Socratic dialogue is a powerful method of engaging in critical thinking through asking and answering questions to stimulate deeper understanding and illuminate ideas. This form of discourse encourages You to explore complex concepts by challenging assumptions and examining beliefs in a collaborative manner. Discover more about how Socratic dialogue can enhance your reasoning skills by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
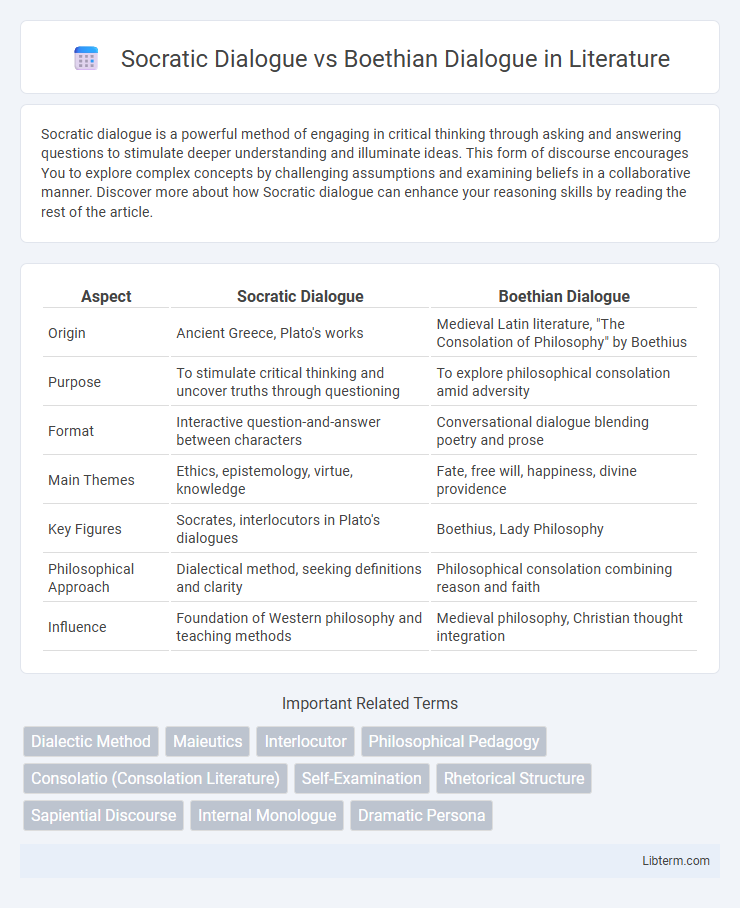
| Aspect | Socratic Dialogue | Boethian Dialogue |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ancient Greece, Plato's works | Medieval Latin literature, "The Consolation of Philosophy" by Boethius |
| Purpose | To stimulate critical thinking and uncover truths through questioning | To explore philosophical consolation amid adversity |
| Format | Interactive question-and-answer between characters | Conversational dialogue blending poetry and prose |
| Main Themes | Ethics, epistemology, virtue, knowledge | Fate, free will, happiness, divine providence |
| Key Figures | Socrates, interlocutors in Plato's dialogues | Boethius, Lady Philosophy |
| Philosophical Approach | Dialectical method, seeking definitions and clarity | Philosophical consolation combining reason and faith |
| Influence | Foundation of Western philosophy and teaching methods | Medieval philosophy, Christian thought integration |
Introduction to Philosophical Dialogues
Socratic dialogue introduces philosophical concepts through questioning techniques aimed at stimulating critical thinking and exposing contradictions, exemplified in Plato's works where Socrates engages interlocutors to uncover truth. Boethian dialogue, as found in Boethius' "Consolation of Philosophy," combines prose and verse to explore fate, free will, and the nature of happiness, emphasizing philosophical reflection during adversity. Both forms serve as foundational methods for presenting and examining ideas in Western philosophy.
Origins of Socratic Dialogue
Socratic dialogue originated in ancient Greece through the teachings of Socrates, who employed dialectical methods to stimulate critical thinking and expose contradictions in his interlocutors' beliefs. This form of dialogue prioritizes questioning and logical reasoning as a means to achieve philosophical insight. In contrast, Boethian dialogue, derived from Boethius's "Consolation of Philosophy," combines prose and poetry to explore themes of fortune and justice through a more reflective and allegorical conversation.
