Ellipsis is a punctuation mark consisting of three dots (...) that indicates the omission of words, a pause, or unfinished thoughts in a sentence. It enhances writing by creating suspense, signaling hesitation, or condensing repetitive information for clearer communication. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mastering ellipsis can improve your writing style and readability.
Table of Comparison
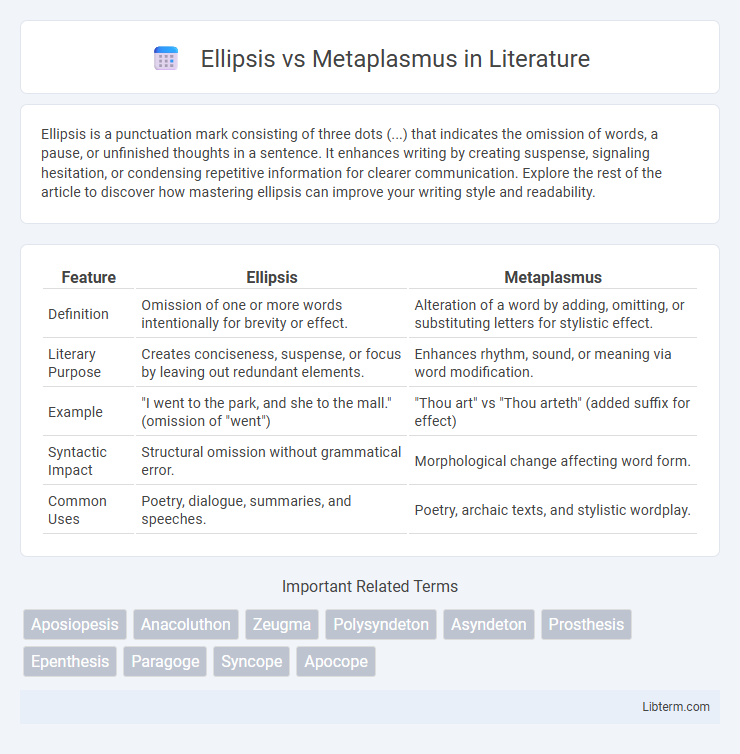
| Feature | Ellipsis | Metaplasmus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Omission of one or more words intentionally for brevity or effect. | Alteration of a word by adding, omitting, or substituting letters for stylistic effect. |
| Literary Purpose | Creates conciseness, suspense, or focus by leaving out redundant elements. | Enhances rhythm, sound, or meaning via word modification. |
| Example | "I went to the park, and she to the mall." (omission of "went") | "Thou art" vs "Thou arteth" (added suffix for effect) |
| Syntactic Impact | Structural omission without grammatical error. | Morphological change affecting word form. |
| Common Uses | Poetry, dialogue, summaries, and speeches. | Poetry, archaic texts, and stylistic wordplay. |
Understanding Ellipsis: Definition and Function
Ellipsis is a linguistic device where one or more words are omitted from a sentence because their meaning is understood from the context, enhancing brevity and coherence in communication. It functions by allowing speakers and writers to avoid redundancy, relying on shared knowledge between the audience and the communicator. In contrast, metaplasmus involves the intentional alteration of word forms, focusing on phonetic and morphological changes rather than omission.
What is Metaplasmus? An Overview
Metaplasmus is a rhetorical device that involves altering the structure of a word by adding, omitting, or rearranging letters to create a specific effect or emphasize a point in speech or writing. Unlike ellipsis, which omits words or phrases for brevity or impact, metaplasmus targets changes within a single word's form, including substitutions such as metathesis, aphaeresis, or apocope. This phonological modification enhances stylistic expression and can influence the tone, rhythm, or meaning in literary and linguistic contexts.
