Mastering your personal style enhances confidence and allows authentic self-expression through clothing choices that reflect your individuality. Understanding how to mix patterns, choose colors, and select fabrics that complement your lifestyle is essential for a polished look. Dive into the article to discover expert tips that will elevate your wardrobe and transform your style.
Table of Comparison
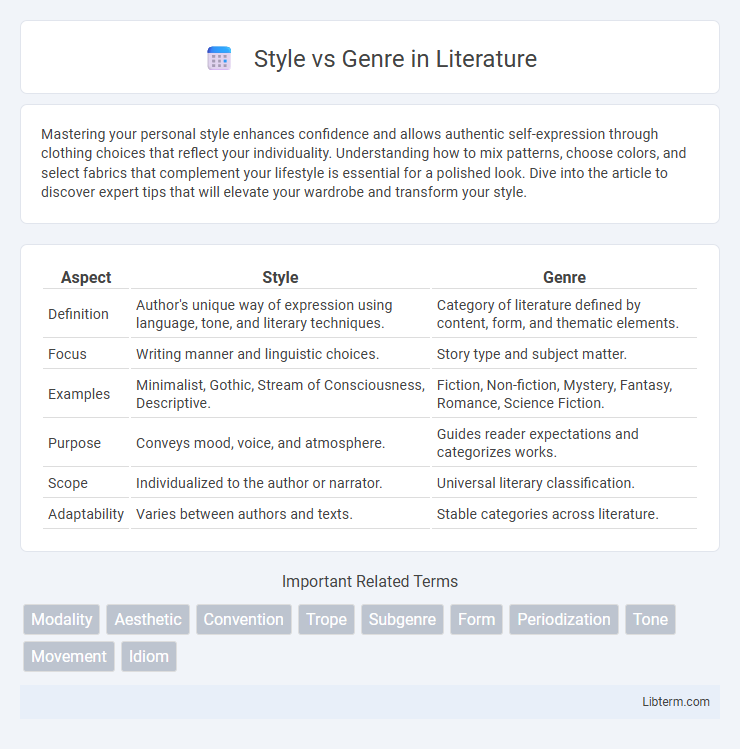
| Aspect | Style | Genre |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Author's unique way of expression using language, tone, and literary techniques. | Category of literature defined by content, form, and thematic elements. |
| Focus | Writing manner and linguistic choices. | Story type and subject matter. |
| Examples | Minimalist, Gothic, Stream of Consciousness, Descriptive. | Fiction, Non-fiction, Mystery, Fantasy, Romance, Science Fiction. |
| Purpose | Conveys mood, voice, and atmosphere. | Guides reader expectations and categorizes works. |
| Scope | Individualized to the author or narrator. | Universal literary classification. |
| Adaptability | Varies between authors and texts. | Stable categories across literature. |
Understanding Style and Genre: Key Definitions
Style refers to the distinctive techniques, choices, and methods an artist uses, characterized by elements like tone, rhythm, and structure, while genre categorizes works based on shared conventions and thematic content, such as horror, romance, or science fiction. Understanding style involves analyzing an individual creator's unique expression, whereas genre provides a framework for grouping similar works to set audience expectations. Mastery of both concepts enhances critical appreciation and effective communication about artistic works across literature, film, and other media.
Historical Evolution of Style and Genre
Historical evolution of style traces distinct artistic expressions shaped by cultural, social, and technological changes, reflecting shifts in aesthetics and technique from classical to modern periods. Genre evolution categorizes artworks or literature by thematic and formal characteristics, adapting to audience preferences and media innovations over centuries. The interplay between style and genre demonstrates how artistic forms constantly redefine boundaries, merging traditional motifs with contemporary influences.
Major Types of Literary Styles
Major types of literary styles include expository, descriptive, narrative, and persuasive, each defined by unique language features and purposes. Expository style aims to inform or explain with clear, concise language, while descriptive style uses vivid imagery and sensory details to create a strong visual impression. Narrative style tells a story with characters and plot, emphasizing sequential events, whereas persuasive style focuses on convincing the reader through logical arguments and emotional appeal.
Common Genres Across Media
Common genres across media include drama, comedy, horror, science fiction, and romance, each characterized by specific narrative conventions and emotional resonances. Style refers to the unique techniques and aesthetic choices employed by creators within these genres, such as visual composition in film or narrative voice in literature. Understanding the distinction between genre's thematic framework and style's expressive execution enriches the analysis of media works.
Style vs Genre: Core Differences
Style refers to the distinct techniques and methods an artist or writer uses, such as tone, vocabulary, and sentence structure, while genre categorizes works based on thematic and structural conventions, like mystery, romance, or science fiction. Style is unique to the creator and can vary widely within the same genre, whereas genre provides a framework that shapes content and audience expectations. Understanding the core differences between style and genre helps in analyzing and classifying creative works accurately.
How Style Influences Genre
Style shapes a genre by defining its unique tone, mood, and narrative techniques, which influence audience expectations and emotional responses. For instance, the gritty, dark style of film noir transforms traditional crime stories into a distinct genre characterized by moral ambiguity and complex characters. Changes in style can lead to the evolution or hybridization of genres, expanding their creative boundaries and appeal.
Genre Conventions and Style Variations
Genre conventions establish the foundational rules and thematic elements that define categories such as horror, romance, or science fiction, guiding audience expectations and narrative structure. Style variations involve the unique choices in tone, language, and technique employed by creators within these genres, allowing for diverse interpretations and innovative storytelling. Understanding the interplay between rigid genre conventions and flexible stylistic expressions enhances both critical analysis and creative writing in literature and film.
Identifying Style Within a Genre
Identifying style within a genre involves analyzing specific techniques, tone, and narrative structures that distinguish an author's or artist's unique approach from others in the same category. While genre categorizes content by shared themes or settings--such as science fiction or romance--style reflects individual expression through elements like sentence structure, imagery, and pacing. Recognizing style within a genre enhances critical understanding by highlighting how creators innovate or adhere to conventional genre expectations.
Impact of Style and Genre on Audience Reception
Style shapes the audience's emotional and cognitive engagement by influencing tone, mood, and aesthetic appeal, while genre sets expectations regarding plot structure, themes, and conventions. The alignment or subversion of style within a genre can enhance or challenge audience reception, affecting satisfaction and interpretation. Understanding the interplay between style and genre helps creators tailor content to target demographics and cultural preferences.
Blurring the Lines: Hybrid Styles and Cross-Genre Works
Hybrid styles and cross-genre works blur the lines between traditional style and genre boundaries by blending elements from multiple categories into a cohesive whole. This fusion creates innovative storytelling experiences that challenge audience expectations and expand creative possibilities. Examples include genre-bending novels, films, and music that combine sci-fi with romance, or jazz with electronic, generating unique aesthetic and narrative forms.
Style Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com