An elegy is a mournful poem expressing sorrow for someone who has passed away, often reflecting on themes of loss and remembrance. It captures deep emotions and offers comfort by honoring the deceased's memory. Discover how understanding elegies can enrich your appreciation of poetry by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
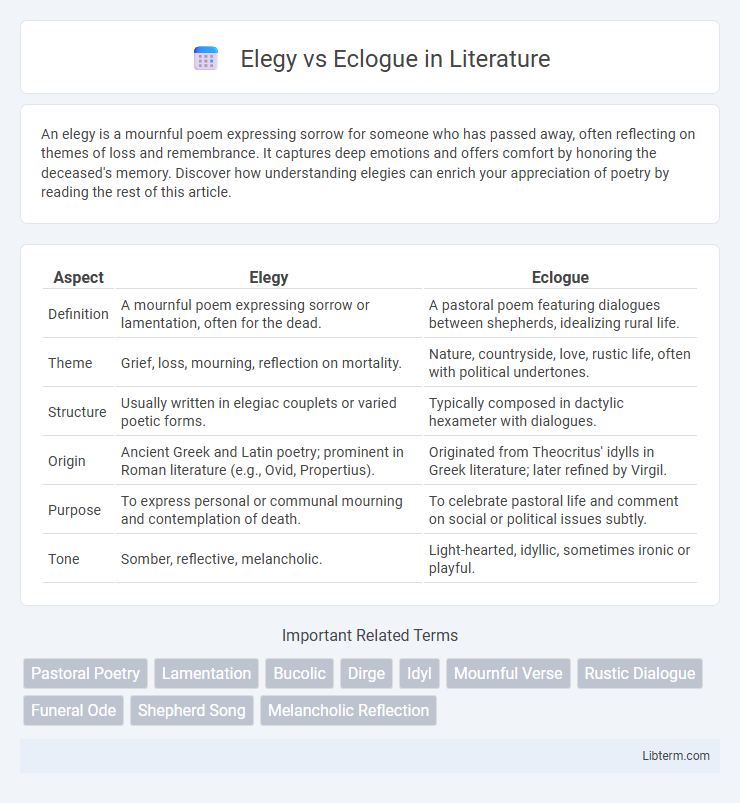
| Aspect | Elegy | Eclogue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A mournful poem expressing sorrow or lamentation, often for the dead. | A pastoral poem featuring dialogues between shepherds, idealizing rural life. |
| Theme | Grief, loss, mourning, reflection on mortality. | Nature, countryside, love, rustic life, often with political undertones. |
| Structure | Usually written in elegiac couplets or varied poetic forms. | Typically composed in dactylic hexameter with dialogues. |
| Origin | Ancient Greek and Latin poetry; prominent in Roman literature (e.g., Ovid, Propertius). | Originated from Theocritus' idylls in Greek literature; later refined by Virgil. |
| Purpose | To express personal or communal mourning and contemplation of death. | To celebrate pastoral life and comment on social or political issues subtly. |
| Tone | Somber, reflective, melancholic. | Light-hearted, idyllic, sometimes ironic or playful. |
Understanding Elegy and Eclogue: Definitions
Elegy is a poetic form characterized by its mournful tone, often expressing sorrow for the deceased or reflecting on loss, typically written in elegiac couplets in classical literature. Eclogue, alternatively known as a pastoral poem, depicts rural life and shepherds, emphasizing idyllic landscapes and dialogues, originating from ancient Greek and Roman traditions. Both forms serve distinct purposes, with elegies focusing on lamentation and eclogues celebrating pastoral simplicity.
Historical Origins of Elegy and Eclogue
Elegy originated in ancient Greece as a poetic form composed in elegiac couplets, often expressing lamentation or mourning, with early practitioners like Archilochus and later Roman poets such as Tibullus and Ovid refining its themes of sorrow and reflection. Eclogue, deriving from the Greek word "ekloge" meaning "selection," is a form of pastoral poetry that emerged in Hellenistic Alexandria and was popularized by Roman poets like Virgil, who used it to depict idyllic rural life and dialogues among shepherds. Both genres reflect significant Hellenistic and Roman literary traditions, with elegy focusing on personal emotion and eclogue emphasizing idealized nature and community.
