A foreword provides valuable context that sets the stage for the main content, often written by an expert or someone with firsthand experience. It helps to build credibility and offers insights that enrich your understanding of the text. Explore the article to uncover detailed perspectives and enhance your reading experience.
Table of Comparison
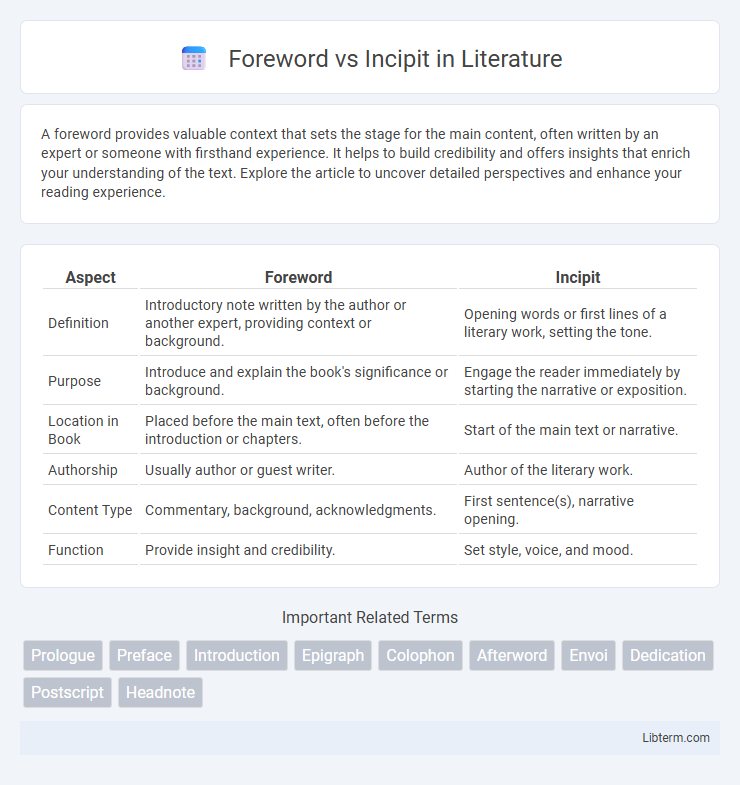
| Aspect | Foreword | Incipit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Introductory note written by the author or another expert, providing context or background. | Opening words or first lines of a literary work, setting the tone. |
| Purpose | Introduce and explain the book's significance or background. | Engage the reader immediately by starting the narrative or exposition. |
| Location in Book | Placed before the main text, often before the introduction or chapters. | Start of the main text or narrative. |
| Authorship | Usually author or guest writer. | Author of the literary work. |
| Content Type | Commentary, background, acknowledgments. | First sentence(s), narrative opening. |
| Function | Provide insight and credibility. | Set style, voice, and mood. |
Understanding Foreword and Incipit
A foreword is a preliminary section of a book, usually written by someone other than the author, offering context, background, or praise to enhance the reader's understanding. The incipit refers to the opening words or the very beginning of the main text, setting the tone and initiating the narrative or argument. Understanding the distinction between a foreword and an incipit helps readers recognize introductory commentary versus the actual start of a literary or academic work.
Definition of Foreword
A foreword is a brief introductory note written by someone other than the author, often an expert or notable figure, providing context, endorsement, or praise for the book. It differs from the incipit, which is the opening text of the main content, typically the first lines of the narrative or body. The foreword aims to guide readers' understanding and establish credibility before they engage with the author's work.
Definition of Incipit
Incipit refers to the opening words or beginning lines of a manuscript or book, serving as the textual starting point that introduces the content. Distinct from a foreword, which is an introductory statement often written by someone other than the author to provide context or endorsement, the incipit is an integral part of the primary text itself. The incipit plays a crucial role in establishing tone, style, and thematic elements right at the outset of the literary work.
Historical Origins of Foreword
The historical origins of the foreword trace back to ancient manuscripts where authors or notable figures provided introductory comments to establish context or authority, often preceding the main text. Unlike the incipit, which marks the actual beginning of a literary work with its opening words or sentences, the foreword serves as a separate, prefatory section to guide readers' understanding and frame the content. Early examples include classical Greek and Latin texts, where forewords were used to honor patrons or explain the purpose and scope of the writing.
Historical Origins of Incipit
The incipit, originating from Latin meaning "it begins," historically served as a textual anchor in medieval manuscripts, marking the opening words and establishing the initial framework of a text. Unlike the foreword, which functions as a modern introductory commentary or preface typically written by someone other than the author, the incipit was integral to codex identification and liturgical readings in monastic scriptoria. Its historical origins reflect a practical need for organization and retrieval in early manuscripts, emphasizing the textual beginning rather than contextual exposition.
Key Differences Between Foreword and Incipit
A foreword is an introductory section usually written by someone other than the author, providing context or endorsement, while an incipit is the opening words or passage of the main text itself. The foreword appears before the book's main narrative and often includes personal reflections or background, whereas the incipit marks the formal beginning of the literary work's story or content. Key differences include authorship, placement in the book, and purpose: the foreword serves as an external introduction, whereas the incipit initiates the primary text.
Purpose and Function of the Foreword
The foreword serves to establish credibility and context by providing insights from an expert or notable figure related to the book's content, often highlighting its significance and relevance. Its function is to prepare readers by framing the author's intentions or the book's impact before the main narrative begins. Unlike the incipit, which marks the opening lines of the text itself, the foreword operates as a supplementary introduction external to the story or main text.
Purpose and Function of the Incipit
The incipit serves as the opening words or passage of a text, establishing the tone, setting, and initial narrative direction to engage readers immediately. Its primary function is to draw the audience into the story or content by presenting a compelling beginning that previews themes or characters. Unlike the foreword, which provides background or context from an external perspective, the incipit operates within the text to immerse readers directly in the literary experience.
Examples of Foreword and Incipit in Literature
Forewords serve as introductory remarks by someone other than the author, often providing context or praise, as seen in J.R.R. Tolkien's foreword to The Hobbit, where he explains the book's origins and intentions. Incipits are the opening lines of a text that set the tone and engage the reader immediately, such as the famous incipit of Charles Dickens' A Tale of Two Cities: "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times." Understanding the distinct purposes of forewords and incipits enhances appreciation of their roles in guiding reader expectations and framing literary works.
Choosing Between Foreword and Incipit
Choosing between a foreword and an incipit depends on their distinct purposes: a foreword is an introductory note written by someone other than the author, providing context or endorsement, while an incipit marks the actual beginning of the text or story. For academic, historical, or literary works, a foreword offers credibility and background, enhancing reader engagement before the main content. In contrast, works prioritizing narrative flow or stylistic impact start directly with the incipit to immerse readers immediately.
Foreword Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com