Carnivalization transforms traditional narratives by blending diverse perspectives, challenging established hierarchies, and promoting a culture of humor and chaos. This concept encourages breaking down social norms and embracing pluralism, fostering a space where multiple voices coexist in vibrant dialogue. Discover how carnivalization reshapes literature and culture by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
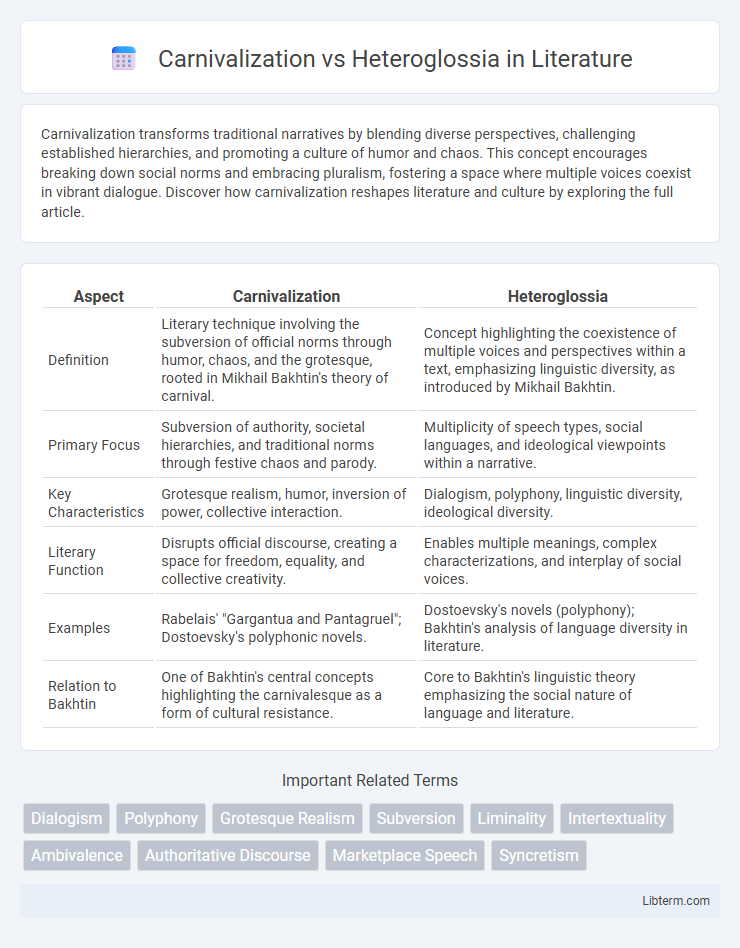
| Aspect | Carnivalization | Heteroglossia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary technique involving the subversion of official norms through humor, chaos, and the grotesque, rooted in Mikhail Bakhtin's theory of carnival. | Concept highlighting the coexistence of multiple voices and perspectives within a text, emphasizing linguistic diversity, as introduced by Mikhail Bakhtin. |
| Primary Focus | Subversion of authority, societal hierarchies, and traditional norms through festive chaos and parody. | Multiplicity of speech types, social languages, and ideological viewpoints within a narrative. |
| Key Characteristics | Grotesque realism, humor, inversion of power, collective interaction. | Dialogism, polyphony, linguistic diversity, ideological diversity. |
| Literary Function | Disrupts official discourse, creating a space for freedom, equality, and collective creativity. | Enables multiple meanings, complex characterizations, and interplay of social voices. |
| Examples | Rabelais' "Gargantua and Pantagruel"; Dostoevsky's polyphonic novels. | Dostoevsky's novels (polyphony); Bakhtin's analysis of language diversity in literature. |
| Relation to Bakhtin | One of Bakhtin's central concepts highlighting the carnivalesque as a form of cultural resistance. | Core to Bakhtin's linguistic theory emphasizing the social nature of language and literature. |
Introduction to Carnivalization and Heteroglossia
Carnivalization, a concept developed by Mikhail Bakhtin, refers to the subversion and liberation from dominant norms through humor, chaos, and the inversion of social hierarchies. Heteroglossia, another Bakhtinian notion, describes the coexistence of multiple voices, languages, and perspectives within a text, reflecting social diversity and ideological conflict. Both concepts emphasize the dynamic interaction of voices but differ in Carnivalization's focus on temporary social upheaval versus Heteroglossia's emphasis on linguistic plurality.
