Dissonance refers to a lack of harmony among musical notes, creating tension and a sense of unresolved conflict. In psychology, it describes the mental discomfort experienced when holding contradictory beliefs or behaviors, prompting a change in attitude or perception. Explore the article further to understand how dissonance influences both music and human decision-making.
Table of Comparison
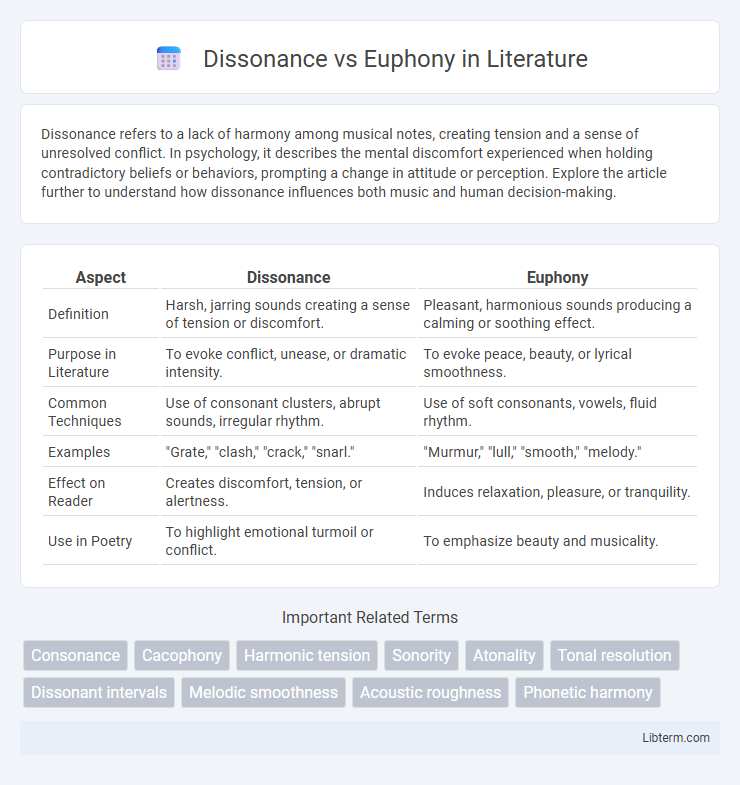
| Aspect | Dissonance | Euphony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Harsh, jarring sounds creating a sense of tension or discomfort. | Pleasant, harmonious sounds producing a calming or soothing effect. |
| Purpose in Literature | To evoke conflict, unease, or dramatic intensity. | To evoke peace, beauty, or lyrical smoothness. |
| Common Techniques | Use of consonant clusters, abrupt sounds, irregular rhythm. | Use of soft consonants, vowels, fluid rhythm. |
| Examples | "Grate," "clash," "crack," "snarl." | "Murmur," "lull," "smooth," "melody." |
| Effect on Reader | Creates discomfort, tension, or alertness. | Induces relaxation, pleasure, or tranquility. |
| Use in Poetry | To highlight emotional turmoil or conflict. | To emphasize beauty and musicality. |
Understanding Dissonance and Euphony
Dissonance refers to a combination of sounds that create tension or a sense of instability, often characterized by clashing or unresolved intervals in music and language. Euphony, in contrast, involves harmonious and pleasant sounds that produce a soothing and melodious effect, typically achieved through smooth consonants and harmonious vowel combinations. Understanding the balance between dissonance and euphony enhances the emotional and aesthetic impact of poetry, prose, and musical compositions.
The Roots of Dissonance in Language
The roots of dissonance in language often stem from phonetic clashes and unexpected sound combinations that disrupt the natural flow of speech, creating tension or discomfort. Harsh consonant clusters, abrupt stops, and jarring vowel transitions contribute to the perception of linguistic dissonance, challenging auditory harmony. Understanding these phonological elements highlights how dissonance contrasts with euphony's smooth, melodious sound patterns that promote ease and aesthetic pleasure in communication.
