Dialogism explores the interaction between multiple voices or perspectives within a text, highlighting how meaning is shaped through conversation and contradiction. This concept reveals the dynamic relationship between author, reader, and culture, enriching interpretation beyond a single viewpoint. Dive deeper to understand how dialogism transforms your reading experience and textual analysis.
Table of Comparison
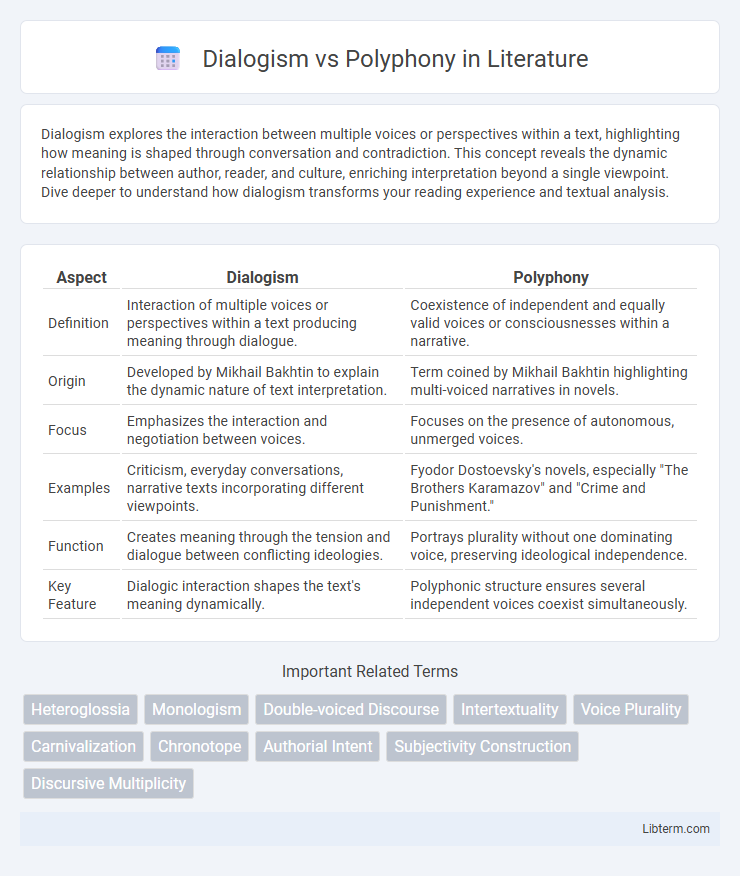
| Aspect | Dialogism | Polyphony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interaction of multiple voices or perspectives within a text producing meaning through dialogue. | Coexistence of independent and equally valid voices or consciousnesses within a narrative. |
| Origin | Developed by Mikhail Bakhtin to explain the dynamic nature of text interpretation. | Term coined by Mikhail Bakhtin highlighting multi-voiced narratives in novels. |
| Focus | Emphasizes the interaction and negotiation between voices. | Focuses on the presence of autonomous, unmerged voices. |
| Examples | Criticism, everyday conversations, narrative texts incorporating different viewpoints. | Fyodor Dostoevsky's novels, especially "The Brothers Karamazov" and "Crime and Punishment." |
| Function | Creates meaning through the tension and dialogue between conflicting ideologies. | Portrays plurality without one dominating voice, preserving ideological independence. |
| Key Feature | Dialogic interaction shapes the text's meaning dynamically. | Polyphonic structure ensures several independent voices coexist simultaneously. |
Understanding Dialogism: A Theoretical Overview
Dialogism, a concept rooted in the work of Mikhail Bakhtin, emphasizes the interaction and coexistence of multiple voices or perspectives within a single text or discourse. It highlights the dynamic relationship between different utterances, where meaning emerges through ongoing dialogue rather than a fixed or authoritative voice. Understanding dialogism involves recognizing that texts are inherently responsive and shaped by diverse social, cultural, and ideological influences that continuously interact.
Polyphony Defined: Beyond Multiple Voices
Polyphony extends beyond the mere presence of multiple voices to emphasize their independent, coexisting perspectives within a single text or discourse. This literary concept, rooted in Mikhail Bakhtin's theories, highlights how diverse voices interact without a dominant, authoritative voice, creating a dynamic and multi-dimensional narrative structure. Unlike dialogism, which centers on interaction between voices, polyphony insists on the equal validity and autonomy of each voice, enriching the text's complexity and depth.
