Materialism emphasizes the importance of physical possessions and wealth as a path to happiness and success. It often prioritizes tangible assets over spiritual or emotional fulfillment, impacting how people view their achievements and relationships. Explore the rest of this article to understand how materialism shapes your values and lifestyle choices.
Table of Comparison
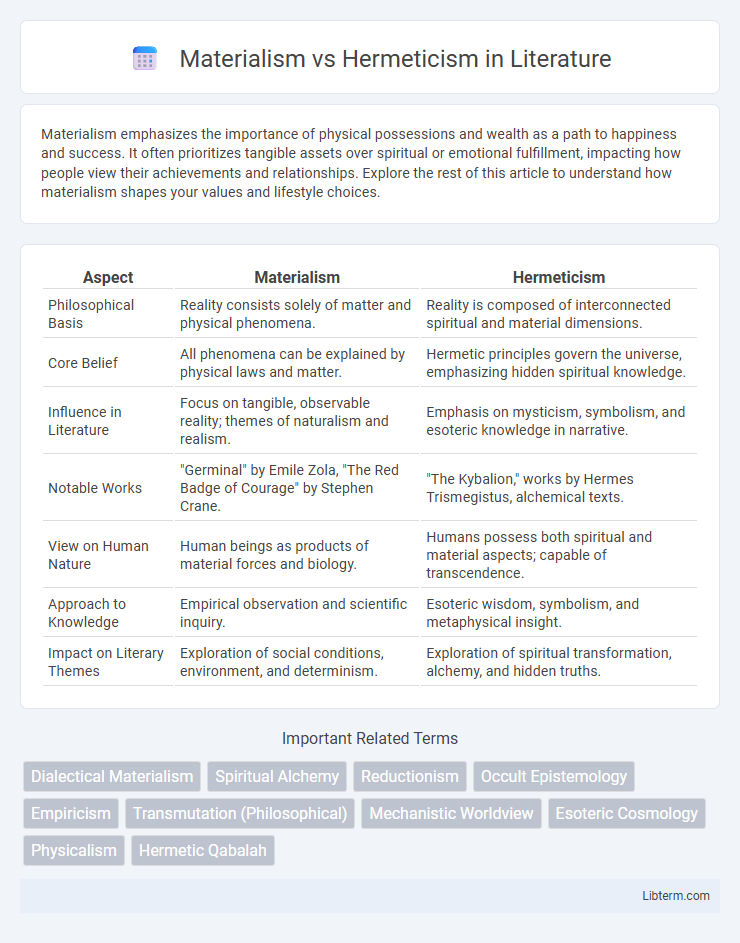
| Aspect | Materialism | Hermeticism |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophical Basis | Reality consists solely of matter and physical phenomena. | Reality is composed of interconnected spiritual and material dimensions. |
| Core Belief | All phenomena can be explained by physical laws and matter. | Hermetic principles govern the universe, emphasizing hidden spiritual knowledge. |
| Influence in Literature | Focus on tangible, observable reality; themes of naturalism and realism. | Emphasis on mysticism, symbolism, and esoteric knowledge in narrative. |
| Notable Works | "Germinal" by Emile Zola, "The Red Badge of Courage" by Stephen Crane. | "The Kybalion," works by Hermes Trismegistus, alchemical texts. |
| View on Human Nature | Human beings as products of material forces and biology. | Humans possess both spiritual and material aspects; capable of transcendence. |
| Approach to Knowledge | Empirical observation and scientific inquiry. | Esoteric wisdom, symbolism, and metaphysical insight. |
| Impact on Literary Themes | Exploration of social conditions, environment, and determinism. | Exploration of spiritual transformation, alchemy, and hidden truths. |
Understanding Materialism: A Brief Overview
Materialism asserts that physical matter is the fundamental substance of reality, and all phenomena, including consciousness, arise from material interactions. It emphasizes empirical evidence and scientific observation as the basis for knowledge, rejecting supernatural explanations or immaterial entities. This worldview contrasts with Hermeticism, which integrates spiritual and metaphysical principles beyond purely physical explanations.