Defining Carnivalization: Origins and Concepts
Carnivalization, rooted in Mikhail Bakhtin's theories, embodies the subversion of dominant norms through humor, chaos, and the inversion of social hierarchies. It originates from the medieval carnival tradition, where temporary liberation from official rules allowed for playful, grotesque interactions and the blending of diverse voices. This concept highlights a dynamic, collective expression that challenges fixed authority and embraces multiplicity in meaning and social roles.
Understanding Heteroglossia: Key Principles
Heteroglossia, a concept introduced by Mikhail Bakhtin, refers to the coexistence of multiple voices, styles, and perspectives within a single text or discourse, reflecting the diversity of social languages. It emphasizes dialogism, where different speech types interact dynamically, resisting uniformity and authorial dominance. Understanding heteroglossia involves recognizing language as inherently stratified, shaped by social structures and power relations, thus enriching meaning through the tension between conflicting ideologies.
Bakhtin’s Influence on Literary Theory
Carnivalization and heteroglossia are central concepts in Mikhail Bakhtin's literary theory, emphasizing the subversion of traditional narrative forms and the coexistence of multiple voices within a text. Carnivalization refers to the temporary suspension of hierarchical norms and the celebration of chaos and plurality, which challenges authoritative discourse. Heteroglossia highlights the diversity of speech types and social languages that interact within a novel, revealing the complex dialogic nature of language and meaning.
Carnivalization in Literature: Examples and Analysis
Carnivalization in literature transforms traditional narratives by incorporating chaos, humor, and subversion, as exemplified in Mikhail Bakhtin's analysis of Rabelais' "Gargantua and Pantagruel," where social hierarchies are inverted and folk culture is celebrated. This literary technique breaks down authoritative voices, allowing multiple perspectives to interact in a dynamic, often grotesque, manner that challenges dominant ideologies. Carnivalization fosters a space for liberation and creative expression, enriching texts with layers of meaning through parody, satire, and the grotesque.
Heteroglossia in Narrative Forms
Heteroglossia in narrative forms refers to the coexistence of multiple voices, languages, and social discourses within a single text, revealing the diversity of perspectives and ideologies. Unlike carnivalization, which emphasizes the subversion of traditional hierarchies and the grotesque, heteroglossia highlights dialogic interaction and the conflict between authoritative and non-authoritative discourses. This concept, rooted in Mikhail Bakhtin's theory, enriches narratives by creating complex, layered meanings through the interplay of varied linguistic and social strata.
Main Differences Between Carnivalization and Heteroglossia
Carnivalization, a concept developed by Mikhail Bakhtin, involves the subversion of dominant norms through humor, chaos, and the temporary suspension of hierarchical structures, often manifesting in literature as grotesque realism and collective folk culture. Heteroglossia refers to the coexistence and interaction of multiple voices, languages, and perspectives within a single text, emphasizing dialogic relationships and the diversity of speech types. The main difference lies in carnivalization's focus on societal inversion and collective festivity, whereas heteroglossia centers on linguistic diversity and the interplay of social voices within discourse.
Intersections: How Carnivalization and Heteroglossia Interact
Carnivalization and heteroglossia intersect through their shared emphasis on the subversion of dominant discourses by incorporating multiple, often conflicting voices that challenge hierarchical structures. Carnivalization, by celebrating chaos and parody, amplifies heteroglossia's dialogic interplay of diverse linguistic and social perspectives, creating a vibrant space for marginalized expressions. This interaction fosters a dynamic literary and cultural environment where power relations are destabilized through the coexistence of contradictory viewpoints and voices.
Carnivalization vs Heteroglossia in Modern Media
Carnivalization in modern media manifests as the subversion of authoritative narratives through humor, chaos, and inversion of social roles, creating a space for alternative voices and collective empowerment. Heteroglossia emphasizes the coexistence of multiple voices, perspectives, and dialects within media texts, highlighting cultural diversity and ideological complexity. While carnivalization disrupts dominant discourse through spectacle and parody, heteroglossia enriches media by fostering dialogic interaction among diverse linguistic and social identities.
Conclusion: The Relevance of Both Concepts Today
Carnivalization and heteroglossia remain crucial for understanding contemporary cultural and literary dynamics by emphasizing the plurality of voices and subversion of dominant narratives. These concepts reveal the ongoing negotiation of power through humor, chaos, and dialogic interaction in both traditional and digital spaces. Their relevance persists in analyzing how diverse perspectives challenge authority and foster inclusive, multi-vocal discourse in today's globalized society.
Carnivalization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com