Picaresque novels feature roguish protagonists navigating a corrupt society through cunning and wit, often highlighting social injustices with humor and satire. This literary genre originated in 16th-century Spain and remains influential in shaping modern storytelling techniques. Discover how the picaresque tradition continues to engage readers by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
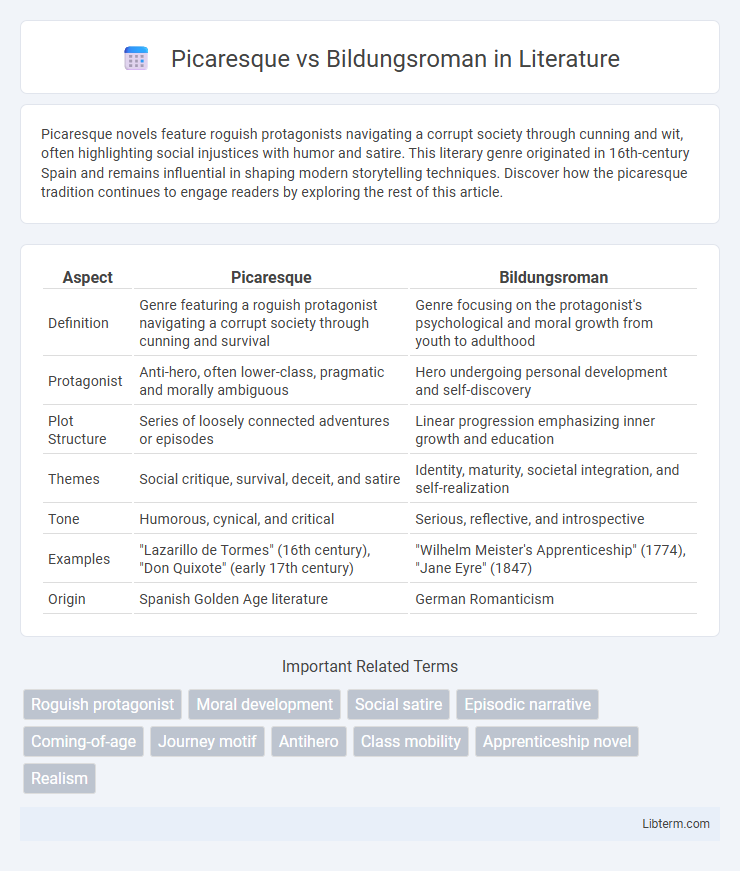
| Aspect | Picaresque | Bildungsroman |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Genre featuring a roguish protagonist navigating a corrupt society through cunning and survival | Genre focusing on the protagonist's psychological and moral growth from youth to adulthood |
| Protagonist | Anti-hero, often lower-class, pragmatic and morally ambiguous | Hero undergoing personal development and self-discovery |
| Plot Structure | Series of loosely connected adventures or episodes | Linear progression emphasizing inner growth and education |
| Themes | Social critique, survival, deceit, and satire | Identity, maturity, societal integration, and self-realization |
| Tone | Humorous, cynical, and critical | Serious, reflective, and introspective |
| Examples | "Lazarillo de Tormes" (16th century), "Don Quixote" (early 17th century) | "Wilhelm Meister's Apprenticeship" (1774), "Jane Eyre" (1847) |
| Origin | Spanish Golden Age literature | German Romanticism |
Introduction to Picaresque and Bildungsroman
Picaresque novels center on the adventures of a roguish, lower-class protagonist navigating corrupt societies through wit and survival, often employing episodic structure and satire. Bildungsroman focuses on the psychological and moral growth of the protagonist from youth to adulthood, emphasizing personal development and self-discovery. Both genres explore individual experiences but differ sharply in tone, narrative style, and thematic goals.
