Existentialism explores the fundamental nature of human existence, emphasizing individual freedom, choice, and responsibility in a seemingly indifferent or absurd world. This philosophy challenges you to find personal meaning despite inherent uncertainties and societal pressures. Dive deeper into the article to understand how existentialism can transform your perspective on life and identity.
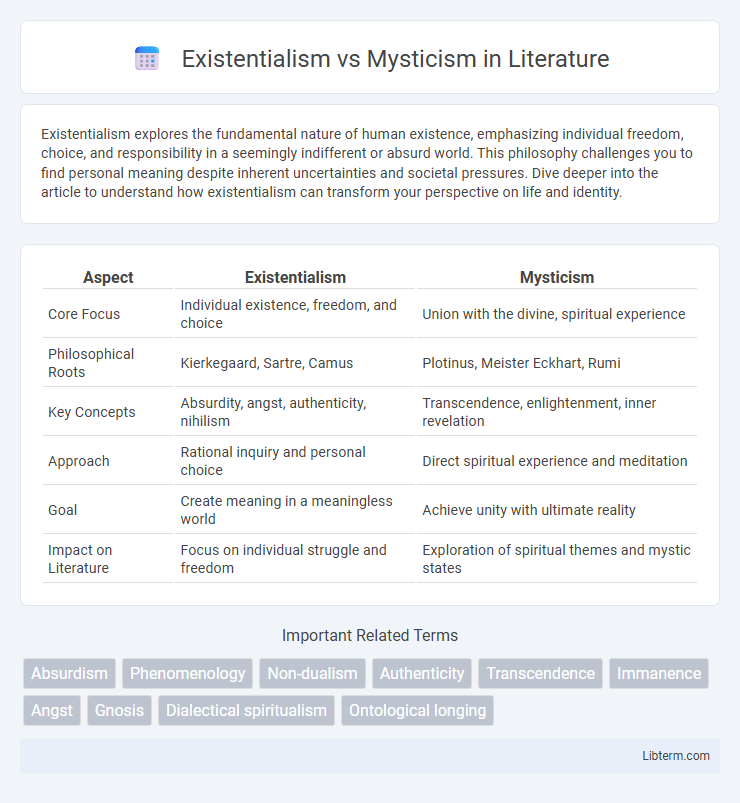
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Existentialism | Mysticism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Individual existence, freedom, and choice | Union with the divine, spiritual experience |
| Philosophical Roots | Kierkegaard, Sartre, Camus | Plotinus, Meister Eckhart, Rumi |
| Key Concepts | Absurdity, angst, authenticity, nihilism | Transcendence, enlightenment, inner revelation |
| Approach | Rational inquiry and personal choice | Direct spiritual experience and meditation |
| Goal | Create meaning in a meaningless world | Achieve unity with ultimate reality |
| Impact on Literature | Focus on individual struggle and freedom | Exploration of spiritual themes and mystic states |
Defining Existentialism and Mysticism
Existentialism is a philosophical movement emphasizing individual freedom, choice, and the search for meaning in an indifferent or absurd universe, often associated with thinkers like Jean-Paul Sartre and Soren Kierkegaard. Mysticism involves direct, personal experience of the divine or ultimate reality, transcending rational understanding through spiritual practices found in traditions such as Sufism, Christian mysticism, and Hindu Vedanta. Both existentialism and mysticism address the human quest for meaning but diverge in method--existentialism relies on conscious human agency, while mysticism emphasizes union with a transcendent reality.
Historical Origins and Influential Thinkers
Existentialism emerged in the 19th and 20th centuries with key figures such as Soren Kierkegaard, Friedrich Nietzsche, and Jean-Paul Sartre, who emphasized individual freedom, choice, and subjective experience. Mysticism traces its roots to ancient religious traditions, including Neoplatonism, early Christian mystics like Meister Eckhart, and Sufism, focusing on direct, transcendent experiences of the divine. Both philosophies address human existence but diverge significantly in methodology and ultimate aims, with existentialism grounded in human agency and mysticism in spiritual union.
Core Philosophical Differences
Existentialism centers on individual existence, freedom, and personal responsibility, emphasizing subjective meaning in an inherently meaningless world. Mysticism focuses on transcendent union with the divine or ultimate reality, seeking direct spiritual experience beyond rational understanding. Core philosophical differences lie in existentialism's stress on human freedom and angst versus mysticism's pursuit of spiritual transcendence and unity.
Perspectives on the Meaning of Life
Existentialism emphasizes individual freedom and choice as the foundation for creating personal meaning in an inherently absurd universe. Mysticism centers on the pursuit of spiritual union with a higher reality, suggesting life's meaning emerges from transcending the self and experiencing divine interconnectedness. Both perspectives explore human existence but diverge on whether meaning arises internally through conscious decision or externally via mystical experience.
The Role of Subjective Experience
Existentialism emphasizes the centrality of subjective experience as a fundamental source of meaning, asserting that individuals create their own essence through personal choice and authentic engagement with existence. Mysticism prioritizes direct, ineffable experiences of unity with the divine or ultimate reality, often transcending rational analysis and individual ego. Both frameworks value personal experiential insight, yet existentialism grounds meaning in human freedom and responsibility, while mysticism seeks transcendence beyond the self.
Attitudes Toward Religion and Spirituality
Existentialism emphasizes individual freedom, choice, and personal responsibility, often maintaining a skeptical or atheistic stance toward traditional religion while exploring meaning through human experience and authenticity. Mysticism centers on direct, transcendent experiences of the divine or ultimate reality, prioritizing spiritual union and inner awakening beyond doctrinal boundaries. The contrasting attitudes highlight existentialism's focus on subjective meaning in a seemingly indifferent universe versus mysticism's pursuit of spiritual connection and transcendence.
Freedom, Authenticity, and Transcendence
Existentialism emphasizes individual freedom and authentic self-creation through conscious choices, asserting that meaning arises from human existence itself without predetermined essence. Mysticism centers on transcendence beyond the self, seeking unity with a higher reality or divine presence that surpasses ordinary consciousness and temporal limitations. While existentialism grounds authenticity in personal responsibility, mysticism locates freedom in relinquishing ego boundaries to achieve spiritual awakening.
Approaches to Suffering and Fulfillment
Existentialism views suffering as an inherent part of human existence, emphasizing personal responsibility and authentic choice as paths to fulfillment. Mysticism interprets suffering as a means to transcend ego and connect with a higher spiritual reality, seeking fulfillment through unity with the divine. Both approaches address human pain but differ fundamentally in focusing on individual agency versus spiritual dissolution.
Influence in Modern Culture and Thought
Existentialism has profoundly shaped modern culture by emphasizing individual freedom, authenticity, and the search for meaning amid an indifferent universe, influencing literature, psychology, and political philosophy. Mysticism contributes to modern thought through its exploration of transcendent experiences and spiritual interconnectedness, impacting art, new age spirituality, and holistic health movements. Both philosophies challenge materialistic worldviews, encouraging deeper introspection and a reevaluation of human existence and consciousness in contemporary society.
Bridging Existentialism and Mysticism
Bridging existentialism and mysticism reveals a shared emphasis on authentic subjective experience and the search for meaning beyond rational explanation. Both philosophies confront the limits of human understanding, with existentialism exploring individual freedom and angst while mysticism seeks unity with the transcendent or divine essence. Integrative approaches emphasize personal transformation through embracing existential absurdity and mystical insight as complementary paths to deeper self-realization.
Existentialism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com