Paronomasia, commonly known as a pun, is a literary device that plays on the multiple meanings or similar sounds of words to create humor or a rhetorical effect. This technique enhances verbal creativity and can make writing more engaging and memorable. Explore the rest of the article to discover how paronomasia can enrich Your communication skills and captivate your audience.
Table of Comparison
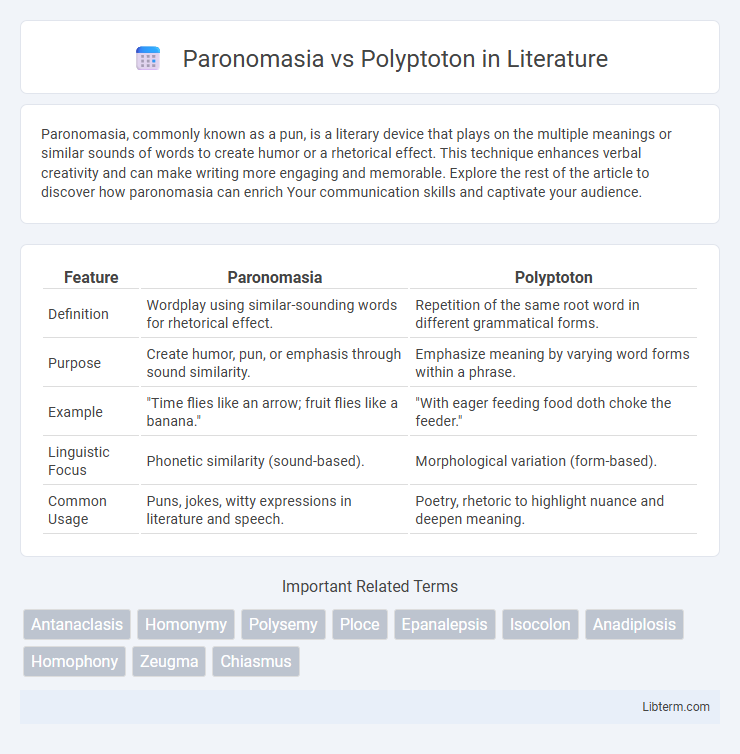
| Feature | Paronomasia | Polyptoton |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wordplay using similar-sounding words for rhetorical effect. | Repetition of the same root word in different grammatical forms. |
| Purpose | Create humor, pun, or emphasis through sound similarity. | Emphasize meaning by varying word forms within a phrase. |
| Example | "Time flies like an arrow; fruit flies like a banana." | "With eager feeding food doth choke the feeder." |
| Linguistic Focus | Phonetic similarity (sound-based). | Morphological variation (form-based). |
| Common Usage | Puns, jokes, witty expressions in literature and speech. | Poetry, rhetoric to highlight nuance and deepen meaning. |
Understanding Paronomasia: Definition and Examples
Paronomasia is a rhetorical device involving the deliberate use of words that sound similar but have different meanings, creating a pun or play on words to enhance expression. Examples include phrases like "time flies like an arrow; fruit flies like a banana," where phonetic similarity drives humor or emphasis. This technique contrasts with polyptoton, which repeats words derived from the same root but with different endings to reinforce a concept rather than create a pun.
Exploring Polyptoton: Meaning and Illustrations
Polyptoton is a rhetorical device where words derived from the same root are repeated within a sentence or phrase, enhancing emphasis and meaning through morphological variation. For example, the phrase "Love is not love which alters when it alteration finds" from Shakespeare's Sonnet 116 illustrates polyptoton by using "alters" and "alteration." This technique creates a rhythmic and semantic resonance that deepens the impact and highlights the nuanced relationship between concepts.
Historical Roots of Paronomasia and Polyptoton
Paronomasia, rooted in ancient Greek rhetoric, originates from the term "paronoma," meaning a pun or play on words that relies on phonetic similarity. Polyptoton, also derived from Greek, involves the repetition of a word in different grammatical forms, enhancing stylistic emphasis and found extensively in classical literature. Both devices reflect the linguistic creativity of antiquity, with paronomasia emphasizing sound-based humor and polyptoton showcasing morphological variation.
Paronomasia vs Polyptoton: Key Differences
Paronomasia involves the use of words that sound similar but have different meanings, creating a pun or wordplay effect, such as "time flies like an arrow; fruit flies like a banana." Polyptoton employs the repetition of words derived from the same root with different endings or forms within a sentence, emphasizing a concept, like "strong and strength." The key difference lies in paronomasia's focus on phonetic similarity for humor or wit, while polyptoton centers on morphological variation to reinforce meaning.
Functions in Rhetoric and Literature
Paronomasia and polyptoton both function as powerful rhetorical devices by exploiting wordplay to enhance meaning and engage readers. Paronomasia relies on the similarity of sounds between words to create humor or emphasize a concept, enriching literary aesthetics and persuasive effect. Polyptoton intensifies the impact of a theme through the repetition of root words in varied grammatical forms, deepening the textual resonance and emotional appeal.
Impact on Reader Engagement and Interpretation
Paronomasia, or punning, stimulates reader engagement by creating humor and wordplay that prompt deeper cognitive involvement and amusement. Polyptoton, the repetition of a root word with different endings, intensifies emotional resonance and thematic emphasis, enhancing interpretive depth. Both devices enrich literary texture but differ in impact: paronomasia triggers immediate wit, while polyptoton fosters reflective interpretation and memorability.
Famous Literary Works Featuring Paronomasia
Paronomasia, or punning, is prominently featured in Shakespeare's *Romeo and Juliet*, where Mercutio's witty wordplay heightens the dramatic tension. This device creates humor and emphasizes double meanings, as seen in the porter scene of *Macbeth* where homophonic puns introduce dark comic relief. In contrast, polyptoton involves repetition of a word's root with different endings, exemplified in John Milton's *Paradise Lost*, but paronomasia's reliance on phonetic similarity makes it a distinctive stylistic tool in famous literary works.
Notable Uses of Polyptoton in Classic Texts
Polyptoton appears prominently in classical literature, such as in Shakespeare's Macbeth where the repetition of "fair" and "fairer" emphasizes the seductive yet perilous nature of ambition. Ancient rhetoric also showcases polyptoton, with Cicero employing it to enhance persuasive impact by repeating words in varied grammatical forms. These notable uses underscore polyptoton's power to create rhythm and reinforce thematic elements in classic texts.
Creative Techniques for Employing Wordplay
Paronomasia employs punning by exploiting words with similar sounds but different meanings, enhancing humor or emphasis through phonetic similarity. Polyptoton involves repetition of words derived from the same root with varied endings, intensifying meaning and stylistic impact by highlighting morphological variations. Both techniques creatively manipulate language structure to enrich textual layers, making wordplay a powerful tool in rhetoric, poetry, and marketing copywriting.
Paronomasia and Polyptoton in Modern Writing
Paronomasia, the deliberate use of wordplay exploiting similar sounds with different meanings, enhances creativity and humor in modern writing, making texts more engaging and memorable. Polyptoton involves the repetition of words derived from the same root with varied endings, reinforcing thematic emphasis and stylistic rhythm in contemporary literature and advertising. Both rhetorical devices contribute to semantic depth, improving reader retention and interpretive richness in digital content and spoken word performances.
Paronomasia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com