Lyrics are the soul of any song, conveying emotions and stories through carefully chosen words and rhythms. They connect listeners to the artist's message and can evoke powerful feelings or memories. Explore the rest of this article to understand how lyrics shape the musical experience and inspire creativity.
Table of Comparison
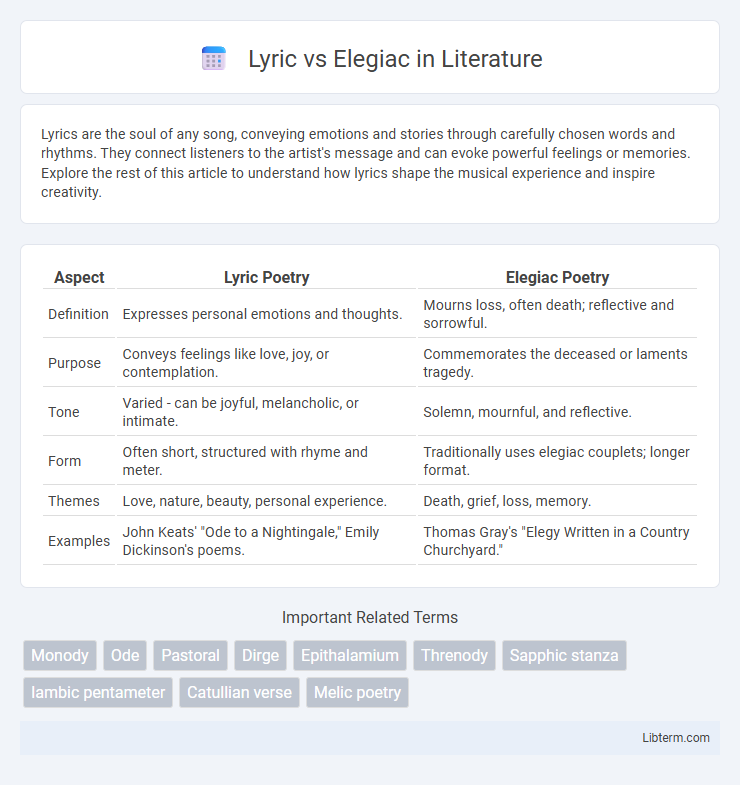
| Aspect | Lyric Poetry | Elegiac Poetry |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expresses personal emotions and thoughts. | Mourns loss, often death; reflective and sorrowful. |
| Purpose | Conveys feelings like love, joy, or contemplation. | Commemorates the deceased or laments tragedy. |
| Tone | Varied - can be joyful, melancholic, or intimate. | Solemn, mournful, and reflective. |
| Form | Often short, structured with rhyme and meter. | Traditionally uses elegiac couplets; longer format. |
| Themes | Love, nature, beauty, personal experience. | Death, grief, loss, memory. |
| Examples | John Keats' "Ode to a Nightingale," Emily Dickinson's poems. | Thomas Gray's "Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard." |
Introduction to Lyric and Elegiac Poetry
Lyric poetry expresses personal emotions and thoughts, often characterized by its musicality and brevity, typically written in the first person. Elegiac poetry mourns the loss of someone or something, traditionally utilizing a specific meter known as elegiac couplets, combining hexameter and pentameter lines. Both forms emerged prominently in ancient Greek literature, with lyric rooted in personal expression and elegiac focused on lamentation and reflection.
Defining Lyric Poetry
Lyric poetry is a concise, emotion-driven form of poetry that expresses personal feelings, thoughts, or moods, often written in the first person, contrasting with elegiac poetry, which specifically mourns loss or death. Lyric poems emphasize melodic qualities and vivid imagery, capturing moments of intense emotion rather than narrating a story or reflecting on death. Key examples of lyric poetry include sonnets, odes, and haikus, showcasing the genre's broad range and focus on subjective experience.
Defining Elegiac Poetry
Elegiac poetry is defined by its expression of mourning and reflection on loss, often characterized by a melancholic tone and themes of death or sorrow. Unlike lyric poetry, which emphasizes personal emotions and individual experiences more broadly, elegiac verses typically follow a structured form such as elegiac couplets and are rooted in memorializing the past. This poetic tradition dates back to ancient Greek and Roman literature, where elegies served as both lamentations and philosophical meditations on human mortality.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Lyric poetry originated in ancient Greece, specifically around the 7th century BCE, characterized by personal emotions and often accompanied by the lyre, evolving through Classical and Hellenistic periods into diverse lyrical forms. Elegiac poetry also traces back to ancient Greece, marked by its distinct elegiac couplet, initially used for laments and later broadening to themes of love and mourning in Roman literature. Over centuries, lyric poetry expanded to express individual feelings in various cultures, while elegiac poetry maintained its association with mourning and reflection, influencing Western literary traditions.
Key Themes in Lyric Poetry
Lyric poetry emphasizes personal emotions, individual experiences, and intimate reflections, often exploring themes such as love, nature, and human beauty. It captures fleeting moments of joy, sorrow, or passion through vivid imagery and musical language. Unlike elegiac poetry, which centers on mourning and loss, lyric poems celebrate life's emotional intensity and subjective perspective.
Central Themes in Elegiac Poetry
Elegiac poetry primarily explores themes of loss, mourning, and reflection on mortality, diverging from the personal emotions and individual experience typical of lyric poetry. Central themes often include sorrow for the dead, the transience of life, and nostalgic remembrance, capturing a collective or universal sense of grief. This genre's contemplative tone underscores the inevitability of change and the passage of time, contrasting with the more immediate and intimate focus found in lyric verse.
Stylistic Differences: Lyric vs Elegiac
Lyric poetry often employs vivid imagery and expressive language to convey personal emotions and thoughts with a musical quality, using various meters and rhyme schemes that enhance its melodic flow. Elegiac poetry, in contrast, adopts a more somber and reflective tone, typically structured in elegiac couplets, emphasizing themes of mourning, loss, and lamentation through restrained and melancholic stylistic devices. The stylistic difference lies in lyric's emotional intensity and celebratory mood versus elegiac's formal, contemplative sadness and elegy-specific metrical pattern.
Major Poets and Notable Works
Lyric poetry, characterized by personal emotion and musicality, includes major poets such as Sappho, whose fragments capture intimate feelings, and William Wordsworth, noted for "Lines Composed a Few Miles Above Tintern Abbey." Elegiac poetry, defined by themes of mourning and loss, features prominent poets like Ovid, famous for "Elegies," and Thomas Gray, whose "Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard" remains a cornerstone of the genre. Both forms have shaped literary traditions through their expression of human experience, with lyric emphasizing individual emotion and elegiac focusing on reflective sorrow.
Emotional Tone and Expression
Lyric poetry is characterized by its intimate, personal emotional tone, often expressing feelings of love, joy, or sorrow through vivid imagery and musicality. Elegiac poetry specifically conveys a mournful, reflective tone, focusing on themes of loss and mourning with a solemn, melancholic expression. Both forms utilize emotional intensity, but lyric poems embrace a broader range of sentiments, while elegies are distinctly somber and contemplative.
Impact and Influence in Modern Literature
Lyric poetry's emphasis on personal emotion and individual experience has profoundly shaped modern literature, inspiring introspective and expressive narrative styles across genres. Elegiac poetry, with its themes of loss and mourning, influenced contemporary works by providing a framework for exploring grief and memory, especially in post-war and trauma literature. Both forms contribute to modern literature's complexity by enriching its emotional depth and thematic diversity.
Lyric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com