Fragmentation refers to the process of breaking down complex data or tasks into smaller, manageable pieces that enhance efficiency and organization. This concept is crucial in fields like computer science, where file fragmentation can impact system performance, and biology, where cellular fragmentation affects development. Discover how fragmentation shapes various industries and what it means for your work in the full article.
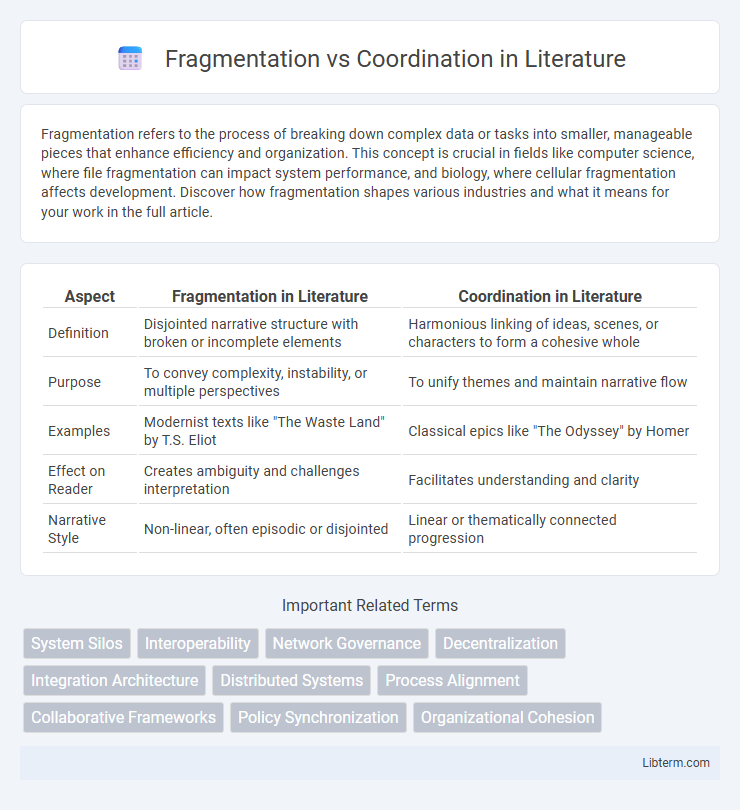
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fragmentation in Literature | Coordination in Literature |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disjointed narrative structure with broken or incomplete elements | Harmonious linking of ideas, scenes, or characters to form a cohesive whole |
| Purpose | To convey complexity, instability, or multiple perspectives | To unify themes and maintain narrative flow |
| Examples | Modernist texts like "The Waste Land" by T.S. Eliot | Classical epics like "The Odyssey" by Homer |
| Effect on Reader | Creates ambiguity and challenges interpretation | Facilitates understanding and clarity |
| Narrative Style | Non-linear, often episodic or disjointed | Linear or thematically connected progression |
Introduction to Fragmentation and Coordination
Fragmentation refers to the division of a system or process into smaller, often disconnected parts, leading to inefficiencies and challenges in communication. Coordination involves aligning and integrating these fragmented components to achieve coherent and efficient outcomes. Effective coordination mitigates the negative impacts of fragmentation by fostering collaboration and streamlined workflows across diverse units or stakeholders.
Defining Fragmentation in Systems
Fragmentation in systems refers to the division or segmentation of processes, data, or components into isolated, disconnected parts that hinder seamless interaction and integration. This condition often leads to inefficiencies, duplicated efforts, and challenges in information flow across different modules or departments. Defining fragmentation involves identifying the lack of unified structure, interoperability, and centralized control within complex systems.
Understanding Coordination: Key Concepts
Coordination involves aligning tasks, resources, and goals across different units or teams to achieve optimal efficiency and synergy. It requires clear communication channels, shared objectives, and well-defined roles to prevent overlap and conflicts. Effective coordination integrates diverse activities, ensuring consistency and timely decision-making within complex organizational structures.
Causes of Fragmentation
Fragmentation often arises from siloed organizational structures, inconsistent policies, and varying technological platforms that limit effective communication. Geographic dispersion and lack of unified leadership exacerbate fragmented workflows, reducing overall efficiency and collaboration quality. Conflicting objectives among departments or stakeholders further contribute to fragmentation by creating misaligned priorities and duplicated efforts.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Fragmentation
Fragmentation allows organizations to specialize and adapt quickly to local needs, enhancing flexibility and innovation within distinct units. However, it can lead to inefficiencies, duplicated efforts, and communication barriers, reducing overall organizational cohesion and increasing operational costs. This trade-off between specialization and integration impacts scalability and consistency in service delivery or product quality.
Advantages of Effective Coordination
Effective coordination streamlines communication and resource allocation, reducing redundancy and operational costs. It enhances team synergy and project alignment, leading to faster decision-making and improved productivity. Coordinated efforts also enable organizations to adapt swiftly to market changes, fostering innovation and competitive advantage.
Fragmentation vs Coordination: Comparative Analysis
Fragmentation in organizational structures leads to isolated units operating independently, resulting in inefficiencies and duplicated efforts, whereas coordination fosters integration and communication, enhancing overall performance and resource optimization. Comparative analysis reveals that fragmented systems struggle with information silos and inconsistent decision-making, while coordinated frameworks promote synergy and streamlined processes. Empirical studies indicate that organizations emphasizing coordination achieve higher adaptability and responsiveness in dynamic environments compared to those experiencing fragmentation.
Impact on Organizational Performance
Fragmentation in organizations often leads to siloed departments, reducing communication efficiency and slowing decision-making processes, which negatively impacts overall organizational performance. Coordination enhances integration across teams, streamlines workflows, and fosters collaboration, driving increased productivity and innovation. Effective coordination mechanisms mitigate the risks of fragmentation, resulting in improved agility and competitive advantage for the organization.
Strategies to Transition from Fragmentation to Coordination
Implementing integrated communication platforms facilitates real-time data sharing among departments, enhancing coordination and reducing operational fragmentation. Establishing cross-functional teams aligns objectives across diverse units, promoting unified decision-making and streamlined workflows. Leveraging standardized processes and centralized databases ensures consistency and transparency, accelerating the transition from disjointed efforts to cohesive organizational collaboration.
Conclusion: Achieving Optimal Balance
Achieving optimal balance between fragmentation and coordination requires leveraging the strengths of both approaches to enhance organizational flexibility and efficiency. Strategic coordination minimizes redundancy and fosters collaboration, while controlled fragmentation allows innovation and responsiveness to local needs. Integrating these elements maximizes resource utilization and drives sustainable growth in complex systems.
Fragmentation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com