Origins and Philosophical Roots of Dialogism
Dialogism finds its origins in the works of Mikhail Bakhtin, a Russian philosopher and literary critic who emphasized the dynamic interaction between multiple voices and perspectives within a text. Rooted in phenomenology and dialogical philosophy, dialogism challenges monologic thinking by advocating for an ongoing dialogue that shapes meaning through the collision of diverse consciousnesses. This concept contrasts with polyphony, which refers more specifically to the coexistence of independently voiced characters in literature, whereas dialogism underscores the continuous, relational process of meaning-making through interaction.
Key Features of Polyphony in Literature
Polyphony in literature features multiple independent voices that coexist without a singular dominating perspective, allowing diverse subjectivities to interact dynamically within the narrative. Each character or voice maintains its own worldview and reasoning, contributing to a complex, multi-layered text that resists authoritative interpretation. This independence of voices differentiates polyphony from dialogism, as it emphasizes heteroglossia and the equal validity of conflicting perspectives within the literary work.
Dialogism vs Polyphony: Core Differences
Dialogism centers on the interaction of multiple voices within a single text, emphasizing the dynamic exchange and mutual influence of varied perspectives. Polyphony, a concept introduced by Mikhail Bakhtin, specifically refers to the coexistence of independent and equally valid voices within a narrative, each maintaining its distinct ideological stance. The core difference lies in dialogism's emphasis on interaction and responsiveness between voices, whereas polyphony highlights the plurality and autonomy of independent voices without subsuming them under a single authorial perspective.
Mikhail Bakhtin’s Contributions to Dialogism and Polyphony
Mikhail Bakhtin profoundly shaped the concepts of dialogism and polyphony by emphasizing the multiplicity of voices within a text, where dialogism refers to the dynamic interaction of diverse perspectives and meanings, and polyphony characterizes a narrative structure featuring independent, unmerged voices. His analysis of Dostoevsky's novels exemplifies polyphony, showcasing characters with fully developed, often conflicting consciousnesses that resist authorial control, embodying genuine dialogic relationships. Bakhtin's theories highlight the intrinsic social and linguistic nature of meaning-making, underscoring the ongoing, open-ended dialogue between varying worldviews in literature and language.
Dialogic Interactions vs Polyphonic Structures
Dialogic interactions emphasize the dynamic exchange between distinct voices, highlighting ongoing communication and responsiveness within discourse. Polyphonic structures refer to the coexistence of multiple independent voices or perspectives that maintain their unique expressions within a unified whole. While dialogism centers on interaction and negotiation between voices, polyphony underscores structural coexistence without necessarily requiring direct engagement.
Real-World Examples: Dialogism in Classic Texts
Dialogism in classic texts manifests through the interaction of distinct voices that challenge or complement each other, such as the conflicting perspectives found in Shakespeare's "Hamlet," where characters engage in continuous exchange of ideas and beliefs. This concept contrasts with polyphony, which features multiple independent voices coexisting without a central authoritative voice, exemplified by Dostoevsky's novels where diverse ideological viewpoints are presented simultaneously. Dialogism emphasizes the dynamic and responsive nature of language, enabling a deeper exploration of truth through continuous dialogue among characters and ideas.
Polyphony in Modern Narratives: Case Studies
Polyphony in modern narratives exemplifies multiple, independent voices coexisting without a single dominating perspective, enriching the storytelling complexity and authenticity. Case studies like Mikhail Bakhtin's analysis of Dostoevsky's novels reveal how characters' diverse viewpoints interact dialogically, reflecting social and ideological heterogeneity. Contemporary literature employs polyphony to challenge monologic narratives, fostering reader engagement through layered, intersecting storylines that mirror fragmented cultural experiences.
Implications for Literary Criticism and Interpretation
Dialogism emphasizes the interaction of multiple voices within a text, promoting an understanding of language as inherently social and dynamic. Polyphony, as conceptualized by Mikhail Bakhtin, identifies distinct, autonomous voices that coexist without being subordinated to a single authorial perspective, fostering interpretations that recognize narrative complexity and ideological diversity. These concepts challenge traditional literary criticism by encouraging analysts to explore the plurality of meanings and resist reductive or single-voiced interpretations, enriching critical engagement with texts.
Dialogism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com