A well-crafted preface sets the tone for your entire book, offering readers insight into your intentions and the journey behind your writing. It connects your message directly to your audience, making your work more relatable and impactful. Explore the rest of this article to discover how to create an engaging preface that captivates your readers from the very first page.
Table of Comparison
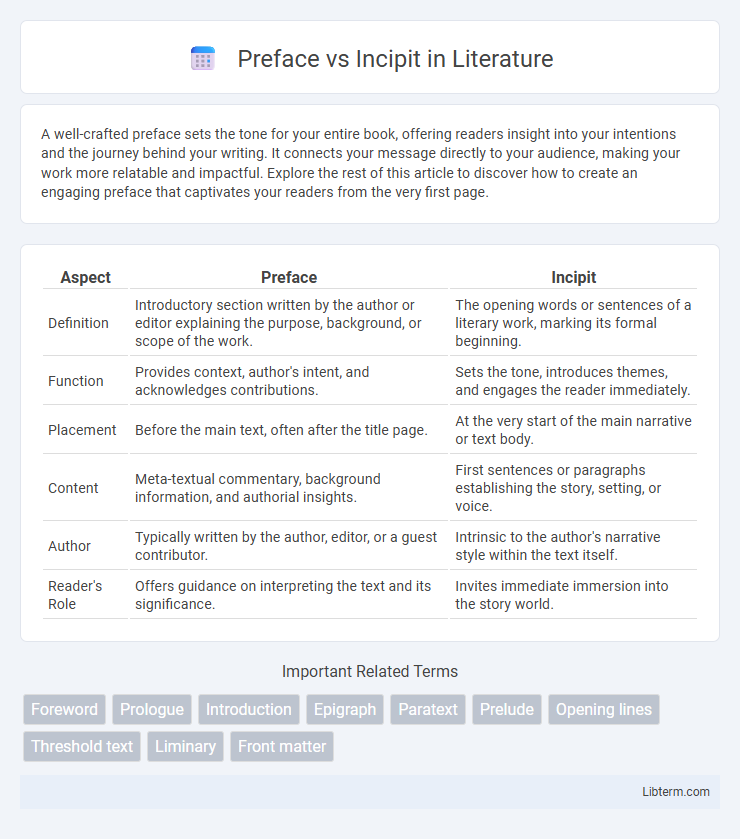
| Aspect | Preface | Incipit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Introductory section written by the author or editor explaining the purpose, background, or scope of the work. | The opening words or sentences of a literary work, marking its formal beginning. |
| Function | Provides context, author's intent, and acknowledges contributions. | Sets the tone, introduces themes, and engages the reader immediately. |
| Placement | Before the main text, often after the title page. | At the very start of the main narrative or text body. |
| Content | Meta-textual commentary, background information, and authorial insights. | First sentences or paragraphs establishing the story, setting, or voice. |
| Author | Typically written by the author, editor, or a guest contributor. | Intrinsic to the author's narrative style within the text itself. |
| Reader's Role | Offers guidance on interpreting the text and its significance. | Invites immediate immersion into the story world. |
Understanding the Terms: Preface and Incipit
The preface is an introductory section of a book where the author explains the purpose, scope, or background of the work, often providing context for the reader. The incipit refers to the opening words or initial lines of a text, marking the beginning of the actual narrative or content. Understanding these terms helps distinguish between the author's contextual introduction (preface) and the start of the text itself (incipit), which is critical for literary analysis and manuscript studies.
Historical Origins of Prefaces and Incipits
Prefaces originated in classical literature as authors' direct addresses to readers, providing context, intents, or acknowledgments, often positioned at the beginning but distinct from the narrative. Incipits trace back to medieval manuscripts where they served as the opening words or phrases of a text, used primarily for identification and cataloging before titles became common. Historically, prefaces evolved to guide interpretation and establish authority, while incipits maintained their functional role in textual organization and reference.
Defining the Preface: Purpose and Function
The preface serves as an introductory section in a book, providing readers with context about the author's intent, background, and the scope of the work. Unlike the incipit, which begins the narrative or main text, the preface often includes acknowledgments, explanations of the writing process, and the objectives behind the publication. It functions to prepare readers for the content, offering insight into the creation and significance of the material presented.
What is an Incipit? Key Characteristics
An incipit is the opening phrase or sentence of a manuscript, early printed book, or literary work, serving as its formal starting point. Key characteristics of an incipit include its role as an identifier for texts, especially in medieval manuscripts where titles were uncommon, and its function to establish tone, context, and authorial intent from the outset. Unlike a preface, which is an introductory section written by the author or editor discussing the work, the incipit is part of the primary text itself, often used in archival and bibliographical references.
Structural Placement: Preface vs Incipit
The preface is typically positioned at the very beginning of a book, preceding the main text and providing context or background information from the author or editor. In contrast, the incipit marks the actual start of the narrative or main content, often the first lines or sentences that initiate the story or discourse. Structural placement differentiates these elements by situating the preface as a preliminary commentary and the incipit as the narrative's initial entry point.
Literary Significance of Preface and Incipit
A preface provides authors with a platform to contextualize their work, offering insights into their motivations, background, and thematic intentions, which enhances readers' understanding and appreciation. The incipit, marking the narrative's opening lines, establishes the tone, setting, and direction, immediately engaging readers through stylistic and thematic cues. Together, the preface and incipit play vital roles in shaping literary experience by framing interpretation and immersion from both an expository and a narrative standpoint.
Examples of Famous Prefaces and Incipits
Famous prefaces often provide insight into the author's intentions, such as Charles Dickens' preface to "A Tale of Two Cities," which sets the thematic tone of resurrection and transformation. Renowned incipits like Herman Melville's opening line in "Moby-Dick," "Call me Ishmael," immediately establish a unique narrative voice and draw readers into the story. While prefaces function as introductory essays or explanations, incipits serve as the actual opening sentences of the text, exemplified by Jane Austen's timeless incipit in "Pride and Prejudice": "It is a truth universally acknowledged...
How Authors Use Prefaces and Incipits
Authors use prefaces to provide context, background information, or intentions behind the work, guiding readers' understanding before the main text begins. Incipits function as the opening words or lines of a text, setting tone, style, and immediate engagement with the narrative or argument. Both prefaces and incipits play crucial roles in framing a literary or academic work, with prefaces offering explicit authorial insight and incipits delivering an immersive entry into the content.
Reader Experience: Impact of Preface and Incipit
The preface provides context, background, and authorial intent, enriching the reader's understanding before the narrative begins. The incipit, as the opening lines of a text, immediately immerses the reader in style, tone, and setting, shaping first impressions and emotional engagement. Both elements influence reader experience by guiding expectations and framing the story's reception.
Choosing Between Preface and Incipit in Writing
Choosing between a preface and an incipit depends on the purpose and tone of the writing; a preface typically offers context, background, or the author's intentions, while an incipit serves as the opening lines that establish mood or setting. Writers aiming to provide readers with insight into the creation process or thematic framing should opt for a preface, whereas those focusing on immersive narrative openings benefit from an incipit. Understanding the distinction enhances reader engagement and aligns the text's introduction with its literary goals.
Preface Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com