A protagonist is the main character around whom the story revolves, often driving the plot through their actions and decisions. Understanding the protagonist's motivations and challenges can deepen your engagement with the narrative. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how protagonists shape compelling stories.
Table of Comparison
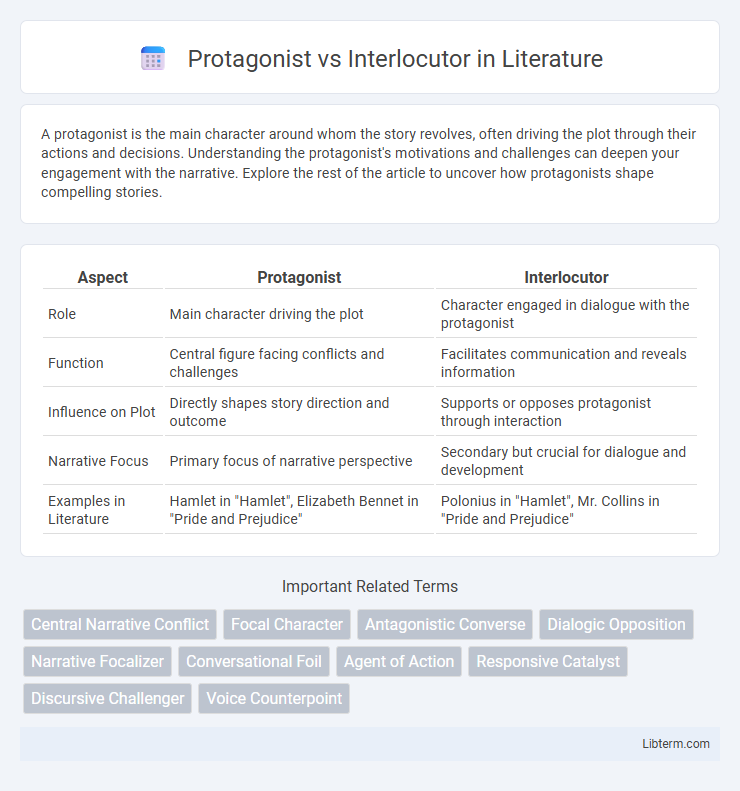
| Aspect | Protagonist | Interlocutor |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Main character driving the plot | Character engaged in dialogue with the protagonist |
| Function | Central figure facing conflicts and challenges | Facilitates communication and reveals information |
| Influence on Plot | Directly shapes story direction and outcome | Supports or opposes protagonist through interaction |
| Narrative Focus | Primary focus of narrative perspective | Secondary but crucial for dialogue and development |
| Examples in Literature | Hamlet in "Hamlet", Elizabeth Bennet in "Pride and Prejudice" | Polonius in "Hamlet", Mr. Collins in "Pride and Prejudice" |
Defining the Protagonist: The Story’s Central Figure
The protagonist serves as the story's central figure, driving the narrative by facing conflicts and making pivotal decisions that shape the plot's progression. Unlike the interlocutor, who facilitates dialogue and interaction within the story, the protagonist embodies the primary perspective through which audiences engage with the thematic and emotional core. Defining the protagonist involves identifying their goals, motivations, and development, which anchors the story's purpose and emotional resonance.
Understanding the Interlocutor: The Key Conversational Catalyst
Understanding the interlocutor is essential for effective communication, as it allows the protagonist to tailor responses that resonate with the listener's perspectives and emotions. Recognizing verbal and non-verbal cues enhances empathy, fostering a collaborative dialogue that drives meaningful exchanges. This dynamic interaction positions the interlocutor not merely as a respondent but as a critical catalyst shaping the flow and depth of the conversation.
Roles and Functions: Protagonist vs Interlocutor
The protagonist drives the narrative forward by initiating actions, making decisions, and facing conflicts that shape the story's progression and emotional core. The interlocutor, serving as the communication partner, facilitates dialogue that reveals the protagonist's thoughts, motivations, and character development, often influencing or challenging the protagonist's decisions. Both roles function complementarily, with the protagonist as the central actor and the interlocutor as the responsive counterpart, enriching the narrative through interaction and exchange of perspectives.
Narrative Impact: How Each Character Drives the Plot
The protagonist propels the plot through their desires, decisions, and growth, creating a dynamic narrative arc central to the story's progression. The interlocutor serves as a catalyst, challenging the protagonist's worldview and prompting critical dialogue that deepens thematic complexity. Together, their interactions generate conflict and resolution essential for advancing the storyline and engaging the audience.
Character Development: Growth Through Dialogue
The protagonist's character development is significantly shaped by interactions with the interlocutor, as dialogue reveals internal conflicts, motivations, and evolving perspectives. Each exchange serves as a catalyst for growth, pushing the protagonist to challenge beliefs and adapt responses. Well-crafted protagonist-interlocutor conversations deepen narrative tension and sharpen the emotional and psychological complexity within the story.
Conflicts and Tension: Protagonist-Interlocutor Dynamics
Conflicts and tension in protagonist-interlocutor dynamics arise from opposing goals, beliefs, or motivations that drive narrative engagement and character development. The interlocutor often challenges the protagonist's worldview, creating moments of confrontation that reveal deeper psychological or moral dilemmas. These interactions intensify the plot by escalating stakes and forcing the protagonist to adapt, resist, or evolve in response to the interlocutor's provocations.
The Interlocutor’s Influence on the Protagonist’s Journey
The interlocutor shapes the protagonist's journey by challenging beliefs and prompting critical self-reflection, driving character development and plot progression. Through pointed questions and dialogue, the interlocutor reveals hidden motivations and internal conflicts within the protagonist, intensifying the narrative tension. This dynamic interaction catalyzes transformation, making the interlocutor a pivotal force in the protagonist's evolution.
Dialogue as a Tool: Revealing Motives and Backstories
Dialogue serves as a crucial tool in distinguishing the protagonist from the interlocutor by unveiling their motives and backstories through nuanced exchanges. The protagonist's dialogue often reveals internal conflicts and driving goals, while the interlocutor's responses expose contrasting perspectives and hidden agendas. Strategic dialogue deepens character development, enhancing narrative tension and emotional engagement.
Case Studies: Memorable Protagonist-Interlocutor Pairings
Iconic case studies such as Sherlock Holmes and Dr. John Watson illustrate the dynamic interplay between protagonist and interlocutor, where Watson's role as a reflective foil enhances Holmes' deductive brilliance. In Harper Lee's *To Kill a Mockingbird*, Scout Finch's interactions with Atticus provide crucial ethical grounding, emphasizing moral growth through dialogue. Another striking pairing is Frodo Baggins and Samwise Gamgee in *The Lord of the Rings*, where Sam's unwavering support amplifies Frodo's internal struggles and heroic journey.
Crafting Effective Interactions: Tips for Writers
Crafting effective interactions between the protagonist and interlocutor requires clear character goals and distinct dialogue voices to enhance narrative tension. Writers should focus on purposeful exchanges that reveal both characters' motivations and advance the plot organically. Utilizing subtext and emotional undercurrents in conversations deepens engagement and realism.
Protagonist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com