Parody creatively mimics the style and content of original works to entertain and offer critical commentary, often highlighting their quirks or flaws. This technique plays with familiar cultural elements to provide humor and insight, making it a powerful tool in satire and social critique. Explore the rest of this article to understand how parody shapes our perception of art and media.
Table of Comparison
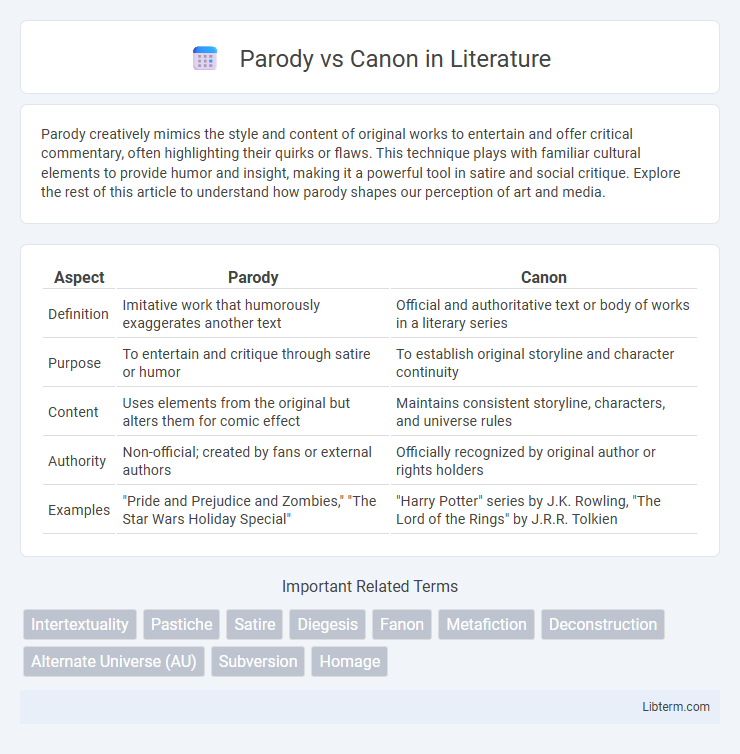
| Aspect | Parody | Canon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Imitative work that humorously exaggerates another text | Official and authoritative text or body of works in a literary series |
| Purpose | To entertain and critique through satire or humor | To establish original storyline and character continuity |
| Content | Uses elements from the original but alters them for comic effect | Maintains consistent storyline, characters, and universe rules |
| Authority | Non-official; created by fans or external authors | Officially recognized by original author or rights holders |
| Examples | "Pride and Prejudice and Zombies," "The Star Wars Holiday Special" | "Harry Potter" series by J.K. Rowling, "The Lord of the Rings" by J.R.R. Tolkien |
Understanding Parody and Canon: Key Definitions
Parody imitates the style or content of an original work, known as the canon, to create humor or critique through exaggeration and distortion. Canon refers to the authentic source material or the officially recognized body of work within a particular fictional universe. Understanding the distinction highlights how parody relies on familiarity with the canon to effectively subvert expectations and generate meaning.
The Origins and Evolution of Canon
Canon originated as a systematic collection of authoritative texts defining foundational narratives and beliefs in religious and literary traditions. It evolved through historical processes involving councils, scholarly debates, and cultural shifts, shaping the accepted body of work against which parodies react by subverting or exaggerating established themes. The dynamic between parody and canon highlights how canonical works maintain cultural significance while inviting reinterpretation and critique through creative divergence.
Parody: Purpose, Techniques, and Impact
Parody serves to humorously imitate or critique the style, themes, or characters of an original work, often highlighting its flaws or exaggerating its features for comedic effect. Techniques commonly used in parody include exaggeration, irony, satire, and mimicry, which distort the source material while maintaining recognizable elements to engage the audience. The impact of parody lies in its ability to offer social commentary, entertain, and provoke reflection on the original work, often fostering a deeper appreciation or critical awareness among viewers.
Canon in Popular Culture and Fandoms
Canon in popular culture and fandoms refers to the official and authoritative source material recognized by creators or rights holders, defining the established storyline, characters, and universe continuity. Fans engage deeply with canon to maintain consistency in discussions, fan fiction, and adaptations, often distinguishing it from fan interpretations or parodies that playfully distort or critique original elements. Understanding canon is essential for preserving narrative integrity and fostering meaningful community discourse within fandoms.
How Parody Challenges and Reinvents Canon
Parody challenges canon by subverting established narratives and character archetypes, exposing underlying assumptions and cultural norms within the original work. It reinvents canon through satirical reinterpretation, blending humor with critique to offer alternative perspectives that question the authority and completeness of the source material. This dynamic interaction fosters a deeper understanding of the canonical text while expanding its cultural relevance and interpretive possibilities.
Legal and Ethical Boundaries: Parody vs Canon
Parody, as a form of transformative work, is protected under fair use laws when it provides commentary or criticism of the original canon, avoiding copyright infringement by adding new meaning and expression. Canon represents the original copyrighted material, and unauthorized use that replicates significant portions without transformative intent can violate intellectual property rights. Ethical boundaries demand respecting the original creator's moral rights while ensuring parody maintains a clear distinction from the source to prevent confusion or harm.
Audience Reception: Embracing Parody and Defending Canon
Audience reception of parody often thrives on humor and subversion, attracting fans who appreciate reinterpretations and critical commentary of the original work. Canon supporters prioritize fidelity to the source material, emphasizing narrative integrity and character authenticity as key to preserving the original's value. Both groups demonstrate passionate engagement, reflecting diverse ways fans connect with and interpret beloved stories.
Iconic Examples: Parody Works vs Canonical Originals
The iconic parody *Scary Movie* lampoons the canonical original *Scream*, exaggerating its horror tropes for comedic effect. *Weird Al Yankovic's* music parodies, such as "Eat It," mirror and mock *Michael Jackson's* "Beat It," highlighting the original's cultural impact. The *Simpsons* regularly parody *The Godfather*, transforming its serious narrative into satirical TV segments, emphasizing differences between parody transformations and canonical storytelling.
Parody’s Role in Shaping and Critiquing Canon
Parody functions as a powerful tool in shaping and critiquing canon by highlighting its inconsistencies and cultural assumptions through humor and exaggeration. It challenges established narratives and encourages audiences to reconsider the legitimacy and relevance of canonical works. This dynamic interplay fosters a more inclusive and evolving understanding of literature and art.
The Future of Parody and Canon in Modern Media
The future of parody and canon in modern media hinges on the evolving relationship between fan creativity and official content creators. As digital platforms empower users to produce and distribute parodic works, canon narratives increasingly incorporate or respond to fan interpretations, blurring the lines between original and derivative content. Advances in AI and interactive media will further transform how parody and canon coexist, enabling more dynamic and participatory storytelling experiences.
Parody Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com