptoms | Observation of natural phenomena or omens, notably birds |
| Purpose in Literature | Foreshadows plot developments through logical clues | Symbolizes fate or divine intervention via foretold signs |
| Common Usage | Rational or scientific predictions in narrative | Mythological or mystical context for future insights |
| Example | Prophecies based on character analysis or context clues | Interpretation of bird flight or songs as omens |
Introduction to Prognostication and Augury
Prognostication involves predicting future events based on signs, patterns, or scientific data, often utilizing statistical models or expert analysis. Augury, rooted in ancient practices, specifically interprets omens or the behavior of birds and natural phenomena to forecast outcomes. Both methods aim to anticipate future occurrences but differ in approach and underlying methodology.
Historical Contexts of Prognostication and Augury
Prognostication and augury both served as crucial tools in ancient civilizations for predicting future events, with prognostication often involving interpreting natural phenomena and celestial patterns, while augury primarily focused on reading the behavior of birds to guide decisions. In historical contexts, societies such as the Romans relied heavily on augury to legitimize political and military strategies, with augurs holding official religious authority. Prognostication, practiced by seers and oracles in cultures like ancient Greece and Mesopotamia, combined astrology and omens to inform rulers and communities about potential outcomes.
Definitions: Prognostication Explained
Prognostication refers to the practice of predicting future events based on data analysis, patterns, and scientific methods, often used in fields like meteorology and medicine. It involves systematic observation and interpretation of current signs to forecast outcomes with a degree of probability. Unlike augury, which relies on interpreting omens or supernatural signs, prognostication is grounded in empirical evidence and logical reasoning.
Definitions: Augury Unveiled
Augury involves interpreting omens or signs, especially from natural phenomena like bird flight or animal behavior, to predict future events rooted in ancient Roman and Etruscan traditions. Prognostication is a broader practice encompassing various methods, including astrology, divination, and scientific analysis, aimed at forecasting future outcomes. While augury specifically relies on symbolic observations, prognostication integrates multiple data sources to provide a comprehensive future outlook.
Methods and Tools of Prognostication
Prognostication employs scientific methods and analytical tools such as statistical modeling, data analysis, and pattern recognition to forecast future outcomes based on empirical evidence. It utilizes technologies including machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics software, and trend analysis to enhance accuracy and reliability. Augury, in contrast, relies on interpretative practices like reading omens, performing rituals, or observing natural signs rather than empirical tools.
Rituals and Practices of Augury
Augury involves interpreting omens or signs, often through ritualistic observation of birds, animal entrails, or natural phenomena to predict future events. Practitioners perform precise ceremonies, such as the reading of flight patterns, feeding habits, or sounds of birds, which require strict adherence to traditional protocols and timing. These rituals are deeply embedded in religious and cultural contexts, aiming to seek divine guidance through symbolic communication with nature.
Scientific Basis vs. Mystical Origins
Prognostication relies on scientific methods such as statistical analysis and pattern recognition to forecast future events, often grounded in empirical data and measurable outcomes. Augury, rooted in ancient mystical traditions, interprets signs and omens, such as bird flight or natural phenomena, with symbolic meanings rather than evidence-based reasoning. The scientific basis of prognostication contrasts sharply with augury's foundation in ritualistic and spiritual practices, highlighting a divergence between measurable prediction and interpretive divination.
Cultural Influence on Prognostication and Augury
Prognostication and augury both reflect deep cultural roots, with prognostication often grounded in widespread societal beliefs and traditions, influencing decision-making across civilizations from ancient Greece to modern times. Augury, specifically tied to the interpretation of bird flight patterns and omens, played a crucial role in Roman culture, shaping political and military actions through ritualistic observation. These practices illustrate how cultural values and spiritual worldviews profoundly shaped methods of predicting the future, embedding prognostication and augury within the social and religious fabric of diverse societies.
Modern Applications and Perceptions
Prognostication in modern contexts leverages data analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling to forecast trends and outcomes in fields such as finance, healthcare, and climate science. Augury, rooted in ancient divination practices, now finds niche applications in cultural studies, historical research, and modern spiritual movements emphasizing symbolic interpretation rather than empirical prediction. Contemporary perceptions distinguish prognostication as a scientific and systematic process while viewing augury as a symbolic and interpretative art form.
Prognostication vs. Augury: Key Differences and Similarities
Prognostication involves forecasting future events based on analysis of data, patterns, or signs, often using scientific or systematic methods, while augury is an ancient practice interpreting omens or the behavior of birds to predict outcomes. Both share the goal of foretelling the future, but prognostication relies on empirical evidence or logical deduction, whereas augury is rooted in symbolic interpretation and ritual. Key differences include the methodological basis--prognostication's analytical approach contrasts with augury's reliance on spiritual or mythological meanings.
Prognostication Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com