Aristotelian treatises delve into the foundational principles of logic, metaphysics, and ethics that have shaped Western philosophy for centuries. These works explore concepts such as causality, substance, and virtue, providing timeless insights into human nature and the structure of reality. Discover how your understanding of philosophy can deepen by exploring the full article on Aristotelian treatises.
Table of Comparison
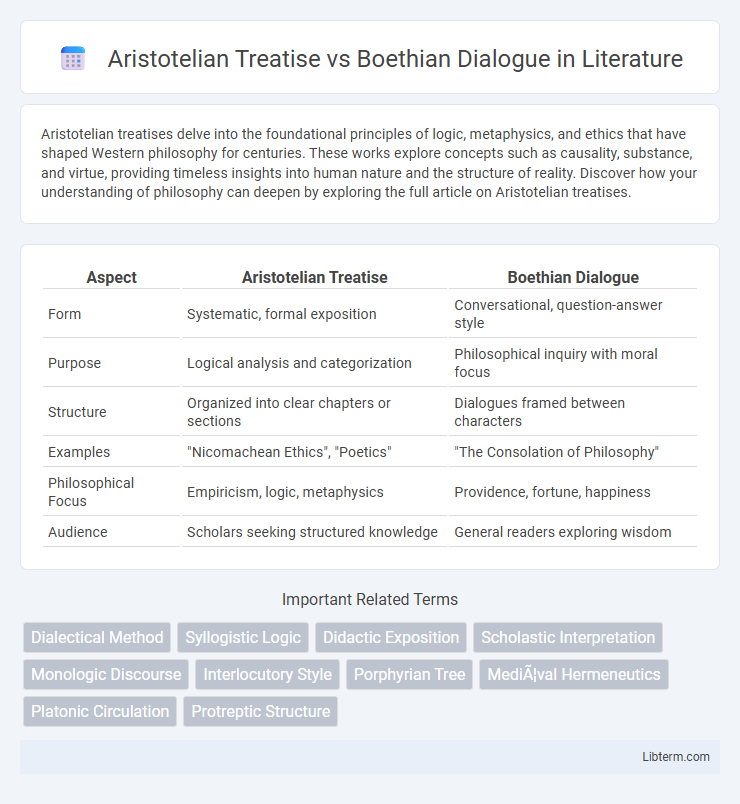
| Aspect | Aristotelian Treatise | Boethian Dialogue |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Systematic, formal exposition | Conversational, question-answer style |
| Purpose | Logical analysis and categorization | Philosophical inquiry with moral focus |
| Structure | Organized into clear chapters or sections | Dialogues framed between characters |
| Examples | "Nicomachean Ethics", "Poetics" | "The Consolation of Philosophy" |
| Philosophical Focus | Empiricism, logic, metaphysics | Providence, fortune, happiness |
| Audience | Scholars seeking structured knowledge | General readers exploring wisdom |
Introduction to Aristotelian Treatise and Boethian Dialogue
The Introduction to Aristotelian Treatise establishes foundational principles of metaphysics and ethics, emphasizing systematic inquiry through rigorous logic and empirical observation. In contrast, the Boethian Dialogue begins with a personal crisis, using a conversational format to explore the nature of fortune, happiness, and divine providence. Both texts serve as critical entry points to their respective philosophical traditions, highlighting distinct methodologies: structured analysis in Aristotle and reflective dialectic in Boethius.
Philosophical Foundations: Aristotle vs. Boethius
Aristotelian Treatises emphasize empirical observation and logical categorization, grounding philosophy in the study of nature, ethics, and metaphysics with a focus on substance and causality. Boethian Dialogues, notably in "The Consolation of Philosophy," center on the reconciliation of divine providence with human free will, exploring the nature of happiness and fortune through a blend of classical philosophy and Christian theology. While Aristotle prioritizes systematic inquiry and tangible reality, Boethius integrates Platonic and Stoic elements to address existential questions within a theological framework.
