Discourse shapes the way ideas are communicated and understood within various contexts, influencing social interactions and knowledge construction. It encompasses spoken, written, and visual forms, each contributing to meaning-making processes and power dynamics. Discover how understanding discourse can enhance your communication skills and critical thinking as you explore the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
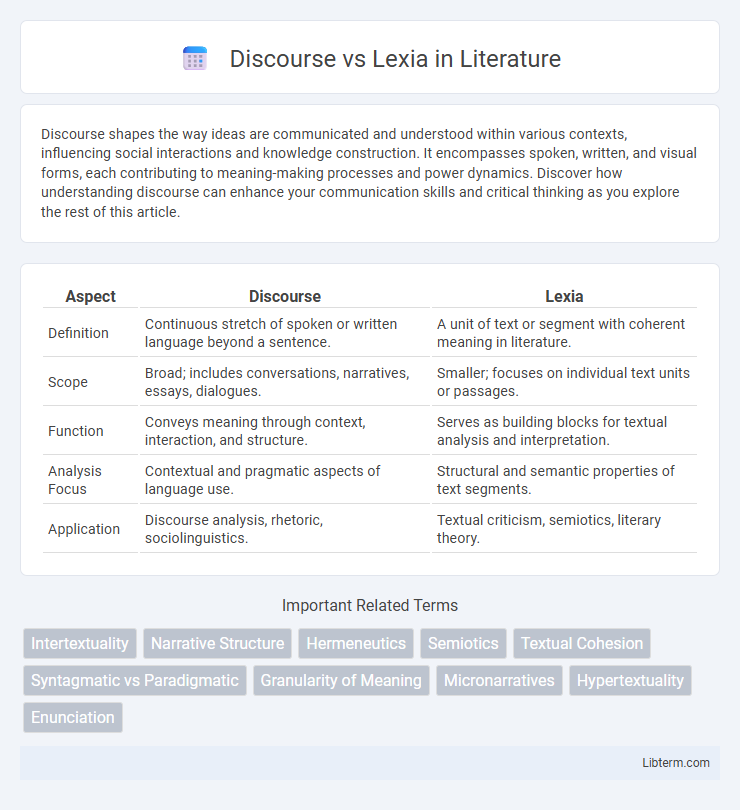
| Aspect | Discourse | Lexia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous stretch of spoken or written language beyond a sentence. | A unit of text or segment with coherent meaning in literature. |
| Scope | Broad; includes conversations, narratives, essays, dialogues. | Smaller; focuses on individual text units or passages. |
| Function | Conveys meaning through context, interaction, and structure. | Serves as building blocks for textual analysis and interpretation. |
| Analysis Focus | Contextual and pragmatic aspects of language use. | Structural and semantic properties of text segments. |
| Application | Discourse analysis, rhetoric, sociolinguistics. | Textual criticism, semiotics, literary theory. |
Introduction to Discourse and Lexia
Discourse is an open-source platform designed for community discussions, combining features of forums, mailing lists, and chat to foster interactive conversations. Lexia, a comprehensive literacy program, focuses on personalized reading instruction using adaptive assessments and targeted skill development to improve student literacy outcomes. Both tools serve distinct educational and communication needs, with Discourse emphasizing engagement and collaboration, and Lexia prioritizing individualized learning paths.
Defining Discourse: Scope and Usage
Discourse encompasses the structured communication and social interaction within spoken, written, or visual texts, focusing on how language shapes meaning in various contexts such as conversations, media, and academic writing. It examines not only linguistic elements like syntax and vocabulary but also the social and cultural frameworks influencing interpretation and usage. Lexia, contrastingly, refers to discrete units or segments of text analyzed in literary or linguistic studies, making discourse broader in scope as it considers entire communicative events and their functional purposes.
Understanding Lexia: Meaning and Function
Lexia refers to the fundamental units of meaning in language, encompassing words, phrases, or sentences that contribute to comprehension and communication. It functions as the building blocks within discourse, enabling the interpretation and construction of coherent messages. Unlike discourse, which represents extended communication beyond isolated units, lexia emphasizes the micro-level elements that carry semantic value and facilitate understanding.
Historical Development of Discourse and Lexia
Discourse, rooted in linguistic and social theory, evolved significantly through the 20th century, emphasizing language's role in structuring knowledge and power, as influenced by thinkers like Michel Foucault and Ferdinand de Saussure. Lexia, originating from Roland Barthes' concept in literary theory, refers to segments or units of text that disrupt linear reading, highlighting the fragmented nature of textual interpretation. Both concepts have shaped contemporary discourse analysis and textual criticism by illuminating the dynamic interplay between language structures and meaning construction.
Structural Differences: Discourse vs Lexia
Discourse structures consist of connected sentences or utterances forming coherent communication, emphasizing relationships and flow in spoken or written language. Lexia refers to minimal units of reading or text segments, often used in digital text analysis, focusing on discrete chunks rather than continuous narrative. Structural differences highlight discourse's emphasis on global coherence and context, while lexia centers on localized, segmented text units for granular analysis.
Contextual Applications in Linguistics
Discourse analysis examines language use beyond sentence boundaries, focusing on context, interaction, and coherence in spoken or written communication, while Lexia refers to textual units or segments used for detailed semantic and syntactic analysis. In linguistics, Discourse enables understanding of pragmatics, conversational implicature, and social dynamics, whereas Lexia supports micro-level examination of lexical cohesion and thematic progression within texts. Contextual applications emphasize Discourse for exploring narrative structures and speech acts, while Lexia aids corpus linguistics through granular text segmentation and annotation.
Discourse Analysis vs Lexical Analysis
Discourse analysis examines language use across sentences to understand context, meaning, and social interaction, focusing on structure, coherence, and pragmatics of text or conversation. Lexical analysis, by contrast, involves parsing text at the word level, identifying tokens, morphemes, and syntactic categories to facilitate natural language processing tasks. Discourse analysis is crucial for interpreting narrative flow and speaker intent, while lexical analysis underpins foundational processes like tokenization and part-of-speech tagging in computational linguistics.
Role of Lexia in Semiotics and Text Interpretation
Lexia in semiotics functions as a fundamental unit of textual interpretation, representing a segment of text that carries discrete meaning within a discourse. Unlike broader discourse analysis which considers the entire communication context, lexia focuses on micro-level signifiers and their associative meanings, enabling deeper semantic decoding. This role of lexia is crucial for understanding how individual text fragments contribute to the construction of larger narrative and interpretive frameworks.
Practical Examples: Discourse and Lexia in Action
Discourse excels in fostering collaborative learning environments by enabling dynamic discussion threads where users can share resources and clarify concepts in real-time, making it ideal for academic forums and professional communities. Lexia, on the other hand, provides adaptive, personalized reading interventions through its data-driven platform, which tailors exercises to individual student performance, demonstrated by improved literacy rates in K-12 classrooms. Practical applications show Discourse enhancing peer-to-peer engagement in technology communities, while Lexia drives measurable reading skill improvements in educational settings.
Conclusion: Integrating Discourse and Lexia in Language Studies
Integrating Discourse and Lexia in language studies enriches textual analysis by combining Discourse's focus on language use and social context with Lexia's detailed examination of individual text units. This synthesis enhances understanding of both macro-level communication patterns and micro-level textual elements, supporting more comprehensive language learning and research. Utilizing both frameworks fosters deeper insights into semantics, pragmatics, and textual cohesion within diverse linguistic environments.
Discourse Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com