Aesthetics explores the principles of beauty and taste, shaping how we perceive art, design, and our environment. Understanding aesthetic theories can enhance Your ability to appreciate and create visually appealing spaces or objects. Discover more about the impact of aesthetics and how it influences daily life in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
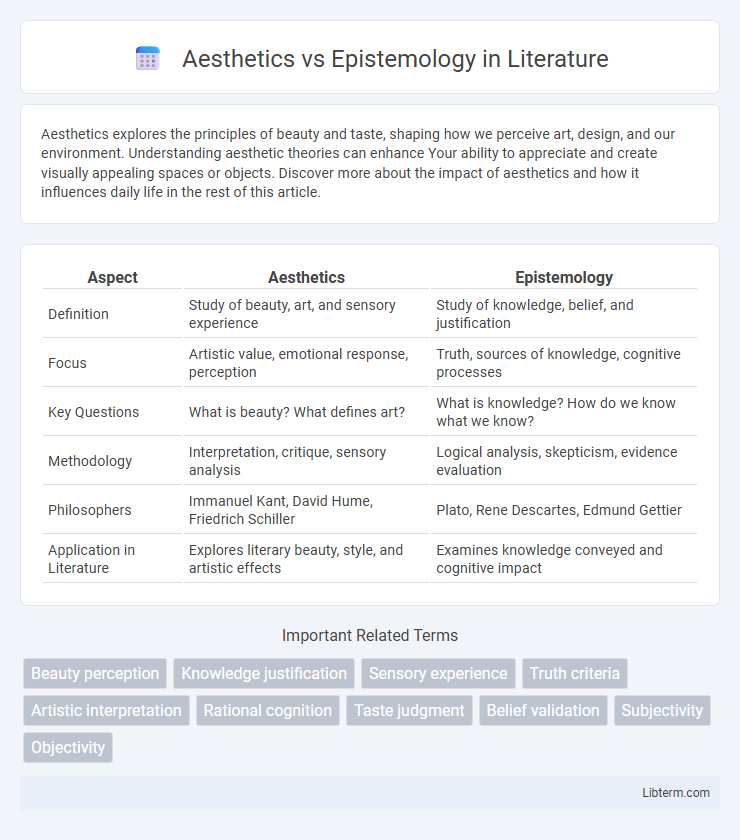
| Aspect | Aesthetics | Epistemology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of beauty, art, and sensory experience | Study of knowledge, belief, and justification |
| Focus | Artistic value, emotional response, perception | Truth, sources of knowledge, cognitive processes |
| Key Questions | What is beauty? What defines art? | What is knowledge? How do we know what we know? |
| Methodology | Interpretation, critique, sensory analysis | Logical analysis, skepticism, evidence evaluation |
| Philosophers | Immanuel Kant, David Hume, Friedrich Schiller | Plato, Rene Descartes, Edmund Gettier |
| Application in Literature | Explores literary beauty, style, and artistic effects | Examines knowledge conveyed and cognitive impact |
Understanding Aesthetics: The Philosophy of Beauty
Understanding aesthetics involves analyzing the nature of beauty, art, and taste, emphasizing how sensory experiences and emotional responses shape our perception of artistic value. Unlike epistemology, which studies knowledge and belief systems, aesthetics prioritizes the interpretation of sensory input and cultural context in forming judgments about beauty. Philosophers such as Immanuel Kant explore the interplay between subjective feelings and objective criteria, highlighting the complexity of aesthetic appreciation.
What Is Epistemology? Foundations of Knowledge
Epistemology is the branch of philosophy that studies the nature, origin, and limits of human knowledge, emphasizing how beliefs are justified and what distinguishes true knowledge from mere opinion. It investigates foundational concepts such as belief, truth, and justification, exploring sources like perception, reason, memory, and testimony. This discipline establishes criteria for knowledge by analyzing the reliability and validity of cognitive processes, crucial for understanding how individuals acquire and evaluate information.
Core Questions in Aesthetics and Epistemology
Core questions in aesthetics explore the nature of beauty, artistic value, and the criteria for aesthetic judgment, examining what makes an experience or object aesthetically pleasing or significant. Epistemology centers on the nature, scope, and limits of knowledge, probing how knowledge is acquired, justified, and differentiated from belief. Both disciplines intersect by questioning how perception, interpretation, and understanding influence human experience and cognition.
Historical Relationships Between Aesthetics and Epistemology
The historical relationship between aesthetics and epistemology reveals how the understanding of knowledge often intertwined with the appreciation of beauty, particularly in the works of philosophers like Immanuel Kant and Plato. In classical philosophy, aesthetics was not merely about art but was linked to the pursuit of truth and the nature of knowing, influencing concepts such as sensory perception and cognition. This fusion has shaped contemporary debates on how aesthetic experiences can contribute to epistemic insight and the validation of knowledge claims.
Methods of Inquiry: Sensory Perception vs Rational Evidence
Aesthetics relies heavily on sensory perception, emphasizing subjective experiences and emotional responses to art, beauty, and sensory stimuli as primary methods of inquiry. Epistemology prioritizes rational evidence, valuing logical reasoning, critical analysis, and empirical data to justify knowledge claims and validate truth. These differing methodologies highlight the contrast between intuitive, experiential understanding and systematic, objective investigation within philosophical discourse.
The Subjective vs Objective Divide
Aesthetics revolves around the subjective experience of beauty and artistic value, emphasizing personal interpretation and emotional response. Epistemology, by contrast, seeks objective knowledge, focusing on the justification and truth of beliefs independent of individual feelings. The divide between subjective aesthetics and objective epistemology highlights fundamental differences in how humans perceive and validate reality.
The Role of Interpretation in Art and Knowledge
Interpretation plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and epistemology by shaping how individuals derive meaning from art and knowledge. In aesthetics, interpretation influences the emotional and intellectual engagement with a work of art, revealing layers of symbolism and cultural context. Epistemologically, interpretation affects the construction and validation of knowledge by guiding how evidence, concepts, and experiences are understood and integrated.
Aesthetic Judgment and Truth Claims
Aesthetic judgment engages sensory experience and emotional response to evaluate beauty or artistic value, while epistemology concerns the justification and truth of knowledge claims. Unlike epistemic assertions, aesthetic judgments lack objective truth conditions but reveal subjective interpretations shaped by cultural and individual contexts. The tension between aesthetics and epistemology highlights how truth claims in art rely on nuanced perceptual insight rather than empirical verification.
Intersections: Where Aesthetics Meets Epistemology
Aesthetics and epistemology intersect in exploring how sensory experiences contribute to knowledge acquisition, revealing that aesthetic appreciation can function as a form of understanding. Artistic expression often embodies epistemic value by conveying complex truths and emotional insights beyond propositional knowledge. This convergence highlights the role of perception, interpretation, and judgment in both appreciating beauty and constructing knowledge.
Contemporary Debates and Future Directions
Contemporary debates in aesthetics versus epistemology explore the tension between subjective experiences of beauty and the objective pursuit of knowledge, emphasizing interdisciplinary methodologies that blend philosophy, cognitive science, and art theory. Current discourse often centers on how aesthetic judgments influence epistemic processes, questioning whether aesthetic values enhance or hinder truth acquisition. Future directions anticipate integrating artificial intelligence and neuroaesthetics to deepen understanding of how sensory perception informs knowledge frameworks and epistemic justification.
Aesthetics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com