Coordination is the process of organizing people or groups to achieve a common goal efficiently and harmoniously. Effective coordination enhances productivity, reduces conflicts, and streamlines communication within teams or organizations. Explore the rest of this article to discover strategies that can improve your coordination skills and drive success.
Table of Comparison
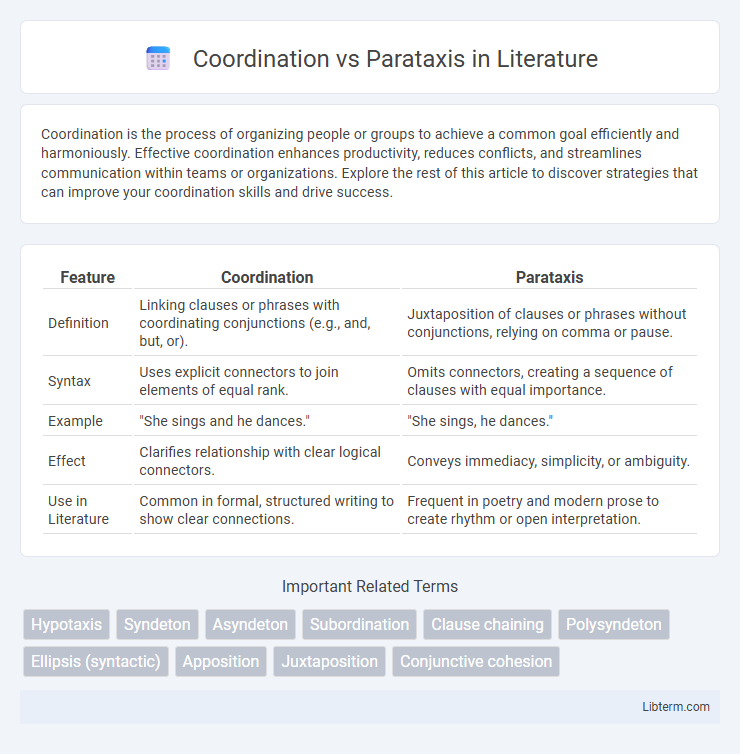
| Feature | Coordination | Parataxis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Linking clauses or phrases with coordinating conjunctions (e.g., and, but, or). | Juxtaposition of clauses or phrases without conjunctions, relying on comma or pause. |
| Syntax | Uses explicit connectors to join elements of equal rank. | Omits connectors, creating a sequence of clauses with equal importance. |
| Example | "She sings and he dances." | "She sings, he dances." |
| Effect | Clarifies relationship with clear logical connectors. | Conveys immediacy, simplicity, or ambiguity. |
| Use in Literature | Common in formal, structured writing to show clear connections. | Frequent in poetry and modern prose to create rhythm or open interpretation. |
Understanding Coordination and Parataxis
Coordination involves linking clauses or phrases with conjunctions like "and," "but," or "or," creating relationships that show equivalence or contrast between ideas. Parataxis places clauses or phrases side by side without explicit conjunctions, relying on the reader to infer connections, often producing a concise and impactful style. Understanding coordination and parataxis is essential for analyzing sentence structure and meaning in language, as they influence clarity, emphasis, and the flow of information.
The Basics of Syntactic Structures
Coordination links two or more independent clauses or phrases of equal syntactic importance using coordinating conjunctions like "and," "but," or "or," forming compound structures. Parataxis arranges clauses or phrases side by side without explicit conjunctions, relying on punctuation or context to establish relationships, often seen in poetic or conversational syntax. Understanding these syntactic structures is crucial for analyzing sentence complexity and the hierarchical organization within language.
Defining Coordination in Grammar
Coordination in grammar involves linking two or more independent clauses, phrases, or words with coordinating conjunctions such as "and," "but," or "or," creating a compound structure that maintains equal syntactic importance. This grammatical process allows the combination of elements that could stand alone as separate sentences, promoting clarity and balance in writing. The coordinated elements share a parallel relationship, ensuring that each part contributes equally to the overall meaning of the sentence.
What is Parataxis?
Parataxis is a syntactic construction that places clauses or phrases side by side without subordinating conjunctions, creating equal grammatical status for each element. It contrasts with coordination, which often uses coordinating conjunctions like "and," "but," or "or" to link similar elements explicitly. Paratactic structures enhance simplicity and clarity by presenting ideas in a straightforward, direct sequence, frequently found in poetry, casual speech, and storytelling.
Key Differences: Coordination vs Parataxis
Coordination links clauses or phrases of equal syntactic importance using coordinating conjunctions like "and," "but," or "or," creating clear, balanced relationships within sentences. Parataxis places clauses or phrases side by side without explicit conjunctions, relying on punctuation or simple juxtaposition, which can convey immediacy or a more fragmented narrative style. The key difference lies in the presence of conjunctions in coordination, whereas parataxis emphasizes independent clauses connected through proximity or punctuation.
Examples of Coordination in Sentences
Coordination connects two or more independent clauses or elements of equal syntactic importance, often using conjunctions like "and," "but," or "or." For example, "She enjoys reading and he likes writing," demonstrates coordination by linking two independent clauses. Another example is "The cat slept, and the dog barked," where both clauses are joined to convey simultaneous actions.
Parataxis in Literary and Everyday Language
Parataxis involves placing clauses or phrases side by side without clear conjunctions, creating a fast-paced, straightforward flow common in both literary and everyday language. Literary uses of parataxis often enhance rhythm, create ambiguity, or reflect stream-of-consciousness, as seen in works by Hemingway or Joyce. Everyday speech favors parataxis for simplicity and immediacy, frequently employing short, independent clauses that convey direct, unelaborated information.
Effects on Meaning and Style
Coordination creates a balanced structure by linking clauses or phrases with conjunctions like "and," "but," or "or," which clarifies relationships and maintains equal emphasis between ideas. Parataxis places clauses or phrases side by side without conjunctions, producing a terse, rapid tone that can emphasize simplicity or immediacy but may leave relationships between elements ambiguous. The choice between coordination and parataxis significantly influences the text's rhythm, clarity, and the reader's interpretation of how ideas interact.
Coordination and Parataxis Across Languages
Coordination and parataxis are syntactic structures that link clauses or phrases, with coordination typically using conjunctions like "and" or "but" to create equal relationships, while parataxis places elements side by side without explicit connectors. Cross-linguistic analysis reveals diverse strategies for coordination, where languages such as English rely heavily on coordinating conjunctions, whereas languages like Mandarin often use paratactic sequences to imply coordination or cause-and-effect relations. Understanding these mechanisms informs linguistic typology, highlighting variations in clause combination and implications for discourse coherence and sentence complexity across language families.
When to Use Coordination or Parataxis
Use coordination when linking independent clauses of equal importance to clarify relationships using conjunctions like "and," "but," or "or." Parataxis suits placing clauses or phrases side by side without conjunctions for a concise, impactful style, especially in narrative or poetic contexts. Choose coordination for explicit connections and parataxis for simplicity and emphasis.
Coordination Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com