Understanding the subtle nuances of language can dramatically enhance your communication skills and deepen your connections with others. Mastery of semantics enables you to express ideas more clearly and interpret the meanings behind words accurately. Explore the rest of this article to unlock powerful techniques for optimizing your linguistic abilities.
Table of Comparison
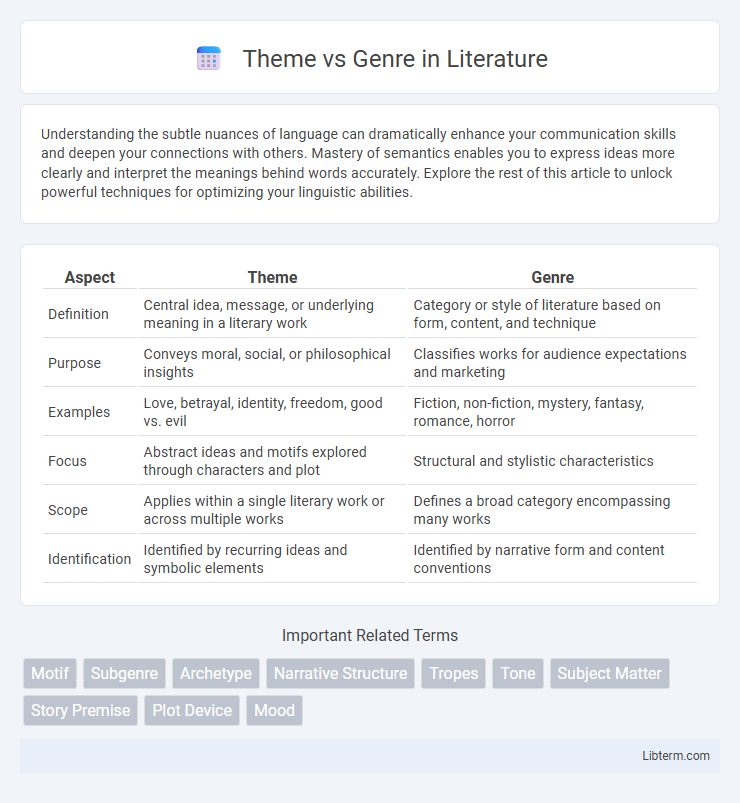
| Aspect | Theme | Genre |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Central idea, message, or underlying meaning in a literary work | Category or style of literature based on form, content, and technique |
| Purpose | Conveys moral, social, or philosophical insights | Classifies works for audience expectations and marketing |
| Examples | Love, betrayal, identity, freedom, good vs. evil | Fiction, non-fiction, mystery, fantasy, romance, horror |
| Focus | Abstract ideas and motifs explored through characters and plot | Structural and stylistic characteristics |
| Scope | Applies within a single literary work or across multiple works | Defines a broad category encompassing many works |
| Identification | Identified by recurring ideas and symbolic elements | Identified by narrative form and content conventions |
Understanding Theme and Genre
Theme represents the underlying message or central idea explored in a literary work, such as love, power, or identity, capturing the emotional or philosophical essence that resonates across narratives. Genre classifies stories based on shared conventions and styles, including categories like mystery, romance, or science fiction, which guide audience expectations and narrative structure. Understanding the distinction between theme and genre enhances comprehension by identifying both the story's core meaning and the framework through which it is delivered.
Defining Theme in Literature
Theme in literature refers to the underlying message, central idea, or insight about life that a work conveys, often expressed through motifs, symbols, and character experiences. Unlike genre, which classifies works by form and style such as tragedy, comedy, or romance, theme delves into abstract concepts like love, power, identity, or morality. Identifying the theme enhances understanding by revealing the author's purpose and the universal truths embedded within a narrative.
Exploring the Concept of Genre
Genre categorizes creative works based on shared stylistic and thematic elements, helping audiences set expectations and creators follow certain conventions. Exploring the concept of genre reveals how it shapes storytelling techniques, narrative structures, and emotional responses across literature, film, and music. Understanding genre classifications enhances critical analysis and guides marketing strategies within the entertainment industry.
Key Differences Between Theme and Genre
Theme represents the underlying message or central idea explored in a narrative, such as love, betrayal, or freedom. Genre categorizes a work based on its style, form, and content, including classifications like thriller, romance, or fantasy. Key differences include theme's focus on conceptual meaning versus genre's emphasis on storytelling conventions and audience expectations.
Examples of Common Themes in Stories
Common themes in stories include love, explored in romances like "Pride and Prejudice," and good versus evil, central to fantasy epics such as "Harry Potter." Themes of identity, destiny, and betrayal frequently appear in dramas and thrillers, exemplified by works like "The Great Gatsby" and "Game of Thrones." These thematic elements provide underlying messages that transcend specific genres, shaping the emotional and moral framework of narratives.
Popular Literary Genres Explained
Popular literary genres include fiction, non-fiction, fantasy, mystery, romance, and science fiction, each characterized by distinct narrative structures and thematic elements. Themes explore universal ideas like love, conflict, or identity, while genres categorize stories based on style, setting, and plot conventions. Understanding genre helps readers anticipate the story's framework, whereas theme reveals the deeper message or moral explored throughout the narrative.
How Theme Influences Genre
Theme directly influences genre by shaping the emotional tone and narrative focus, guiding the story's atmosphere and style. For example, a theme centered on love or relationships often aligns with genres like romance or drama, while themes of survival and conflict typically drive action or thriller genres. Understanding the core theme helps writers and creators select or blend genres to effectively convey their intended message and engage the target audience.
How Genre Shapes Storytelling
Genre establishes the framework of storytelling by defining specific conventions, plot structures, and character archetypes that guide the narrative's development. It influences the tone, pacing, and audience expectations, thereby shaping how themes are explored and conveyed throughout the story. Understanding genre conventions allows writers to craft compelling narratives that resonate within cultural and market contexts, enhancing thematic depth and emotional impact.
Identifying Theme and Genre in Popular Works
Theme represents the central idea or underlying message in popular works, such as love, betrayal, or freedom, while genre categorizes these works based on stylistic and structural elements like mystery, romance, or science fiction. Identifying the theme involves analyzing characters, plot, and motifs to uncover the deeper meaning, whereas recognizing the genre depends on narrative conventions and audience expectations. For example, "The Great Gatsby" explores themes of decadence and the American Dream within the genre of literary fiction, while "The Hunger Games" combines dystopian themes with the science fiction genre.
Why Theme and Genre Matter to Writers and Readers
Theme reveals the underlying message or central idea that gives a story depth and resonates emotionally with readers, while genre categorizes the narrative into familiar types like mystery or romance, guiding audience expectations. Writers use theme to convey meaning and provoke thought, and genre to structure their storytelling approach and market their work effectively. Readers rely on genre to select stories aligned with their preferences and on theme to find connections that enrich their reading experience.
Theme Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com