Cumulative effects refer to the gradual buildup of impacts over time, often resulting from repeated exposures or actions. Understanding these effects is essential for accurate risk assessment and long-term planning in various fields such as health, environment, and finance. Explore the rest of the article to learn how cumulative processes influence your decisions and outcomes.
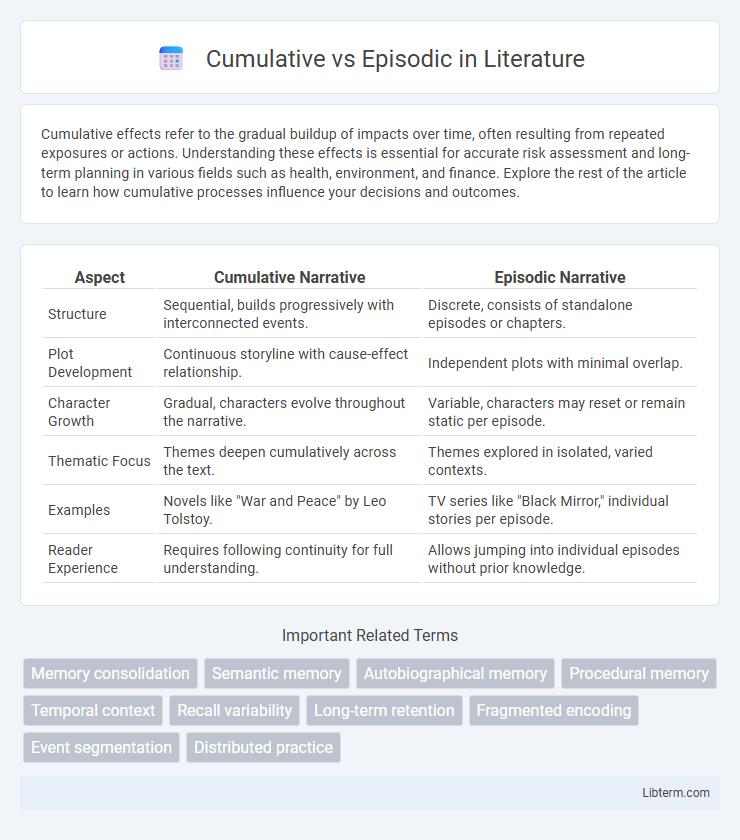
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cumulative Narrative | Episodic Narrative |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Sequential, builds progressively with interconnected events. | Discrete, consists of standalone episodes or chapters. |
| Plot Development | Continuous storyline with cause-effect relationship. | Independent plots with minimal overlap. |
| Character Growth | Gradual, characters evolve throughout the narrative. | Variable, characters may reset or remain static per episode. |
| Thematic Focus | Themes deepen cumulatively across the text. | Themes explored in isolated, varied contexts. |
| Examples | Novels like "War and Peace" by Leo Tolstoy. | TV series like "Black Mirror," individual stories per episode. |
| Reader Experience | Requires following continuity for full understanding. | Allows jumping into individual episodes without prior knowledge. |
Introduction to Cumulative vs Episodic
Cumulative memory integrates information gradually over time, building a comprehensive knowledge base from repeated experiences. Episodic memory, in contrast, captures specific events as distinct, contextualized moments, allowing for detailed recollection of particular experiences. Understanding the differences between these memory types is crucial for applications in cognitive psychology and artificial intelligence.
Defining Cumulative Memories
Cumulative memories refer to the aggregated retention of information acquired over multiple occasions, reflecting a continuous and integrative learning process. These memories build upon past experiences without specific contextual details, enabling the formation of generalized knowledge or skills. Unlike episodic memories that store distinct events with contextual time and place, cumulative memories emphasize the accumulation and refinement of knowledge through repeated exposure.
Understanding Episodic Events
Episodic events are specific, detailed occurrences anchored in particular contexts, times, and places, allowing individuals to recall personal experiences vividly. Understanding episodic events involves recognizing their unique temporal and spatial features, which distinguish them from cumulative events that represent aggregated data over periods. This distinction is crucial in fields like psychology and data analysis to accurately interpret memory formation and event tracking.
Key Differences Between Cumulative and Episodic
Cumulative memory involves the gradual accumulation of information over time, enabling long-term knowledge retention, while episodic memory stores specific personal experiences and events tied to particular contexts. Cumulative memory supports general knowledge and skills by integrating repeated exposures, whereas episodic memory is highly contextual and time-stamped, allowing individuals to recall detailed autobiographical moments. The key difference lies in cumulative memory's abstract, generalized nature compared to episodic memory's detailed, event-specific retrieval.
Benefits of Cumulative Experiences
Cumulative experiences build a rich knowledge base by integrating learning over time, enhancing decision-making and problem-solving skills through continuous exposure and practice. They foster deeper expertise and adaptability by reinforcing concepts and skills across multiple contexts, leading to sustained personal and professional growth. This ongoing accumulation enables improved memory retention and the ability to apply lessons learned in novel situations, driving long-term success and resilience.
Significance of Episodic Occurrences
Episodic occurrences represent discrete events with distinct beginnings and endings, providing critical data points essential for understanding temporal patterns and fluctuations within a process. Unlike cumulative measures that aggregate continuous data over time, episodic events enable precise identification of causality and the impact of specific interventions. This distinction is vital in fields such as healthcare and environmental monitoring, where episodic data reveal transient phenomena that cumulative statistics might obscure.
Real-World Examples: Cumulative vs Episodic
Cumulative memory involves the gradual accumulation of knowledge over time, exemplified by mastering a musical instrument or learning a new language through continuous practice. Episodic memory refers to recalling specific events or experiences, such as remembering a birthday party or a vacation. Real-world examples highlight that cumulative memory supports skill development and expertise, while episodic memory enriches personal narratives and contextual understanding.
Implications for Learning and Memory
Cumulative memory integrates information gradually over multiple experiences, enhancing long-term knowledge retention and facilitating complex skill development. Episodic memory involves recalling specific events, supporting contextual learning and the ability to adapt behavior based on unique past situations. Understanding the distinct mechanisms of cumulative and episodic memory informs targeted strategies for improving educational outcomes and memory rehabilitation.
Practical Applications in Daily Life
Cumulative memory enables individuals to build knowledge over time, supporting skills like language learning and routine task management, essential for daily productivity. Episodic memory allows recall of specific personal experiences, aiding decision-making and social interactions by providing contextual details about past events. Together, these memory types enhance adaptability by combining factual understanding with experiential insights in everyday situations.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Cumulative and Episodic
Choosing between cumulative and episodic memory hinges on the specific learning goals and context. Cumulative memory suits tasks requiring long-term integration and gradual knowledge build-up, while episodic memory excels in capturing unique, context-rich events for immediate recall. Selecting the appropriate memory type enhances cognitive efficiency and task performance based on whether generalization or detailed recollection is prioritized.
Cumulative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com