A sememe represents the smallest unit of meaning within a language, crucial for understanding how words convey concepts and ideas. It plays a vital role in linguistic analysis, natural language processing, and semantic studies by breaking down complex meanings into manageable parts. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge of sememes and their impact on language comprehension.
Table of Comparison
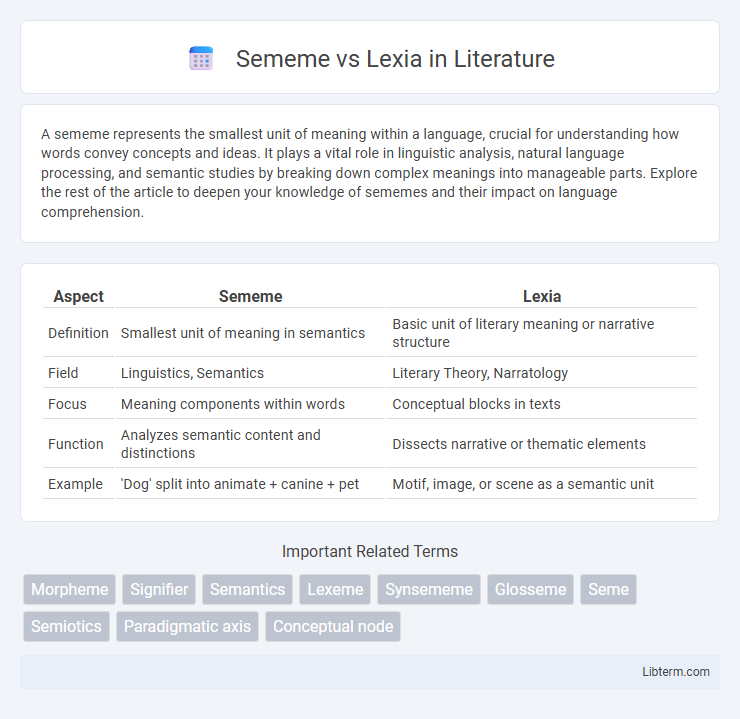
| Aspect | Sememe | Lexia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Smallest unit of meaning in semantics | Basic unit of literary meaning or narrative structure |
| Field | Linguistics, Semantics | Literary Theory, Narratology |
| Focus | Meaning components within words | Conceptual blocks in texts |
| Function | Analyzes semantic content and distinctions | Dissects narrative or thematic elements |
| Example | 'Dog' split into animate + canine + pet | Motif, image, or scene as a semantic unit |
Introduction to Sememe and Lexia
Sememes represent the smallest units of meaning in linguistic semantics, serving as foundational building blocks for understanding word senses and relationships. Lexia refers to discrete lexical units or entries in a text, encompassing words or phrases as organized components within a language system. Differentiating sememes from lexia highlights the contrast between fundamental semantic elements and complex lexical manifestations in language analysis.
Defining Sememe: The Smallest Unit of Meaning
Sememe represents the smallest unit of meaning in linguistics, capturing the core semantic content that distinguishes one concept from another. Unlike lexia, which denotes broader lexical units or textual segments, sememes function as atomic semantic elements underlying word meaning. Understanding sememes is critical for natural language processing and semantic analysis as they enable precise semantic disambiguation and knowledge representation.
What is Lexia? Understanding the Lexical Unit
Lexia refers to the smallest unit of meaning within a language, encompassing words or phrases that function as distinct lexical entities. It captures how vocabulary is organized and accessed in the mental lexicon, highlighting the relationship between form and meaning. Understanding lexia is essential for analyzing language structure, semantics, and lexical semantics in linguistics.
Key Differences Between Sememe and Lexia
Sememe represents the smallest unit of meaning in a language, capturing the fundamental semantic content of a word or morpheme, while lexia refers to any unit of written or spoken language, including words, phrases, or sentences analyzed in discourse or text linguistics. Sememe is primarily concerned with semantic features and meaning representation, whereas lexia focuses on textual units and their function within language structure or narrative analysis. The key difference lies in sememe's role in semantics and lexical meaning compared to lexia's role in analyzing language segments at different levels within communication or literary studies.
The Role of Sememe in Semantic Analysis
Sememes serve as the fundamental units of meaning in semantic analysis, enabling precise representation and interpretation of word senses beyond surface-level lexemes. By decomposing complex meanings into sememes, computational linguistics can enhance natural language understanding, improve machine translation, and enable more accurate semantic search results. In contrast to lexia, which refers to basic lexical units or words, sememes capture the inherent semantic components that reveal subtle nuances and relationships within language.
Lexia and Its Importance in Linguistic Structure
Lexia represents the fundamental units of meaning in linguistic theory, serving as the building blocks for constructing complex semantic structures. Unlike sememes, which denote minimal semantic units, lexia encompass broader contextual elements that influence interpretation within discourse. Their importance lies in facilitating nuanced language analysis, enabling more accurate parsing of syntax and semantics for advanced computational linguistics and cognitive studies.
Applications of Sememe in Computational Linguistics
Sememes play a crucial role in computational linguistics by providing a fine-grained semantic representation that enhances word sense disambiguation and machine translation accuracy. Unlike lexia, which focuses on the structural aspects of language units, sememes capture the minimal units of meaning, enabling more precise semantic parsing and knowledge representation in natural language processing systems. Applications leveraging sememes include semantic search optimization, improved sentiment analysis, and more effective ontology development for artificial intelligence.
Lexia in Language Processing and Text Analysis
Lexia in language processing refers to the smallest unit of meaning or lexical item that can stand alone semantically, playing a critical role in text analysis by enabling more precise semantic parsing and disambiguation. Unlike sememes, which represent atomic units of meaning within a semantic structure, lexia focuses on the individual lexical tokens as they contribute to the overall semantic context of a text. Its application in natural language processing enhances tasks such as tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, and semantic role labeling, improving the accuracy of syntactic and semantic interpretation.
Challenges in Distinguishing Sememe from Lexia
Distinguishing sememes from lexia presents challenges due to their overlapping roles in representing meaning units within linguistic analysis. Sememes function as the smallest semantic units conveying inherent meaning, while lexia refers to units of lexical analysis, often encompassing complex or multi-word expressions that complicate clear boundaries. This semantic overlap creates difficulties in precise annotation and computational modeling, impacting natural language processing tasks such as word sense disambiguation and semantic parsing.
Conclusion: Integrating Sememe and Lexia in Language Study
Integrating sememe and lexia enhances language study by combining the precise meaning units of sememes with the textual structures of lexia, offering a holistic approach to semantics and discourse analysis. This synergy facilitates deeper comprehension of linguistic meaning and context, improving both language teaching and computational linguistics applications. The combined framework supports more nuanced semantic interpretation and effective language processing models.
Sememe Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com