Defining Hermeticism: Origins and Core Principles
Hermeticism originates from the writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, blending Greco-Egyptian philosophical, spiritual, and esoteric traditions central to its teachings. Core principles include the concepts of as above, so below; the unity of all existence; and the pursuit of alchemical transformation--both physical and spiritual. This worldview contrasts materialism by emphasizing metaphysical realities and inner knowledge over purely physical matter and empirical evidence.
Historical Roots: From Ancient Thought to Modern Debate
Materialism traces its origins to ancient Greek philosophers such as Democritus and Epicurus, who posited that all phenomena result from the interactions of matter. Hermeticism, rooted in the Hermetic Corpus attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, blends mystical, philosophical, and esoteric traditions from Hellenistic Egypt, emphasizing the interconnectedness of the cosmos and spiritual transformation. The historical evolution of these doctrines has fueled modern debates contrasting empirical, scientific materialism with esoteric, symbolic Hermetic knowledge.
Key Philosophical Differences
Materialism asserts that physical matter is the fundamental substance of reality, emphasizing empirical evidence and observable phenomena as the basis of knowledge. Hermeticism centers on spiritual and mystical principles, positing that the universe operates through hidden correspondences and the unity of all things beyond physical perception. The key philosophical difference lies in materialism's reliance on tangible, measurable reality versus Hermeticism's focus on esoteric, metaphysical truths.
Material Reality: The Pillars of Materialism
Materialism asserts that material reality forms the foundation of existence, emphasizing physical matter and tangible phenomena as the ultimate constituents of the universe. This philosophy prioritizes empirical evidence and observable patterns in nature, reducing consciousness and thought to material interactions. In contrast, Hermeticism often explores spiritual and metaphysical principles beyond the physical realm, challenging the materialist view that reality is solely material-based.
Spiritual Perspective: Hermeticism's View on the Universe
Hermeticism perceives the universe as a living, interconnected whole where spiritual and material realms are inseparable, emphasizing the principle of "as above, so below." This esoteric tradition teaches that spiritual enlightenment arises through understanding cosmic laws and inner transformation, contrasting materialism's focus on physical matter and empirical evidence. Hermeticism regards the universe as a divine manifestation, encouraging seekers to align their consciousness with universal wisdom to unlock hidden spiritual truths.
Science vs. Spirituality: Bridging or Dividing?
Materialism emphasizes empirical evidence and physical phenomena as the foundation of reality, aligning closely with scientific methods that prioritize observation and experimentation. Hermeticism, rooted in esoteric spirituality and metaphysical principles, explores inner transformation and cosmic interconnectedness beyond material perception. The ongoing dialogue between science and spirituality seeks to bridge the gap by integrating objective inquiry with subjective experience, challenging the dichotomy and fostering a holistic understanding of existence.
Impacts on Society and Culture
Materialism influences society by emphasizing empirical evidence and technological progress, driving consumer culture and economic growth while often promoting secular values. Hermeticism shapes culture through mystical traditions and esoteric philosophies, fostering spiritual exploration and alternative worldviews that challenge mainstream religious and scientific paradigms. The tension between materialism and hermeticism manifests in cultural debates over spirituality, science, and the meaning of existence, impacting art, literature, and social movements.
Personal Fulfillment: Material vs. Hermetic Lifestyles
Materialism emphasizes personal fulfillment through the accumulation of physical possessions and external achievements, reflecting societal values of success and status. Hermeticism advocates for inner growth and spiritual enlightenment, promoting a lifestyle focused on self-awareness, meditation, and esoteric knowledge. This contrast highlights material fulfillment as transient and externally driven, whereas Hermetic fulfillment seeks enduring inner peace and deep metaphysical understanding.
Contemporary Relevance and Future Perspectives
Materialism, emphasizing physical reality and empirical evidence, remains dominant in scientific and technological advancements shaping contemporary society, influencing fields like artificial intelligence and neuroscience. Hermeticism, with its focus on spiritual knowledge and metaphysical principles, continues to inspire holistic wellness practices and esoteric philosophy, offering alternative frameworks for understanding consciousness. Future perspectives suggest an integrative approach where materialism's empirical rigor and Hermeticism's introspective insights could collaboratively address complex issues in human experience and cosmology.
Materialism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com