Didactic content is designed to teach or instruct, often focusing on conveying clear lessons or moral principles through storytelling or direct explanation. This approach enhances learning by providing structured knowledge and practical applications that help readers absorb and retain information effectively. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how didactic methods can improve your understanding and teaching techniques.
Table of Comparison
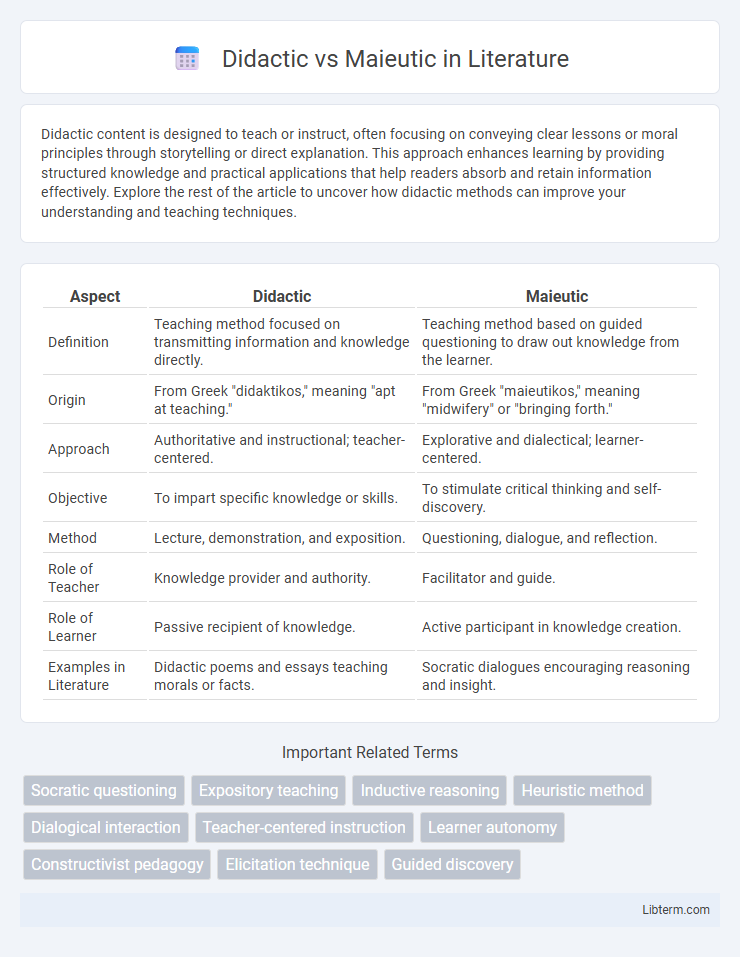
| Aspect | Didactic | Maieutic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teaching method focused on transmitting information and knowledge directly. | Teaching method based on guided questioning to draw out knowledge from the learner. |
| Origin | From Greek "didaktikos," meaning "apt at teaching." | From Greek "maieutikos," meaning "midwifery" or "bringing forth." |
| Approach | Authoritative and instructional; teacher-centered. | Explorative and dialectical; learner-centered. |
| Objective | To impart specific knowledge or skills. | To stimulate critical thinking and self-discovery. |
| Method | Lecture, demonstration, and exposition. | Questioning, dialogue, and reflection. |
| Role of Teacher | Knowledge provider and authority. | Facilitator and guide. |
| Role of Learner | Passive recipient of knowledge. | Active participant in knowledge creation. |
| Examples in Literature | Didactic poems and essays teaching morals or facts. | Socratic dialogues encouraging reasoning and insight. |
Introduction to Didactic and Maieutic Methods
Didactic methods emphasize direct instruction and systematic presentation of knowledge, where the teacher imparts information for students to absorb. Maieutic methods focus on eliciting knowledge through guided questioning, encouraging learners to develop understanding independently. Both approaches serve distinct educational roles: didactic for foundational knowledge transfer, and maieutic for critical thinking and self-discovery.
Historical Origins of Each Approach
Didactic teaching traces back to ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, where knowledge was transmitted through direct instruction and memorization, emphasizing the teacher's authority and structured lessons. Maieutic methodology originates from Socratic dialogues in classical Greece, pioneered by Socrates, who used probing questions to stimulate critical thinking and self-discovery in learners. These historical roots highlight didactic learning's foundation in authoritative teaching and maieutic learning's emphasis on guided inquiry and intellectual development.
Core Principles of Didactic Teaching
Didactic teaching centers on structured knowledge delivery through clear, authoritative instruction and systematic presentation of content, ensuring learners acquire specific facts and skills efficiently. It emphasizes the teacher's role as an expert who guides students via lectures, demonstrations, and direct explanations, fostering comprehension through repetition and reinforcement. Core principles include clarity, curriculum alignment, measurable objectives, and teacher-led assessment to support knowledge retention and mastery.
Fundamentals of the Maieutic Method
The maieutic method, rooted in Socratic dialogue, emphasizes eliciting knowledge through guided questioning, fostering critical thinking and self-discovery rather than direct instruction. Its fundamentals include fostering an interactive environment, encouraging reflective thought, and enabling learners to articulate and refine their understanding independently. Unlike the didactic approach, which relies on explicit teaching and information delivery, the maieutic method prioritizes learner-driven exploration and internalization of knowledge.
Key Differences Between Didactic and Maieutic
Didactic teaching focuses on direct instruction where knowledge is explicitly conveyed by the teacher, emphasizing structured content delivery and clear learning objectives. Maieutic methods prioritize eliciting students' latent knowledge through guided questioning, encouraging critical thinking and self-discovery without providing direct answers. The key difference lies in didactic's authoritative transmission of information versus maieutic's facilitative process for knowledge construction.
Advantages of Didactic Instruction
Didactic instruction efficiently delivers structured knowledge through clear, systematic teaching methods, ensuring consistent content comprehension across diverse learners. It maximizes time management in educational settings by providing direct explanations and focused practice, which enhances retention and accelerates learning outcomes. This approach is particularly advantageous in environments requiring standardized curricula, such as professional training and formal education systems.
Benefits of Maieutic Questioning
Maieutic questioning promotes deeper critical thinking by encouraging individuals to explore their own knowledge and beliefs, leading to enhanced self-awareness and conceptual understanding. This method stimulates active learning and intellectual autonomy, fostering problem-solving skills rather than passive absorption of information typical in didactic teaching. The benefits include improved retention, greater engagement, and the development of independent reasoning abilities through guided discovery.
Contexts Best Suited for Each Method
Didactic methods excel in structured learning environments such as classrooms or technical training where clear, direct transmission of knowledge is required. Maieutic approaches thrive in contexts that demand critical thinking and self-discovery, like philosophical discussions, counseling, or mentorship settings. Educators seeking to foster independent reasoning and deeper insight often prefer the maieutic style, whereas those aiming for efficient knowledge transfer favor the didactic method.
Combining Didactic and Maieutic Strategies
Combining didactic and maieutic strategies enhances learning by integrating direct instruction with guided discovery, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking. Didactic methods provide clear, structured knowledge delivery, while maieutic approaches encourage students to draw out ideas through questioning and reflection. This blended approach supports both knowledge acquisition and cognitive development, promoting active engagement and long-term retention.
Choosing the Right Method for Effective Learning
Selecting the most effective learning method depends on the educational goals and learner engagement. Didactic approaches emphasize structured knowledge delivery and clear instruction, ideal for foundational concepts and large groups. Maieutic methods foster critical thinking and self-discovery through guided questioning, making them suitable for developing deeper understanding and problem-solving skills.
Didactic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com