Intradiegesis refers to the narrative elements that exist within the story world and are perceived or experienced by the characters themselves. It contrasts with extradiegesis, where the narrator or storytelling voice operates outside the story's internal environment. Discover how understanding intradiegesis can deepen your appreciation of narrative structures in literature and film by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
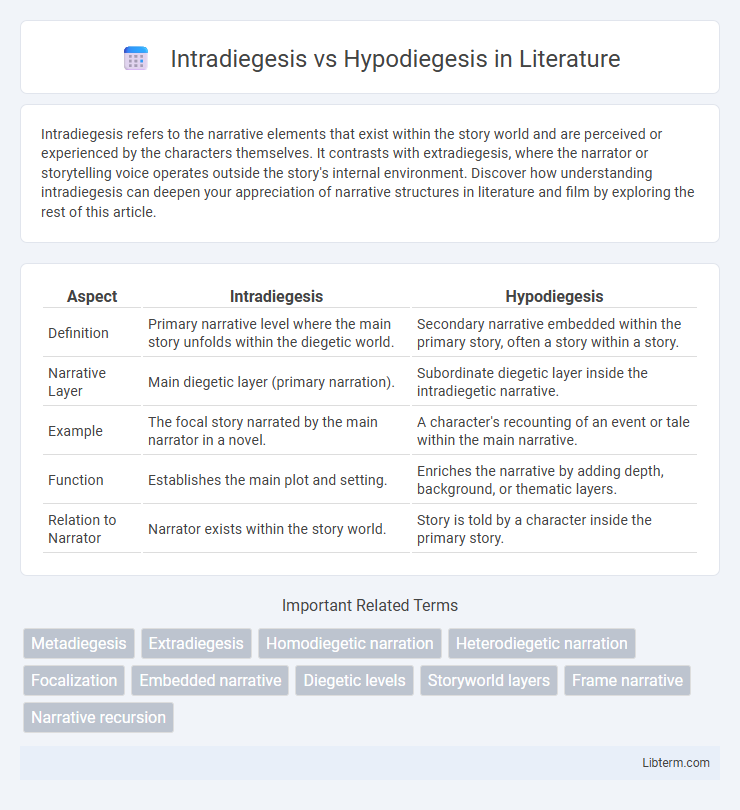
| Aspect | Intradiegesis | Hypodiegesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Primary narrative level where the main story unfolds within the diegetic world. | Secondary narrative embedded within the primary story, often a story within a story. |
| Narrative Layer | Main diegetic layer (primary narration). | Subordinate diegetic layer inside the intradiegetic narrative. |
| Example | The focal story narrated by the main narrator in a novel. | A character's recounting of an event or tale within the main narrative. |
| Function | Establishes the main plot and setting. | Enriches the narrative by adding depth, background, or thematic layers. |
| Relation to Narrator | Narrator exists within the story world. | Story is told by a character inside the primary story. |
Understanding Intradiegesis: Definition and Scope
Intradiegesis refers to the narrative level where the story is told from within the primary fictional world, involving characters who directly participate in or witness events. It encompasses the main narrative layer, grounding the plot and character experiences within the diegetic reality created by the author. Understanding intradiegesis involves recognizing how this primary narrative layer shapes audience perception through internal viewpoints and character-driven storytelling.
Decoding Hypodiegesis: Meaning and Context
Decoding hypodiegesis involves understanding a secondary narrative embedded within the primary story, often serving as a story-within-a-story that enriches the main plot by providing additional layers of meaning or context. This narrative device contrasts with intradiegesis, where the narration occurs within the main storyline, making hypodiegesis crucial for exploring metafictional elements and complex storytelling techniques. Analyzing hypodiegetic content reveals how authors manipulate narrative structures to deepen thematic exploration and engage readers through multiple interpretative frameworks.
