Form shapes the foundation of effective communication by structuring content clearly and coherently, ensuring your message is easily understood. A well-designed form captures attention and guides readers through information smoothly, enhancing engagement. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mastering form can elevate your writing and communication skills.
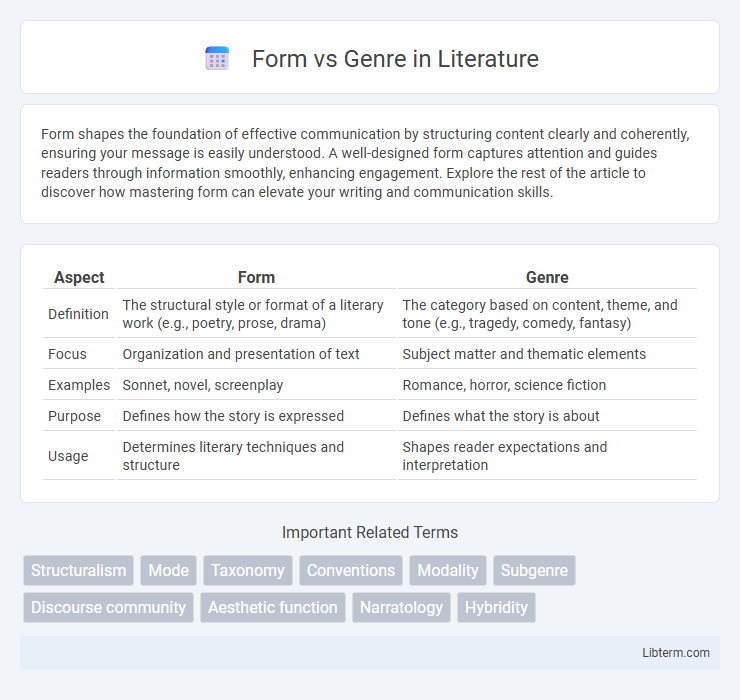
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Form | Genre |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The structural style or format of a literary work (e.g., poetry, prose, drama) | The category based on content, theme, and tone (e.g., tragedy, comedy, fantasy) |
| Focus | Organization and presentation of text | Subject matter and thematic elements |
| Examples | Sonnet, novel, screenplay | Romance, horror, science fiction |
| Purpose | Defines how the story is expressed | Defines what the story is about |
| Usage | Determines literary techniques and structure | Shapes reader expectations and interpretation |
Understanding the Concepts: Form and Genre
Form refers to the structural elements and features that define a work, such as its format, style, and organization, while genre classifies works into categories based on shared thematic content and conventions. Understanding form involves recognizing patterns like narrative structure or poetic meter, whereas grasping genre requires identifying recurring motifs and audience expectations, such as horror, romance, or comedy. Both concepts interact to shape how audiences interpret and engage with creative works across different media.
Defining Form in Literature and Art
Form in literature and art refers to the structural elements and techniques that organize content into a recognizable pattern, such as stanza arrangements in poetry or compositional balance in visual art. It encompasses aspects like narrative style, rhythm, and format that shape the work's presentation and audience interpretation. Defining form highlights the craftsmanship and framework that distinguish a piece beyond its thematic genre classification.
What is Genre? A Comprehensive Overview
Genre represents a category or classification of artistic works, particularly in literature, film, music, and art, defined by shared conventions, themes, and stylistic elements. It provides audiences and creators with recognizable patterns and expectations, facilitating communication and interpretation. Unlike form, which refers to the structural framework or medium, genre emphasizes the content and thematic nature of the work, categorizing narratives into types such as romance, thriller, science fiction, or drama.
Key Differences Between Form and Genre
Form refers to the structural aspects that define how a piece of content is organized, such as poetry, novel, or essay, whereas genre classifies content based on thematic and stylistic criteria, including categories like mystery, romance, or science fiction. Key differences between form and genre include the fact that form emphasizes the method of expression and the layout, while genre centers on the subject matter and audience expectations. Understanding these distinctions aids in accurate content analysis and effective communication across various media types.
The Role of Form in Shaping Content
Form plays a crucial role in shaping content by dictating the structural framework within which ideas are developed and communicated. It influences how narratives unfold, how arguments are presented, and how emotional responses are elicited, directly affecting the audience's interpretation and engagement. Different forms, such as sonnets, essays, or documentaries, impose unique constraints and opportunities that mold the content's expression and meaning.
How Genre Influences Audience Expectations
Genre shapes audience expectations by establishing familiar conventions and thematic patterns that guide their interpretation and emotional response. Specific genres like horror evoke anticipation of suspense and fear, while comedy primes viewers for humor and lightheartedness. These predefined narrative structures and stylistic elements help audiences predict plot progression and character behavior, enhancing engagement and satisfaction.
Examples of Common Forms and Genres
Forms such as sonnets, haikus, and free verse represent specific structures within poetry, while genres like mystery, romance, and science fiction categorize works based on thematic content and style. For example, a narrative poem is a form that tells a story, whereas the horror genre includes works designed to evoke fear and suspense. Understanding these distinctions helps readers identify the formal elements and thematic conventions that define different literary works.
Intersections: When Form and Genre Overlap
Form and genre intersect when structural elements of a work align with recognizable thematic or stylistic categories, creating hybrid expressions that challenge traditional classifications. This overlap allows for innovative storytelling, where formal techniques like narrative structure or visual style merge with genre conventions such as mystery, romance, or science fiction. Examining these intersections reveals how creators manipulate both form and genre to enrich meaning and engage diverse audiences.
Why Differentiating Form and Genre Matters
Differentiating form and genre clarifies the distinct structures and conventions that shape creative works, enabling more precise analysis and interpretation. Form refers to the physical or formal aspects, such as poetry, prose, or film, while genre categorizes works based on thematic elements like horror, romance, or mystery. Understanding this distinction enhances critical thinking, aids creators in targeting audiences, and supports academic study by providing clearer frameworks for evaluating artistic expression.
Evolving Forms and Genres in Modern Media
Evolving forms and genres in modern media reflect the blending and hybridization of traditional categories, driven by digital platforms and interactive technologies. Formats such as web series combine episodic storytelling with transmedia elements, while genres like sci-fi and fantasy incorporate cross-genre influences, adapting to audience demands for immersive experiences. This fluidity between form and genre enables creators to innovate narrative techniques and engage diverse, global audiences effectively.
Form Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com