Vernacular refers to the everyday language spoken by ordinary people in a particular region or country, distinct from formal or literary language. Understanding vernacular is essential for grasping cultural nuances and communication styles. Explore the rest of the article to discover how vernacular shapes identity and social interaction.
Table of Comparison
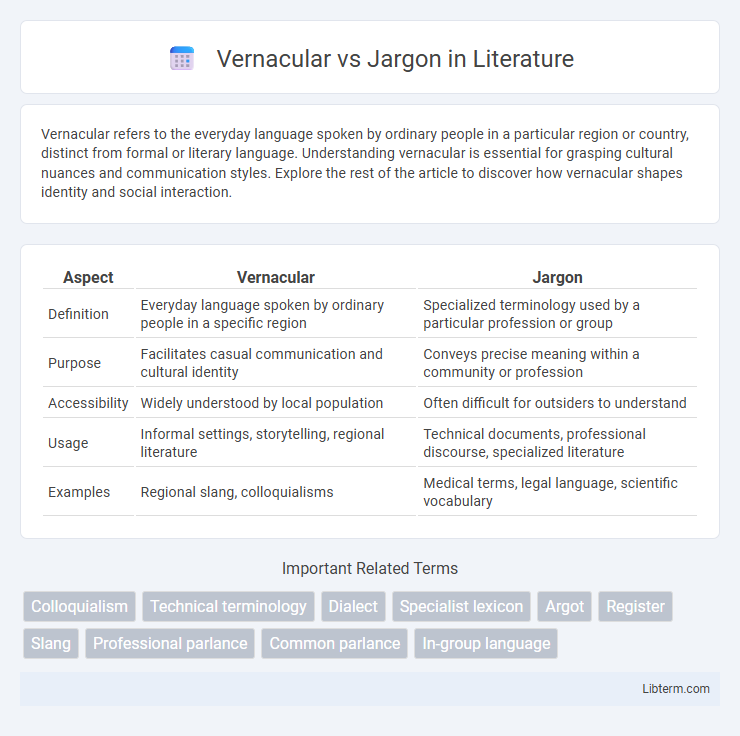
| Aspect | Vernacular | Jargon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Everyday language spoken by ordinary people in a specific region | Specialized terminology used by a particular profession or group |
| Purpose | Facilitates casual communication and cultural identity | Conveys precise meaning within a community or profession |
| Accessibility | Widely understood by local population | Often difficult for outsiders to understand |
| Usage | Informal settings, storytelling, regional literature | Technical documents, professional discourse, specialized literature |
| Examples | Regional slang, colloquialisms | Medical terms, legal language, scientific vocabulary |
Introduction to Vernacular and Jargon
Vernacular refers to the everyday language spoken by ordinary people within a particular region or community, characterized by its informal and natural use. Jargon consists of specialized terms and expressions used by professionals or members of a specific group, often difficult for outsiders to understand. Understanding the distinction between vernacular and jargon is crucial for effective communication across diverse audiences.
Defining Vernacular: Everyday Language
Vernacular refers to the everyday language spoken by ordinary people within a specific region or community, characterized by its natural, informal usage. It encompasses common expressions, slang, and idiomatic phrases that reflect cultural identity and social context. Unlike jargon, vernacular is widely understood by the general population without requiring specialized knowledge.
What is Jargon? Specialized Communication
Jargon refers to specialized terminology used within particular professional or interest groups to facilitate precise and efficient communication. This language often consists of technical words or phrases that may be unintelligible to outsiders, enhancing clarity among experts but creating barriers for general audiences. Understanding jargon is essential for professionals to engage effectively in their fields, while avoiding it is crucial in contexts requiring broader accessibility.
Historical Evolution of Vernacular and Jargon
Vernacular languages have evolved historically as the native speech forms of specific regions, rooted in cultural traditions and everyday communication among common people. Jargon, by contrast, developed within specialized professional or social groups to facilitate precise and efficient communication, often creating linguistic boundaries between insiders and outsiders. Over time, while vernacular preserved local identities and oral histories, jargon expanded rapidly with advancements in science, technology, and industry, reflecting the dynamic nature of expertise and group identity.
Key Differences Between Vernacular and Jargon
Vernacular refers to the everyday language spoken by ordinary people in a particular region or community, often characterized by informal and widely understood expressions. Jargon consists of specialized terms and phrases used by specific professional or interest groups, designed to convey precise meanings within those contexts but often confusing to outsiders. The key difference lies in vernacular's broad accessibility versus jargon's niche usage and technical specificity.
The Role of Vernacular in Society
Vernacular language serves as a vital tool for cultural identity and social cohesion, reflecting the everyday speech of a community. It facilitates effective communication within local contexts, preserving traditions and fostering inclusivity among speakers. Unlike jargon, which is specialized and exclusive, vernacular language promotes accessibility and shared understanding in society.
Impact of Jargon in Professional Fields
Jargon in professional fields facilitates precise communication among experts by encapsulating complex concepts into concise terms, enhancing efficiency and clarity. However, excessive use of jargon can create barriers to understanding for clients and non-specialists, potentially hindering collaboration and knowledge transfer. Balancing jargon with accessible language is crucial to maintain professionalism while ensuring inclusivity and effective communication across diverse audiences.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vernacular
Vernacular language enhances communication by making content accessible and relatable to a wider audience, promoting inclusivity and cultural identity. However, its informal nature may lead to misunderstandings in professional or technical contexts where precision is crucial. The limited reach beyond local or specific groups can hinder broader communication compared to jargon, which offers specialized clarity within expert circles.
Pros and Cons of Using Jargon
Using jargon enhances communication efficiency among experts by enabling precise and specialized terminology, which streamlines complex discussions. However, jargon often creates barriers to understanding for non-experts, leading to confusion and potential exclusion in broader audiences. Overreliance on jargon can diminish clarity and hinder effective communication outside specialized fields.
Bridging the Gap: When Vernacular Meets Jargon
Bridging the gap between vernacular and jargon enhances communication by translating specialized terminology into everyday language that diverse audiences can understand. This approach fosters inclusivity in fields such as medicine, law, and technology, where complex jargon often creates barriers. Implementing clear explanations and contextual examples helps demystify jargon while preserving its precision, facilitating better knowledge sharing and collaboration.
Vernacular Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com