Prolixity refers to the use of excessive words or overly long expressions that dilute clarity and hinder effective communication. Streamlining your writing by eliminating redundant phrases enhances readability and keeps your audience engaged. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for overcoming prolixity and sharpening your language.
Table of Comparison
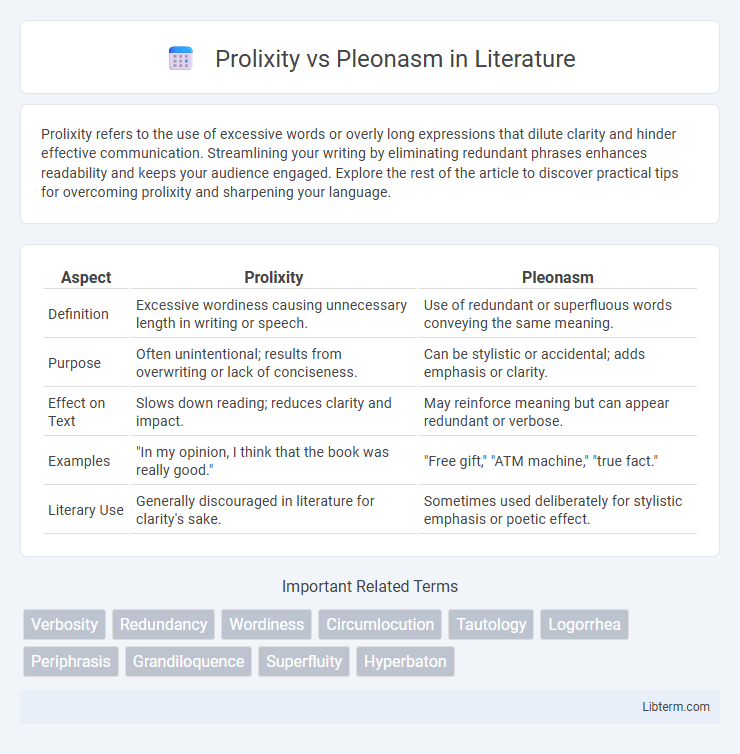
| Aspect | Prolixity | Pleonasm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive wordiness causing unnecessary length in writing or speech. | Use of redundant or superfluous words conveying the same meaning. |
| Purpose | Often unintentional; results from overwriting or lack of conciseness. | Can be stylistic or accidental; adds emphasis or clarity. |
| Effect on Text | Slows down reading; reduces clarity and impact. | May reinforce meaning but can appear redundant or verbose. |
| Examples | "In my opinion, I think that the book was really good." | "Free gift," "ATM machine," "true fact." |
| Literary Use | Generally discouraged in literature for clarity's sake. | Sometimes used deliberately for stylistic emphasis or poetic effect. |
Understanding Prolixity and Pleonasm
Prolixity refers to the use of excessive words that unnecessarily prolong communication, often leading to verbosity and a lack of clarity. Pleonasm is the use of redundant words or phrases that do not add meaningful information, such as "free gift" or "advance warning," which can clutter language without enhancing understanding. Understanding prolixity helps improve concise and effective expression, while recognizing pleonasm aids in eliminating superfluous language for clearer communication.
Origins and Etymology of Both Terms
Prolixity, derived from the Latin "prolixitas," meaning "lengthiness," emphasizes extended or lengthy expression, often considered tedious in communication. Pleonasm originates from the Greek "pleonasmos," signifying "excess" or "superfluity," and refers to the use of redundant or unnecessary words to convey meaning. Both terms share a focus on excess in language, but prolixity deals with excessive length, while pleonasm centers on redundancy.
Prolixity: Definition and Key Characteristics
Prolixity refers to the use of excessive words to express an idea, often leading to lengthy and tedious speech or writing. Key characteristics include verbosity, lack of conciseness, and a tendency to include unnecessary details that dilute the main message. Unlike pleonasm, which involves redundancy at the word level, prolixity concerns overall length and repetitiveness in communication.
Pleonasm: Definition and Key Characteristics
Pleonasm is the use of more words than necessary to convey meaning, often resulting in redundancy or tautology. It typically involves the inclusion of superfluous terms that do not add new information, such as "free gift" or "true fact," which can dilute clarity and conciseness in communication. Key characteristics of pleonasm include semantic redundancy, unnecessary repetition, and lack of economy in language usage, distinguishing it from prolixity, which refers to excessive verbosity without necessarily redundant content.
Linguistic Functions: When Are They Used?
Prolixity manifests in language as extended and often unnecessary verbosity, primarily serving functions such as detailed explanation or emphasis, especially in academic or formal discourse where thoroughness is valued. Pleonasm involves the use of redundant words or phrases to reinforce meaning, commonly appearing in everyday speech and literary contexts to enhance clarity or stylistic effect. Both linguistic phenomena fulfill distinct communicative roles: prolixity aids in exhaustive description, while pleonasm contributes to emphasis and rhetorical reinforcement.
Common Examples in Literature and Speech
Prolixity often appears in literature as lengthy descriptions or excessive wordiness, exemplified by Charles Dickens' elaborate narratives, while pleonasm involves redundancy, such as the phrase "true fact" found in everyday speech. Common examples in speeches include prolix phrases like verbose government reports and pleonastic expressions such as "free gift" or "advance warning." Understanding these distinctions helps writers and speakers avoid unnecessary verbosity and redundancy, enhancing clarity and impact.
Prolixity vs Pleonasm: Critical Differences
Prolixity refers to the overuse of words that leads to lengthy, often tiresome, explanations, whereas pleonasm involves redundancy through the use of unnecessary or repetitive words that do not add meaning. The critical difference lies in prolixity's focus on excessive length and verbosity, while pleonasm deals with superfluous elements that duplicate the same idea within a phrase. Understanding these distinctions enhances clarity and efficiency in both written and spoken communication.
Effects on Communication and Clarity
Prolixity, characterized by unnecessarily lengthy expressions, often obscures the main message, reducing communication clarity by overwhelming readers with excessive detail. Pleonasm involves redundant words that add no new information, which can distract or confuse the audience, weakening the effectiveness of the communication. Both prolixity and pleonasm hinder comprehension and dilute the impact of the intended message, making concise and precise language essential for clear and effective communication.
How to Avoid Prolixity and Pleonasm in Writing
Avoid prolixity and pleonasm in writing by choosing precise words and eliminating redundant phrases, ensuring clarity and conciseness. Use active voice and strong verbs to convey meaning efficiently, and review sentences to remove unnecessary repetition of ideas or words. Employ editing tools and read aloud to identify verbose or repetitive passages that dilute the message.
Mastering Concise and Effective Expression
Prolixity refers to the use of excessive words that unnecessarily extend communication, while pleonasm involves redundant expressions that repeat the same idea. Mastering concise and effective expression requires eliminating prolixity by focusing on clarity and brevity, and avoiding pleonasm to ensure precise and impactful language. Effective writing balances complete ideas with minimal verbosity, enhancing readability and comprehension.
Prolixity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com