Polysyndeton enhances your writing by intentionally using multiple conjunctions to create a deliberate, rhythmic emphasis on each element in a list or series. This technique slows the reader down, making the message more impactful and memorable. Discover more about how polysyndeton can elevate your prose in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
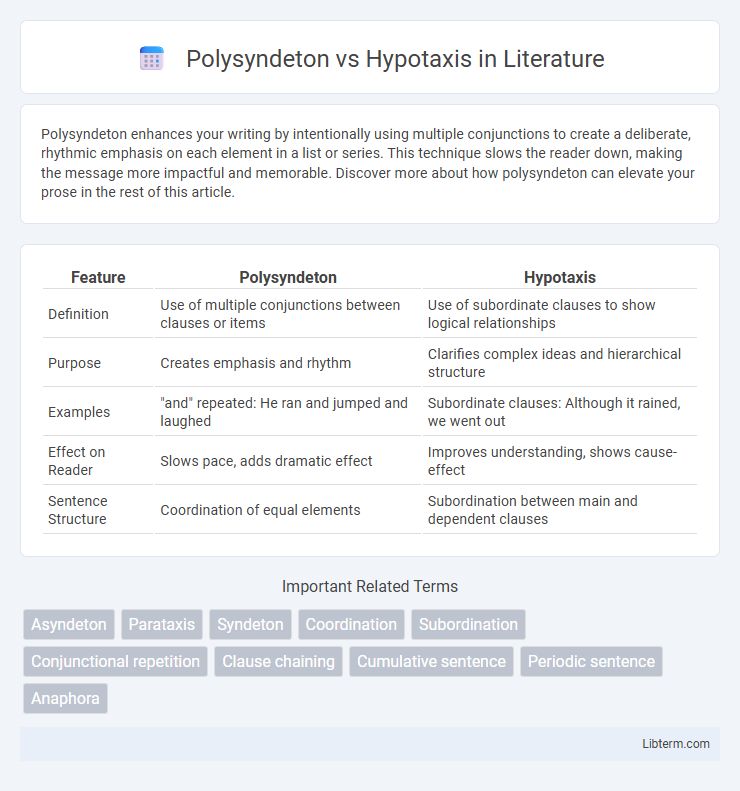
| Feature | Polysyndeton | Hypotaxis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of multiple conjunctions between clauses or items | Use of subordinate clauses to show logical relationships |
| Purpose | Creates emphasis and rhythm | Clarifies complex ideas and hierarchical structure |
| Examples | "and" repeated: He ran and jumped and laughed | Subordinate clauses: Although it rained, we went out |
| Effect on Reader | Slows pace, adds dramatic effect | Improves understanding, shows cause-effect |
| Sentence Structure | Coordination of equal elements | Subordination between main and dependent clauses |
Introduction to Polysyndeton and Hypotaxis
Polysyndeton is a rhetorical device characterized by the deliberate repetition of conjunctions in close succession to create a rhythmic effect or emphasize each item in a list. Hypotaxis, in contrast, involves the use of subordinate clauses to establish clear hierarchical relationships between ideas, enhancing clarity and logical flow in sentences. Understanding the distinction between polysyndeton's additive emphasis and hypotaxis's structural subordination is crucial for effective sentence construction and stylistic nuance in writing.
Defining Polysyndeton
Polysyndeton is a rhetorical device characterized by the deliberate use of multiple conjunctions between clauses, often slowing the rhythm and emphasizing each element in a series. Unlike hypotaxis, which involves complex, subordinate clause relationships to show hierarchy and logical connections, polysyndeton creates a cumulative effect that can convey abundance, intensity, or a sense of overwhelming detail. This technique is commonly used in literature and speeches to add weight and a rhythmic flow through repeated conjunctions such as "and," "or," and "but.
Defining Hypotaxis
Hypotaxis is a syntactic structure that arranges clauses in a hierarchical and subordinated manner, emphasizing the relationship between dependent and main clauses. It contrasts with polysyndeton, which uses multiple coordinating conjunctions to link clauses with equal syntactic status. Hypotaxis enhances clarity and complexity in sentence construction by explicitly indicating cause, condition, or sequence through subordinate conjunctions.
Grammatical Structure Differences
Polysyndeton employs multiple conjunctions to connect clauses or phrases, creating a rhythmic and additive effect, often emphasizing each element equally. Hypotaxis uses subordinating conjunctions and dependent clauses to establish clear hierarchical relationships between ideas, reflecting logical and syntactic dependency. The key grammatical difference lies in polysyndeton's coordination of elements versus hypotaxis's subordination, shaping sentence complexity and meaning.
Stylistic Effects of Polysyndeton
Polysyndeton, characterized by the deliberate use of multiple conjunctions in close succession, creates a rhythmic and emphatic effect that heightens the emotional intensity or urgency of a passage. This stylistic device slows down the reading pace, allowing each item or idea to stand out distinctly, thereby enhancing the overall impact and memorability. In contrast to hypotaxis, which uses subordinating conjunctions to establish clear hierarchical relationships between clauses, polysyndeton emphasizes accumulation and continuity, often evoking a sense of abundance or overwhelm.
Stylistic Effects of Hypotaxis
Hypotaxis employs subordinate clauses to create complex sentence structures that enhance clarity and emphasize relationships between ideas, fostering a logical and coherent narrative flow. This stylistic device allows authors to convey detailed information and nuanced arguments, promoting a more formal and sophisticated tone. The controlled pacing achieved through hypotaxis helps readers process intricate concepts by delineating cause and effect or hierarchical connections within the text.
Examples of Polysyndeton in Literature
Polysyndeton, characterized by the deliberate use of multiple conjunctions, appears prominently in literature to create rhythm and emphasize each element in a series, as seen in the phrase "and milk and honey and bread" from the King James Bible. William Shakespeare often employed polysyndeton to enhance dramatic effect, such as in Julius Caesar's "and that's by the lowliness of women's hands." This literary device contrasts with hypotaxis, which relies on subordination to connect clauses, highlighting the stylistic choice authors make for emphasis or flow.
Examples of Hypotaxis in Literature
Hypotaxis, characterized by the use of subordinate clauses to show the relationship between ideas, is vividly illustrated in classic literature such as Charles Dickens' "A Tale of Two Cities," where complex sentences like "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times" create depth and contrast through dependent clauses. Another notable example appears in Jane Austen's "Pride and Prejudice," where hypotactic structures like "Though she was kind, she remained firm" enhance the narrative by clarifying cause and effect. These intricate sentence structures enable writers to convey nuanced meanings and intricate relationships between thoughts, distinguishing hypotaxis from the more straightforward, repetitive style of polysyndeton.
Impact on Reader’s Perception
Polysyndeton, characterized by the deliberate use of multiple conjunctions, creates a rhythmic and emphatic effect that can intensify the reader's emotional engagement and highlight the complexity or abundance of ideas. In contrast, hypotaxis employs subordinating conjunctions to establish clear, hierarchical relationships between clauses, facilitating comprehension and guiding the reader through a logical progression of thoughts. The impact on reader's perception varies as polysyndeton evokes a sense of urgency or overwhelming detail, while hypotaxis promotes clarity and structured reasoning.
Choosing Between Polysyndeton and Hypotaxis
Choosing between polysyndeton and hypotaxis depends on the desired stylistic effect and clarity in writing. Polysyndeton employs multiple conjunctions to create a rhythmic, emphatic tone and can intensify the pacing or emotional impact of a sentence. Hypotaxis uses subordinate clauses to establish clear relationships between ideas, enhancing logical flow and complexity for analytical or formal texts.
Polysyndeton Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com