Core Principles of Boethian Dialogue
Boethian Dialogue centers on the pursuit of wisdom through philosophical inquiry in the context of life's uncertainties, emphasizing the resolution of apparent contradictions between fate and free will. It employs a dialectical method where the interlocutor, often personified as Lady Philosophy, guides the protagonist toward understanding divine providence and the nature of true happiness. Core principles include the reconciliation of temporal suffering with eternal truths, fostering insight into the soul's immortality and the importance of virtuous living.
Structural Differences Between Socratic and Boethian Dialogues
Socratic dialogues typically feature a question-and-answer format aimed at stimulating critical thinking and exposing contradictions in the interlocutor's beliefs, often involving multiple participants led by Socrates himself. Boethian dialogues, as exemplified in "The Consolation of Philosophy," combine prose and poetry with a more introspective and allegorical structure, focusing on internal philosophical reflection rather than external debate. The structural difference lies in Socratic dialogue's dialectical, conversational exchange versus Boethian dialogue's hybrid form that interweaves narrative, philosophical discourse, and poetic meditation.
Purposes and Goals of Each Dialogue Form
Socratic Dialogue aims to stimulate critical thinking and uncover underlying assumptions through a question-and-answer method designed to achieve clarity and philosophical insight. Boethian Dialogue, exemplified in Boethius's "The Consolation of Philosophy," focuses on reconciling practical life issues with philosophical wisdom by blending prose and poetry to explore themes like fate and happiness. While Socratic Dialogue seeks to dismantle ignorance through dialectic inquiry, Boethian Dialogue pursues the integration of personal reflection and universal truths for moral consolation.
Approaches to Truth and Knowledge
Socratic Dialogue emphasizes dialectical questioning to uncover definitions and expose contradictions, aiming for knowledge through rigorous inquiry and self-examination. Boethian Dialogue, rooted in theological and philosophical synthesis, seeks truth by integrating reason and divine revelation, focusing on the alignment of human understanding with divine providence. Both approaches prioritize truth, but Socratic Dialogue relies on logical refutation and epistemic humility, whereas Boethian Dialogue combines metaphysical insight with spiritual wisdom.
Role of Questioning and Response
Socratic Dialogue employs probing, open-ended questions to stimulate critical thinking and self-examination, encouraging interlocutors to refine their beliefs through continuous questioning and dialectical reasoning. In contrast, Boethian Dialogue integrates philosophical inquiry with a consolatory purpose, where questioning serves to reconcile human suffering with divine providence, often leading to authoritative responses that provide existential clarity. The role of questioning in Socratic Dialogue is primarily exploratory and dialectical, whereas in Boethian Dialogue, it is more didactic, aiming to impart wisdom and comfort through structured philosophical discourse.
Influence on Later Philosophical Tradition
Socratic dialogue profoundly shaped Western philosophy by introducing dialectical methods that emphasize questioning and critical thinking, which influenced thinkers like Plato and Aristotle. Boethian dialogue, particularly in "The Consolation of Philosophy," blends classical philosophy with Christian thought, impacting medieval scholasticism and later Renaissance humanism. Both forms established foundational frameworks for exploring ethics, metaphysics, and epistemology in subsequent philosophical traditions.
Contemporary Applications and Relevance
Socratic Dialogue fosters critical thinking and ethical inquiry through questioning methods widely used in modern education, therapy, and conflict resolution to encourage reflective thinking and clarity. Boethian Dialogue, rooted in the merging of philosophy and theology, informs contemporary discussions on fate, free will, and existential meaning in literature, counseling, and philosophical counseling practices. Both dialogue forms remain relevant by addressing timeless human concerns and promoting deeper self-understanding in diverse professional and academic settings.
Conclusion: Comparing Philosophical Legacies
Socratic Dialogue emphasizes dialectical reasoning to uncover truth through questioning, fostering critical thinking and ethical self-examination that shaped Western philosophy. Boethian Dialogue integrates metaphysical reflection with personal consolation, blending classical philosophy and Christian theology to address fate and providence. The philosophical legacy of Socratic Dialogue lies in its method of inquiry and Socratic irony, while Boethian Dialogue's legacy endures through its synthesis of ancient wisdom and medieval scholastic thought.
Socratic Dialogue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com