Digestive health plays a crucial role in overall well-being, influencing energy levels, immune function, and nutrient absorption. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and hydration supports optimal digestion and helps prevent common issues like bloating and constipation. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies to improve your digestive health and enhance your daily comfort.
Table of Comparison
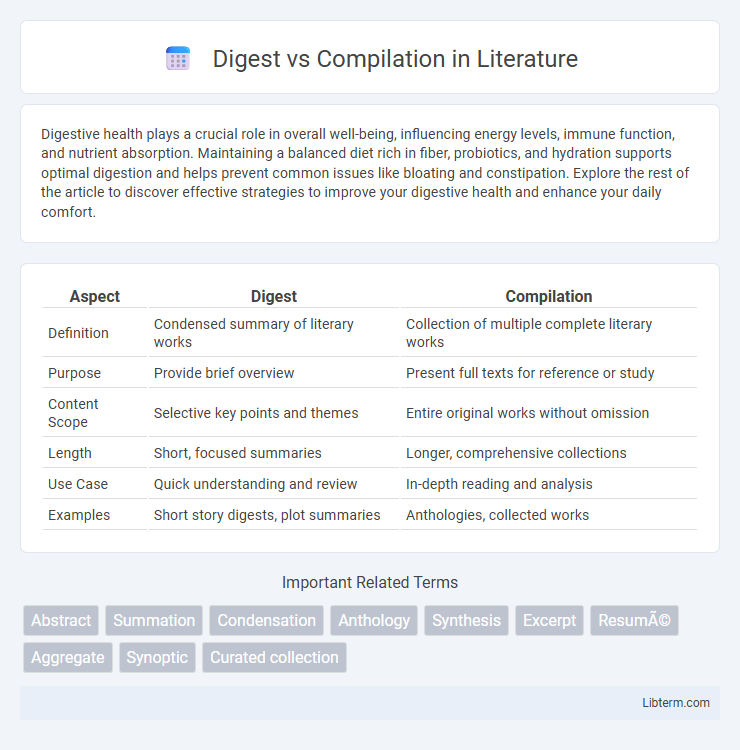
| Aspect | Digest | Compilation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Condensed summary of literary works | Collection of multiple complete literary works |
| Purpose | Provide brief overview | Present full texts for reference or study |
| Content Scope | Selective key points and themes | Entire original works without omission |
| Length | Short, focused summaries | Longer, comprehensive collections |
| Use Case | Quick understanding and review | In-depth reading and analysis |
| Examples | Short story digests, plot summaries | Anthologies, collected works |
Introduction to Digest and Compilation
A digest is a summarized collection of legal cases, statutes, or regulations organized by topic to facilitate quick reference and understanding of legal principles. A compilation is a comprehensive gathering of related legal materials, including full texts of statutes, regulations, or case reports, often intended to offer exhaustive coverage of a particular subject. Both digests and compilations serve as essential research tools, with digests emphasizing concise summaries and compilations prioritizing complete documentation.
Defining Digest: Key Features
Digest refers to a summarized collection of information or articles, often focusing on essential points for quick understanding. Key features include concise presentation, thematic grouping, and easy accessibility to core insights or data. It serves as a valuable resource for readers seeking a snapshot of comprehensive content without extensive detail.
Understanding Compilation: Essential Characteristics
Compilation involves aggregating multiple legal decisions or documents into a single, organized reference resource that categorizes content by topics or legal issues. It provides comprehensive access to primary sources such as statutes, cases, and regulations, often arranged systematically for ease of research. Essential characteristics of compilation include accuracy, completeness, and systematic organization to support efficient legal analysis and citation.
Historical Evolution of Digests and Compilations
The historical evolution of digests began in ancient Rome, where jurists consolidated legal opinions into organized collections, influencing modern legal research. Compilations emerged as comprehensive assemblies of statutes and case laws, aiming to provide authoritative legal references during the medieval and early modern periods. The transition from Roman digests to systematic compilations marks the foundation of contemporary legal codification and jurisprudence analysis.
Differences Between Digest and Compilation
Digests summarize and organize case law by extracting key points from multiple decisions, enabling quick reference to precedent, whereas compilations collect complete legal materials such as statutes, regulations, or full case reports without summarization. Digests provide headnotes and topic classifications to aid legal research efficiency, while compilations serve as comprehensive repositories for direct consultation of original texts. The primary difference lies in digests offering synthesized insights for rapid understanding, compared to compilations presenting exhaustive, unabridged legal documents.
Common Uses of Digests
Digests serve as concise summaries of larger texts, commonly utilized in legal, academic, and professional fields to highlight essential information quickly. They enable efficient review and reference by distilling key points from complex documents, facilitating faster decision-making and research. Compilation, in contrast, involves collecting and organizing complete documents or data sets without summarization, often used for in-depth analysis or record-keeping.
Typical Applications of Compilations
Compilations are typically used in software development environments where source code written in high-level programming languages needs to be converted into executable machine code, enabling efficient performance on target hardware. Unlike digests that summarize or condense information, compilations aggregate and translate extensive codebases, supporting applications such as operating systems, mobile apps, and embedded systems. Common tools for compilations include GCC for C/C++ and javac for Java, which optimize code for runtime efficiency and platform compatibility.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Digest vs Compilation
Digest organizes and summarizes information from multiple sources, offering concise and easily accessible insights but may omit context and detailed explanations. Compilation gathers original documents or complete texts, providing comprehensive and authentic data but often requires more time to review and analyze. Digest advantages include efficiency and quick understanding, while compilations ensure depth and accuracy at the cost of increased complexity.
Selecting the Right Format: Digest or Compilation?
Selecting the right format between digest and compilation depends on the intended purpose and audience engagement; a digest provides concise summaries ideal for quick updates and efficient information scanning, while a compilation offers detailed, comprehensive collections suited for in-depth study and reference. Consider the volume and complexity of content, as digests excel in condensing vast information into easily digestible segments, whereas compilations are preferable when preserving the original context and full content is critical. Evaluating user needs for brevity versus thoroughness ensures optimal content delivery through the appropriate format.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Digest and Compilation
Choosing between a digest and a compilation depends on the need for concise summaries versus comprehensive collections of information. Digests provide brief, focused insights ideal for quick reference, while compilations offer detailed, extensive data suitable for in-depth analysis. Evaluating the context and purpose of use ensures selecting the most effective format for legal research or academic study.
Digest Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com