Gothic architecture features pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses, creating awe-inspiring cathedrals with stunning stained glass windows. This style emerged in the High Middle Ages and revolutionized building techniques, emphasizing verticality and light. Discover how Gothic design transformed medieval Europe and continues to influence modern architecture in the full article.
Table of Comparison
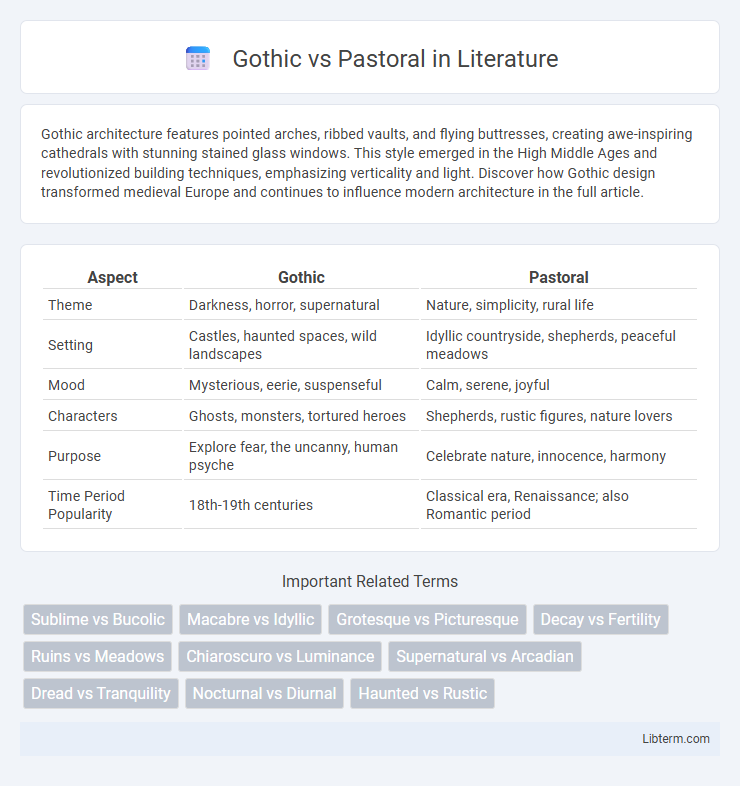
| Aspect | Gothic | Pastoral |
|---|---|---|
| Theme | Darkness, horror, supernatural | Nature, simplicity, rural life |
| Setting | Castles, haunted spaces, wild landscapes | Idyllic countryside, shepherds, peaceful meadows |
| Mood | Mysterious, eerie, suspenseful | Calm, serene, joyful |
| Characters | Ghosts, monsters, tortured heroes | Shepherds, rustic figures, nature lovers |
| Purpose | Explore fear, the uncanny, human psyche | Celebrate nature, innocence, harmony |
| Time Period Popularity | 18th-19th centuries | Classical era, Renaissance; also Romantic period |
Introduction to Gothic and Pastoral Styles
Gothic style is characterized by its dark, mysterious, and supernatural elements, often featuring medieval settings, haunted castles, and themes of horror and decay. Pastoral style emphasizes idyllic countryside landscapes, simplicity, tranquility, and harmony with nature, portraying rural life as peaceful and uncorrupted. Both styles reflect contrasting worldviews: Gothic explores fear and chaos, while Pastoral celebrates serenity and natural beauty.
Defining Gothic: Darkness, Mystery, and Romance
Gothic literature is characterized by its exploration of darkness, mystery, and an intense romanticism that often intertwines with elements of horror and the supernatural. Central to the Gothic genre are settings such as haunted castles, desolate landscapes, and shadowy interiors that evoke a sense of dread and the unknown. This contrasts with pastoral themes, as Gothic narratives delve into human psychology and the macabre rather than idealizing rural life and tranquility.
Understanding Pastoral: Nature, Simplicity, and Harmony
Pastoral literature emphasizes the idealization of rural life, highlighting nature's tranquility, simplicity, and harmonious existence with the environment. It often portrays shepherds and rustic settings as symbols of innocence and peace, contrasting urban complexity and societal corruption. This genre celebrates the balance between humans and nature, promoting a serene escape from industrialization and modern chaos.
Historical Origins and Influences
Gothic literature originated in the late 18th century, influenced by medieval architecture, Romanticism, and an interest in the supernatural, aiming to evoke suspense and terror through settings like castles and dark landscapes. Pastoral literature dates back to Ancient Greece and Rome, drawing inspiration from rural life and nature's simplicity as an idealized escape from urban complexities, often highlighting themes of innocence and harmony. Both genres reflect contrasting worldviews: Gothic emphasizes darkness and human fears, while Pastoral celebrates nature and tranquility through poetic and idyllic imagery.
Key Themes in Gothic Literature
Gothic literature centers on themes of horror, decay, and the supernatural, often exploring the terror of the unknown and the conflict between reason and emotion. It features haunted settings, psychological torment, and the intrusion of dark forces, emphasizing mortality and isolation. This contrasts with pastoral literature, which idealizes nature, simplicity, and harmony, focusing on peaceful rural life and human connection to the natural world.
Key Themes in Pastoral Literature
Pastoral literature emphasizes themes of nature's idealized beauty, simplicity of rural life, and harmonious coexistence between humans and the environment. It often explores innocence, nostalgia, and the contrast between rustic purity and urban corruption. Central motifs include shepherds, natural landscapes, and a longing for a utopian existence away from societal complexities.
Visual Aesthetics: Gothic vs Pastoral Art
Gothic art features dramatic contrasts, intricate details, and towering verticality that evoke a sense of mystery and spiritual transcendence, often using dark color palettes and elaborate ornamentation. Pastoral art emphasizes serene landscapes, soft color tones, and naturalistic details that celebrate rural life and harmony with nature, showcasing gentle curves and expansive vistas. The visual aesthetics of Gothic art convey tension and grandeur, while Pastoral art highlights tranquility and simplicity through its depiction of bucolic scenes.
Emotional Tones and Atmosphere
The Gothic genre evokes intense emotions of fear, dread, and suspense through dark, eerie settings filled with haunted castles, supernatural elements, and oppressive atmospheres. In contrast, Pastoral literature generates tranquility, harmony, and nostalgia by idealizing rural life with serene landscapes, peaceful nature, and simple, wholesome characters. The emotional tones in Gothic works are unsettling and mysterious, while Pastoral works evoke calmness and a soothing connection to the natural world.
Notable Works and Authors in Each Genre
Gothic literature flourished with notable works such as Mary Shelley's *Frankenstein* and Edgar Allan Poe's *The Tell-Tale Heart*, emphasizing dark, supernatural themes and psychological horror. Pastoral literature is exemplified by Christopher Marlowe's *The Passionate Shepherd to His Love* and William Wordsworth's *The Prelude*, celebrating nature, simplicity, and rural life. These distinct genres showcase contrasting thematic focuses through their influential authors and seminal texts.
Cultural Impact and Modern Revivals
Gothic literature profoundly influenced cultural narratives by exploring themes of horror, darkness, and the supernatural, shaping modern horror genres and visual arts. Pastoral literature, celebrating nature and rural life, inspired cultural movements advocating environmental preservation and simplicity, resonating in contemporary eco-literature and lifestyle trends. Modern revivals of Gothic motifs appear in popular media, fashion, and architecture, while Pastoral themes resurface in sustainable living campaigns and artistic celebrations of the countryside.
Gothic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com