Historical Origins of Ellipsis and Metaplasmus
Ellipsis, originating from ancient Greek rhetoric, is a linguistic device that omits needless words to create concise and impactful expressions, frequently seen in classical texts and speech. Metaplasmus, with roots in Latin philology, involves the alteration of word forms by adding, omitting, or rearranging letters to achieve phonetic or stylistic effects, commonly used in poetry and prose evolution. Both figures of speech illustrate historical linguistic creativity, shaping language through deliberate structural economy and phonological modification.
Structural Differences: Ellipsis vs Metaplasmus
Ellipsis involves the omission of one or more words from a sentence, creating a gap that the reader must infer, while metaplasmus pertains to deliberate alterations in word forms through the addition, deletion, or substitution of letters. Structurally, ellipsis affects syntactic completeness by removing elements yet maintaining intelligibility, whereas metaplasmus modifies morphological structures without omitting entire syntactic components. The key difference lies in ellipsis operating at the phrase or clause level by omission, whereas metaplasmus functions at the word level through deliberate orthographic or phonological changes.
Uses of Ellipsis in Modern Writing
Ellipsis in modern writing enhances conciseness by deliberately omitting words that are implied by context, allowing for efficient communication and a more engaging narrative style. It is frequently used in dialogue to reflect natural speech patterns or to create dramatic pauses that emphasize key points without redundancy. Unlike metaplasmus, which involves altering word forms for stylistic effect, ellipsis strategically relies on omission to streamline information while maintaining clarity and reader comprehension.
Examples of Metaplasmus in Literature
Metaplasmus involves deliberate alterations of words through processes like addition, omission, or substitution of letters to create stylistic effects, as seen in Shakespeare's plays where "beseeming" becomes "beseeming" with added syllables for emphasis. Examples include the alteration of "welcome" to "welcometh" and the use of archaic spellings like "faery" instead of "fairy" to evoke a particular tone or era. Such metaplasmic modifications enrich literary texture by manipulating phonetics and morphology to enhance meaning and rhythm.
Grammatical Implications of Each Device
Ellipsis involves the omission of one or more words that are understood from context, maintaining grammatical coherence while enhancing brevity and focus. Metaplasmus, by contrast, alters the internal structure of words through additions, omissions, or substitutions, impacting morphological form rather than syntactic structure. The grammatical implication of ellipsis lies in its reliance on shared context for sentence completion, whereas metaplasmus directly modifies word forms, affecting phonological and morphological rules without altering sentence syntax.
Stylistic Effects: How Ellipsis and Metaplasmus Influence Tone
Ellipsis enhances tone by creating suspense or urgency through the deliberate omission of words, encouraging readers to infer meaning and engage actively with the text. Metaplasmus, involving the alteration of word forms, adds stylistic flair and emotional intensity, often evoking irony or emphasis in tone. Both devices manipulate linguistic structure to shape reader perception and enrich the expressive quality of language.
Common Mistakes When Using Ellipsis or Metaplasmus
Ellipsis often causes confusion when users omit essential words, leading to ambiguous or incomplete sentences, while metaplasmus mistakes typically involve incorrect alterations to word forms that distort meaning or produce nonstandard variants. Common errors with ellipsis include dropping necessary elements that hinder clarity, such as omitting subjects or verbs in complex sentences, whereas metaplasmus misuse results from improper vowel or consonant substitutions, deletions, or insertions that obscure the intended word. Proper understanding of grammatical context and adherence to standard forms help avoid semantic distortion and improve communication accuracy.
Choosing the Right Device: Ellipsis or Metaplasmus?
Ellipsis and metaplasmus serve distinct rhetorical functions; ellipsis involves the intentional omission of words to create concise, impactful statements, while metaplasmus focuses on altering word forms to achieve stylistic effects such as emphasis or rhythm. Choosing ellipsis is ideal for enhancing clarity and brevity in communication, especially when the omitted elements are easily inferred by the audience. Opt for metaplasmus when the goal is to embellish language or evoke emotion through phonetic or morphological modifications, making it suitable for poetry or expressive prose.
Ellipsis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com