Euphony: Beauty and Harmony in Words
Euphony in language creates a pleasing auditory experience through the use of harmonious sounds, gentle consonants, and flowing vowels that enhance the beauty of words and phrases. Literary devices such as alliteration, assonance, and rhyme contribute to euphony by producing melodic patterns that evoke emotional resonance and aesthetic pleasure. Writers and poets employ euphonic techniques to craft lyrical passages that engage the reader's senses and convey tranquility, elegance, and musicality in their work.
Historical Perspectives on Sound Harmony
Ancient Greek philosophers like Pythagoras laid the foundation for understanding sound harmony by associating mathematical ratios with euphony, emphasizing pleasing and harmonious intervals. Medieval scholars further developed these ideas through the study of consonance and dissonance in Gregorian chant, defining accepted intervals that evoke stability or tension. The Baroque era refined these concepts, with theorists like Rameau systematizing harmony rules that balanced dissonance resolution and euphony to enhance musical expression.
The Psychological Impact of Dissonance
Dissonance in music triggers psychological tension by creating a sense of instability and anticipation within the listener's brain, often activating regions associated with emotional processing such as the amygdala. This tension can evoke feelings of unease or discomfort, compelling listeners to seek resolution, which enhances emotional engagement and cognitive stimulation. Understanding the psychological impact of dissonance reveals its crucial role in shaping emotional responses and narrative dynamics in auditory experiences.
Euphony in Poetry and Literature
Euphony in poetry and literature refers to the use of harmonious and melodious sounds to create a pleasing auditory effect, enhancing the reader's emotional experience. Poets often employ consonants like l, m, n, r, s, and vowels with open, flowing qualities to achieve euphonic lines that evoke calmness, beauty, or joy. This technique contrasts with dissonance, which uses harsh, jarring sounds to convey tension or discomfort, making euphony crucial for reinforcing positive mood and aesthetic appeal in literary works.
Dissonance vs Euphony: A Comparative Approach
Dissonance and euphony represent contrasting auditory qualities where dissonance involves harsh, clashing sounds that create tension, while euphony features harmonious, pleasant tones that evoke a sense of beauty. Analyzing dissonance versus euphony from a comparative approach highlights how poets and composers use dissonance to generate conflict or unease, whereas euphony enhances lyrical smoothness and emotional comfort. This contrast underscores the deliberate artistic choices in sound patterns impacting audience perception and emotional engagement.
Techniques for Achieving Euphony
Techniques for achieving euphony in poetry and prose include the use of soft consonants such as "l," "m," "n," and "r," which produce a smooth and harmonious sound. Incorporating elongated vowel sounds and melodic rhythm patterns enhances the pleasurable auditory effect, while alliteration and assonance contribute to a fluid and soothing tone. Writers often balance syllable stress and avoid harsh, abrupt sounds to maintain a consistent, melodious flow that appeals to readers' auditory senses.
When to Use Dissonance in Writing
Dissonance in writing creates tension and discomfort by employing harsh, jarring sounds or ideas that challenge the reader's expectations and provoke emotional responses. Use dissonance to highlight conflict, emphasize turmoil, or underscore unsettling themes, as it intensifies the narrative and engages readers on a visceral level. Strategic deployment of dissonance evokes realism in character struggles and amplifies dramatic impact in poetry, prose, or dialogue.
Balancing Dissonance and Euphony for Literary Effect
Balancing dissonance and euphony in literature enhances emotional impact and reader engagement by creating a dynamic auditory experience. Strategic use of harsh, discordant sounds (dissonance) juxtaposed with pleasing, harmonious rhythms (euphony) can evoke tension and relief, mirroring narrative conflict and resolution. Mastery of this balance sharpens thematic expression and deepens the sensory resonance of prose or poetry.
Dissonance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com