Defining the Picaresque Novel
The picaresque novel is defined by its episodic structure and the adventures of a roguish protagonist, often of low social class, who navigates a corrupt society with wit and cunning. Unlike the Bildungsroman, which centers on the character's psychological and moral growth, the picaresque emphasizes satire and social critique through the picaro's encounters and survival strategies. Its narrative typically lacks a cohesive plot, focusing instead on a series of loosely connected episodes highlighting societal flaws.
Defining the Bildungsroman Genre
The Bildungsroman genre centers on the protagonist's psychological and moral growth from youth to adulthood, emphasizing inner development and self-discovery. Unlike the episodic and often satirical structure of picaresque novels, Bildungsromans follow a cohesive narrative arc that charts emotional and intellectual maturation. These novels typically explore themes of identity, social integration, and the quest for meaning, making them foundational in coming-of-age literature.
Historical Origins and Evolution
The picaresque novel emerged in 16th-century Spain, characterized by episodic adventures of a roguish protagonist surviving in a corrupt society, reflecting social critique through satire. The Bildungsroman originated in late 18th-century Germany, emphasizing the psychological and moral growth of a young protagonist toward maturity, often highlighting individual development and self-discovery. Over time, both genres evolved to incorporate diverse narrative techniques, with the picaresque influencing social realism and the Bildungsroman shaping modern coming-of-age stories.
Key Characteristics of Picaresque Narratives
Picaresque narratives feature a roguish protagonist of low social class who survives through cunning and wit in a corrupt society, often presented in episodic adventures with satirical tone. These stories emphasize realism and social critique over character development, highlighting the protagonist's adaptability rather than growth or moral improvement seen in Bildungsroman. The episodic structure, first-person narration, and focus on external experiences distinguish picaresque from the introspective, developmental journey central to Bildungsroman.
Core Elements of Bildungsroman Stories
Bildungsroman stories center on the psychological and moral growth of the protagonist from youth to adulthood, emphasizing self-discovery and identity formation. Core elements include a sensitive main character facing conflicts that lead to personal development, a journey or quest symbolizing the maturation process, and the resolution where the protagonist integrates into society with a transformed worldview. These narratives often explore themes of education, social integration, and the challenges of transitioning into adulthood.
Notable Examples of Each Genre
Notable examples of the picaresque genre include "Lazarillo de Tormes," which features a roguish protagonist navigating a corrupt society through cunning and survival. In contrast, Bildungsroman is exemplified by "Jane Eyre" by Charlotte Bronte, where the story follows the protagonist's psychological and moral growth from youth to adulthood. Other key Bildungsroman works include "Great Expectations" by Charles Dickens, emphasizing personal development and self-discovery.
Thematic Differences and Overlaps
Picaresque novels emphasize episodic adventures of a rogue protagonist navigating a corrupt society, highlighting themes of survival, social satire, and moral ambiguity. Bildungsroman narratives focus on the psychological and moral growth of the protagonist, exploring themes of identity, self-discovery, and maturation within a structured life journey. Both genres overlap in depicting individual struggles against social constraints but differ in purpose: picaresque critiques societal flaws through episodic misadventures, while bildungsroman tracks internal development culminating in personal integration.
Narrative Structure and Character Development
Picaresque narratives unfold through episodic adventures featuring a roguish protagonist navigating a corrupt society, emphasizing external events over psychological growth. Bildungsroman stories follow a linear progression centered on the protagonist's internal development and moral maturation, highlighting a transformative journey from youth to adulthood. The picaresque's fragmented structure contrasts with the bildungsroman's cohesive narrative arc, reflecting differing focuses on social critique versus personal development.
Influence on Modern Storytelling
Picaresque novels, characterized by episodic adventures of a roguish protagonist, introduced a narrative style emphasizing wit, social critique, and survival, which deeply influenced the development of modern antiheroes and serialized storytelling. Bildungsroman, centered on the psychological and moral growth of the protagonist, shaped contemporary narratives by prioritizing character development and internal conflict resolution. Together, these genres underpin modern storytelling techniques that blend external action with inner transformation, enriching plot complexity and emotional depth.
Picaresque Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com