Key Themes in Elegiac Poetry
Elegiac poetry primarily explores themes of love, loss, and mourning, often reflecting personal emotions and human vulnerability through expressive lamentation. The elegy contrasts with the eclogue, which typically features pastoral scenes and dialogues between shepherds, focusing on rural life and nature. Elegies emphasize introspection and sorrow, capturing the transient nature of life and relationships with profound emotional depth.
The Bucolic World of the Eclogue
The Bucolic world of the Eclogue paints an idealized pastoral landscape populated by shepherds who express themes of love, nature, and rural life, contrasting sharply with the elegy's focus on personal loss and mourning. Eclogues, originating from Virgil's "Eclogues," emphasize dialogue and poetic imagery rooted in the simplicity and harmony of countryside existence. This genre celebrates rustic beauty and communal life, using natural settings as metaphors for emotional and philosophical reflections.
Structure and Form: Elegy vs Eclogue
Elegies traditionally follow a formal structure composed of couplets or quatrains, often employing elegiac couplets with alternating hexameter and pentameter lines to convey themes of mourning and reflection. Eclogues are pastoral poems typically structured as short dialogues or monologues in hexameter, featuring rural characters that explore nature and rustic life. The rigid metric pattern of elegies contrasts with the more conversational and varied form of eclogues, highlighting their distinct thematic and structural intentions.
Prominent Elegists and Eclogue Poets
Prominent elegists such as Propertius, Tibullus, and Ovid are renowned for their lyric poetry centered on themes of love, loss, and personal reflection, employing elegiac couplets to express deep emotional nuance. In contrast, notable eclogue poets like Virgil and Theocritus specialize in pastoral poetry that celebrates rural life and nature, often featuring dialogues between shepherds set in idealized landscapes. The distinction highlights elegy's intimate and melancholic tone versus eclogue's bucolic and dialogic style within classical Latin and Greek literature.
Emotional Tone: Lamentation vs Pastoral Peace
Elegy embodies a somber emotional tone characterized by lamentation, expressing grief, loss, and reflection on mortality. Eclogue, contrastingly, conveys pastoral peace through idyllic rural settings and harmonious dialogue between shepherds, evoking tranquility and simplicity. The elegy's mournful intensity contrasts with the eclogue's serene celebration of nature and rustic life.
Influences on Classical and Modern Literature
Elegies and eclogues have profoundly shaped both classical and modern literature by influencing thematic exploration and poetic form. Elegies, rooted in mourning and reflection, have inspired countless poets from Ovid and Propertius to contemporary writers addressing loss and mortality with deep emotional resonance. Eclogues, with their pastoral settings and dialogues, established a tradition of idealizing rural life that echoes in Renaissance poetry, such as Virgil's work, and continues to influence modern pastoral and ecological literature.
Cultural Significance Through the Ages
Elegies and eclogues have significantly shaped literary culture, with elegies expressing profound grief and loss across civilizations, reflecting societal attitudes toward death and mourning. Eclogues, originating in pastoral poetry, celebrate rural life and idealized nature, influencing Renaissance and Romantic literature by idealizing simplicity and harmony. Both forms offer valuable insights into cultural values, emotional expression, and artistic priorities throughout history.
Choosing Between Elegy and Eclogue: When and Why
Elegy is best chosen for themes of mourning, loss, or personal reflection, emphasizing emotional depth and solemn tone, while eclogue suits pastoral scenes, idealizing rural life and dialogue between shepherds. Poets select elegies to explore grief or philosophical contemplation, whereas eclogues capture natural beauty and social interactions in rustic settings. Understanding the desired mood and subject matter helps determine whether the elegy's introspective melancholy or the eclogue's bucolic dialogue better conveys the intended message.
Elegy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com