Structure and Format Comparison
Aristotelian treatises typically follow a systematic, analytical structure divided into books and chapters, emphasizing logical argumentation and categorization of knowledge to explore philosophical concepts. Boethian dialogues employ a conversational format featuring a protagonist and interlocutors engaging in question-and-answer exchanges, which makes complex ideas accessible through dialectical reasoning. The Aristotelian format prioritizes formal exposition, while the Boethian dialogue relies on dramatic interaction to unfold philosophical inquiry.
Approaches to Knowledge and Truth
Aristotelian Treatises emphasize empirical observation and logical analysis as foundational methods for acquiring knowledge, relying on systematic categorization and demonstration to arrive at objective truths. Boethian Dialogues adopt a dialectical approach, using conversational inquiry and philosophical questioning to explore the nature of truth, often integrating theological insights with reason. Both frameworks prioritize rational understanding, but Aristotelian Treatises focus on concrete evidence and formal logic, whereas Boethian Dialogues highlight introspective discourse and metaphysical reflection.
Methods of Argumentation
Aristotelian treatises emphasize structured syllogistic reasoning grounded in empirical observation and logical deduction, fostering clarity through methodical argument development. Boethian dialogues employ a dialectical method characterized by conversational exchanges and mythic allegory to explore philosophical ideas dynamically. This contrast highlights Aristotle's systematic approach versus Boethius's reflective, dialogic style in philosophical argumentation.
Rhetorical Devices and Persuasion
Aristotelian treatises emphasize structured argumentation through ethos, pathos, and logos, systematically guiding readers with logical proofs and ethical appeals to ensure persuasive clarity. In contrast, Boethian dialogues employ a conversational style rich in rhetorical questions and irony, fostering reflection and emotional engagement to subtly influence the audience's reasoning. Both forms harness rhetorical devices effectively but differ in their modes of persuasion: the Aristotelian favoring direct, analytical discourse while the Boethian prefers dialectical interplay and nuanced moral inquiry.
Historical Contexts and Influences
Aristotelian treatises emerged in 4th-century BCE Greece, laying foundational work in logic, metaphysics, and ethics under the influence of Plato and the sociopolitical milieu of Athens. Boethian dialogues, written in the 6th century CE during the late Roman Empire, reflect the synthesis of classical philosophy with Christian thought amid the decline of imperial authority. The historical context shaped Aristotelian treatises toward systematic categorization, while Boethian dialogues emphasized consolation and theodicy, illustrating their distinct intellectual and cultural influences.
Impact on Medieval Scholasticism
Aristotelian treatises, characterized by systematic exposition and logical rigor, provided the foundational framework for medieval scholasticism by emphasizing deductive reasoning and categorization of knowledge. Boethian dialogues, by contrast, employed a dialectical and conversational method that encouraged ethical reflection and metaphysical inquiry, influencing medieval scholars to integrate classical philosophy with Christian theology. The synthesis of Aristotelian logic and Boethian dialogue shaped scholasticism's approach to reconciling faith and reason, profoundly impacting medieval intellectual discourse.
Enduring Legacies in Philosophy
The Aristotelian treatise established a foundational framework for logic, metaphysics, and ethics that continues to influence contemporary philosophical discourse through its systematic approach and empirical observation. Boethian dialogue, notably "The Consolation of Philosophy," endures by integrating classical philosophy with Christian thought, shaping medieval scholasticism and providing a dialogical method that emphasizes human suffering and divine providence. Together, these works underpin the Western philosophical tradition by merging rigorous analysis with existential inquiry, ensuring their relevance in both academic and theological contexts.
Conclusion: Relevance in Modern Thought
Aristotelian treatises systematically present philosophical arguments through rigorous logical analysis, emphasizing empirical observation and categorization, which remains foundational in contemporary scientific methodology and ethical theory. Boethian dialogues, characterized by their conversational format and exploration of philosophical themes like fate and providence, continue to influence modern discussions on metaphysics and existential inquiry. Both forms contribute uniquely to modern thought by blending analytical precision with reflective discourse, enriching philosophical and literary traditions.
Aristotelian Treatise Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com