Paleography is the study of ancient handwriting and scripts, providing essential insights into historical documents and texts. Mastery of paleography enables researchers to authenticate, date, and interpret manuscripts, revealing valuable information about past cultures and societies. Explore this article to deepen your understanding of how paleography uncovers the secrets of written history.
Table of Comparison
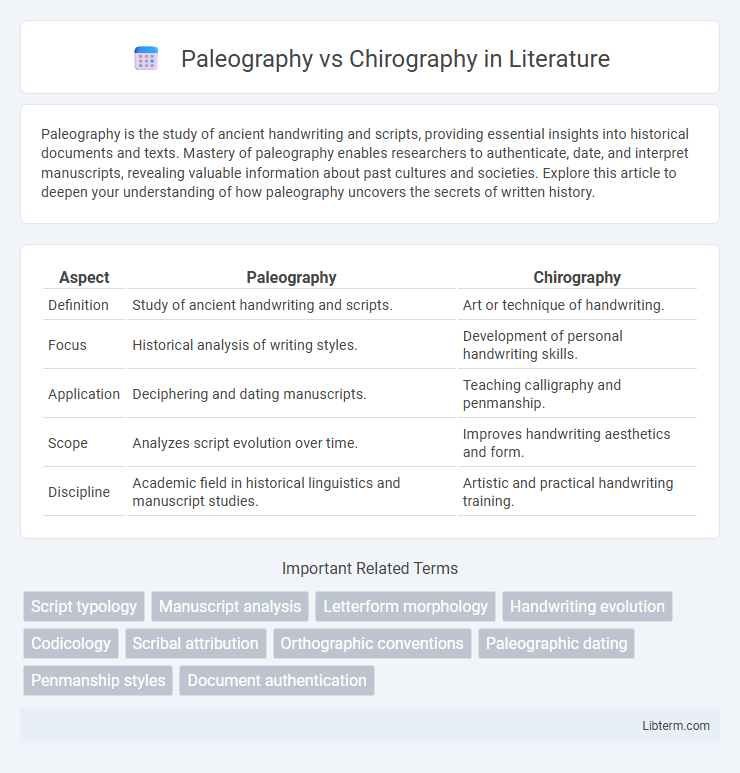
| Aspect | Paleography | Chirography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of ancient handwriting and scripts. | Art or technique of handwriting. |
| Focus | Historical analysis of writing styles. | Development of personal handwriting skills. |
| Application | Deciphering and dating manuscripts. | Teaching calligraphy and penmanship. |
| Scope | Analyzes script evolution over time. | Improves handwriting aesthetics and form. |
| Discipline | Academic field in historical linguistics and manuscript studies. | Artistic and practical handwriting training. |
Introduction to Paleography and Chirography
Paleography is the study of ancient handwriting and scripts, focusing on analyzing historical manuscripts to understand writing styles, materials, and cultural contexts. Chirography refers to the art or skill of writing by hand, emphasizing penmanship, letter formation, and the manual techniques involved in producing legible and aesthetically pleasing scripts. Together, these disciplines provide insights into the evolution of written communication and the interpretation of historical documents.
Defining Paleography: The Study of Ancient Writing
Paleography is the scientific study of ancient writing systems, analyzing historical scripts to understand their development, use, and cultural context through manuscripts, inscriptions, and archival documents. It focuses on deciphering, dating, and authenticating texts by examining handwriting styles, materials, and ink characteristics from different historical periods. Unlike chirography, which refers specifically to the art or skill of handwriting, paleography encompasses a broader academic discipline essential for interpreting historical records and preserving written heritage.
Understanding Chirography: The Art of Handwriting
Chirography is the specialized study and practice of handwriting, emphasizing the formation, style, and personal expression of individual letterforms. Unlike paleography, which analyzes ancient scripts and historical manuscripts for linguistic and cultural insights, chirography focuses on the dynamic techniques and aesthetics of contemporary penmanship. Mastery in chirography involves understanding stroke patterns, pressure control, and the fluidity of script to enhance legibility and artistic value in handwritten communication.
Historical Development of Paleography
Paleography, the study of ancient handwriting, traces its historical development back to the examination of early manuscripts, such as those from Mesopotamian cuneiform and Egyptian hieroglyphs, evolving through classical Latin and Greek scripts to medieval and Renaissance handwriting. In contrast, chirography specifically focuses on the art and skill of handwriting, emphasizing calligraphy and penmanship techniques rather than the historical and linguistic analysis central to paleography. Scholars use paleographic methods to date manuscripts and understand historical contexts, which is crucial for interpreting documents ranging from ancient papyri to medieval codices.
Evolution and Scope of Chirography
Chirography, the study and art of handwriting, has evolved from basic script formation to encompass diverse styles, techniques, and tools reflecting cultural and technological changes over centuries. Unlike paleography, which primarily analyzes ancient manuscripts to decipher historical scripts and contextual origins, chirography focuses on the development, aesthetics, and practical applications of handwriting in both historical and modern contexts. The scope of chirography extends to handwriting instruction, calligraphy, forensic analysis, and digital penmanship, highlighting its ongoing relevance in education, art, and technology.
Key Differences Between Paleography and Chirography
Paleography examines ancient handwriting to understand historical documents' origins, styles, and dating, while chirography centers on the art and technique of modern handwriting and penmanship. Paleography involves analysis of scripts such as Gothic, Carolingian, and uncial, emphasizing the cultural and temporal context, whereas chirography emphasizes personal handwriting development, letter formation, and writing tools. The primary distinction lies in paleography's historical manuscript study versus chirography's focus on the aesthetic and functional aspects of contemporary handwriting.
Techniques and Tools in Paleography
Paleography involves the study and analysis of ancient handwriting, utilizing specialized techniques such as script comparison, character identification, and ink analysis to determine the origin and date of manuscripts. Tools in paleography include magnifying glasses, ultraviolet light sources for ink examination, digital imaging technology, and databases of known scripts to facilitate detailed inspection and comparison. In contrast, chirography focuses on the art of handwriting itself, emphasizing penmanship techniques and the physical act of writing rather than historical manuscript analysis.
Methods and Styles in Chirography
Chirography, the study and art of handwriting, employs various methods and styles including cursive, print, and calligraphy, emphasizing individual penmanship techniques and personal expression. Techniques such as pressure variation, stroke order, and letter spacing define distinct handwriting styles, influencing legibility and aesthetic appeal. Unlike paleography, which analyzes ancient scripts primarily for historical context, chirography focuses on the functional and artistic aspects of modern handwriting methods.
Applications in Modern Research and Practice
Paleography, the study of ancient handwriting, is essential for interpreting historical manuscripts, authenticating documents, and preserving cultural heritage in modern research. Chirography, focusing on the art and technique of handwriting, supports forensic analysis, personalized education methods, and digital handwriting recognition technologies. Both disciplines enhance understanding of script evolution, enabling advancements in archival science and handwriting-based biometric security systems.
The Future of Paleographic and Chirographic Studies
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming paleographic and chirographic studies by enabling more accurate analysis and interpretation of ancient manuscripts and handwriting samples. Digital imaging technologies combined with big data analytics facilitate the preservation and decipherment of historical scripts, expanding the scope of research in these fields. Collaborative platforms and open-access databases are fostering global scholarship and accelerating discoveries in the evolution of writing systems and human communication.
Paleography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com