Core Differences Between Intradiegesis and Hypodiegesis
Intradiegesis refers to the narrative level within the primary story world where characters and events exist directly in the diegetic reality, while hypodiegesis involves a subordinate or embedded narrative inside the main story, such as a story within a story. The core difference lies in the narrative hierarchy: intradiegetic elements operate in the primary diegesis, whereas hypodiegetic elements function at a subordinate narrative level, often providing metatextual or interpretive depth. This distinction affects narrative perspective, with intradiegetic narratives reflecting the main plot's reality and hypodiegetic narratives expanding world-building through embedded storytelling.
Narrative Levels: Exploring Diegetic Hierarchies
Intradiegesis refers to the primary narrative level where the main story unfolds within the diegetic world, while hypodiegesis involves embedded sub-narratives or stories within the primary narrative, forming a secondary diegetic layer. These narrative levels establish diegetic hierarchies, allowing complex storytelling structures through the interaction between the overarching narrative and nested tales. Understanding the relationship between intradiegesis and hypodiegesis is crucial for analyzing multilayered narratives in literature, film, and media studies.
The Role of Intradiegesis in Storytelling
Intradiegesis refers to the narrative level within the primary story world where characters and events exist and unfold, playing a crucial role in immersing the audience in the plot. This narrative layer enables the unfolding of events through the perspective of characters embedded within the story, enhancing emotional engagement and cohesion. Intradiegetic storytelling techniques, such as first-person narration or character-driven dialogue, deepen the audience's connection by presenting the narrative from within the story's internal reality.
Hypodiegesis and Embedded Narratives
Hypodiegesis refers to an embedded narrative or secondary story within the primary diegetic world, often conveyed through a character's recounting or a thematic flashback. These embedded narratives enhance the main plot by offering additional perspectives, background information, or exploring subplots that deepen the overall storytelling experience. The study of hypodiegesis reveals complex narrative layers, where multiple story levels coexist, enriching the reader's or viewer's engagement with the diegesis.
Examples of Intradiegesis in Literature and Film
Intradiegesis refers to the narrative level within the primary story world where characters experience and recount events directly, exemplified in literature by Nick Carraway's first-person narration in "The Great Gatsby," providing an internal viewpoint of the plot. In film, intradiegetic narration occurs in "Fight Club" where the protagonist narrates his experiences and inner thoughts, embedding the story within the diegetic reality. These instances anchor the audience inside the narrative, creating immersive storytelling through perspectives belonging to characters who exist within the fictional world.
Illustrative Cases of Hypodiegesis in Popular Media
Hypodiegesis refers to the embedded or nested narratives within a primary story, often presented as tales told by characters inside the main diegesis. Illustrative cases of hypodiegesis appear prominently in popular media such as the movie *Inception*, where dreams within dreams create multiple narrative layers, and in *The Princess Bride*, where a grandfather reads a story that unfolds as the main plot. These examples demonstrate how hypodiegetic narratives enrich storytelling by adding depth and complexity through secondary fictional worlds or accounts.
Narrative Techniques: Manipulating Diegetic Layers
Intradiegesis involves narrative elements occurring within the primary story world, while hypodiegesis refers to embedded narratives or stories within the main diegesis, creating multiple story layers. Manipulating these diegetic levels enhances narrative complexity by allowing shifts between different temporalities, perspectives, and reliability of narration. Techniques such as frame narratives and embedded storytelling intensify reader engagement by intertwining primary and secondary diegetic realms.
Impact of Intradiegesis and Hypodiegesis on Reader Engagement
Intradiegesis enhances reader engagement by immersing them directly into the primary narrative world, creating a seamless and relatable storytelling experience. Hypodiegesis introduces a secondary narrative layer that enriches the main story with depth and complexity, prompting readers to actively interpret and connect multiple narrative levels. The interplay between intradiegesis and hypodiegesis increases cognitive involvement, intensifying emotional investment and fostering a dynamic reader-text interaction.
Intradiegesis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com