Synonymy refers to the relationship between words or phrases that have the same or very similar meanings, enhancing clarity and variety in language use. Understanding synonymy helps you choose the most precise terms for effective communication and enriches vocabulary. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mastering synonymy can improve your writing and speaking skills.
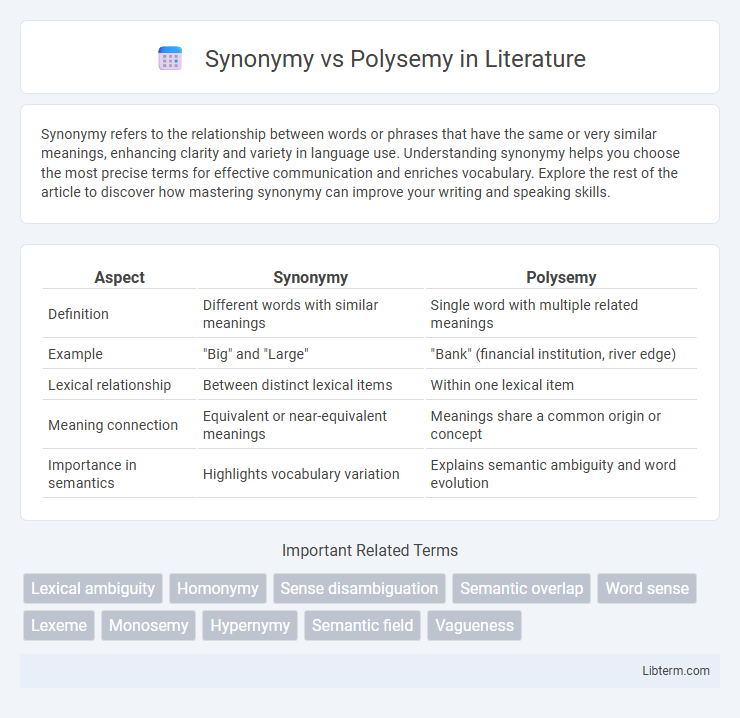
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Synonymy | Polysemy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Different words with similar meanings | Single word with multiple related meanings |
| Example | "Big" and "Large" | "Bank" (financial institution, river edge) |
| Lexical relationship | Between distinct lexical items | Within one lexical item |
| Meaning connection | Equivalent or near-equivalent meanings | Meanings share a common origin or concept |
| Importance in semantics | Highlights vocabulary variation | Explains semantic ambiguity and word evolution |
Introduction to Synonymy and Polysemy
Synonymy refers to the relationship between words that have similar or identical meanings, such as "happy" and "joyful," whereas polysemy describes a single word possessing multiple related meanings, like "bank" referring to a financial institution or the side of a river. Understanding synonymy aids in vocabulary expansion and synonym substitution, while polysemy highlights the importance of context for accurate interpretation. Both concepts are fundamental in lexicography, semantics, and natural language processing for handling word meaning variations.
Defining Synonymy: Concepts and Examples
Synonymy refers to the relationship between words that have the same or very similar meanings, such as "big" and "large," which can often be used interchangeably in many contexts without changing the sentence's meaning. It is essential to distinguish synonyms from related but distinct terms, as perfect synonymy is rare and may depend on context, register, or connotation. Examples of synonymy include pairs like "happy" and "joyful," which convey the same basic emotion despite subtle semantic differences.
Understanding Polysemy: Meaning Variations
Polysemy refers to a single word having multiple related meanings, such as "bank," which can mean a financial institution or the side of a river. Unlike synonymy, where different words share similar meanings, polysemy reflects the flexibility of one word adapting to different contexts. Understanding polysemy is crucial in natural language processing and semantics to accurately interpret meaning variations based on context.
Key Differences Between Synonymy and Polysemy
Synonymy refers to different words with similar meanings, such as "big" and "large," while polysemy involves a single word having multiple related meanings, like "bank" referring to a financial institution or river edge. Synonyms maintain distinct lexical entries, whereas polysemous words share a single lexical entry with multiple senses. Understanding this distinction aids in precise language interpretation, lexical semantics, and natural language processing.
Linguistic Significance of Synonymy
Synonymy in linguistics enhances semantic precision by providing multiple lexical options with similar meanings, facilitating nuanced expression and stylistic variation in language use. It plays a crucial role in language learning, translation, and lexicography by aiding in vocabulary expansion and refining semantic boundaries within a language. Understanding synonymy also contributes to natural language processing tasks, such as word sense disambiguation and semantic search optimization.
The Role of Polysemy in Language Evolution
Polysemy plays a crucial role in language evolution by enabling a single word to develop multiple related meanings, enhancing linguistic efficiency and creativity. This semantic flexibility allows speakers to adapt vocabulary to new contexts without creating entirely new words, facilitating communication and cognitive processing. Unlike synonymy, which involves different words with similar meanings, polysemy enriches a language's expressiveness through interconnected semantic networks within the same lexical item.
Challenges in Distinguishing Synonymy and Polysemy
Distinguishing synonymy and polysemy poses challenges due to semantic overlap and contextual variability, where multiple meanings of a polysemous word may resemble different synonyms. Homogeneity in usage contexts makes it difficult to separate polysemous senses from near-synonymous lexical variants, complicating automatic semantic analysis. Furthermore, the absence of clear semantic boundaries in language resources limits the precision of computational models in differentiating true synonyms from polysemous terms.
Impact on Language Learning and Translation
Synonymy involves different words with similar meanings, challenging language learners to discern subtle contextual differences for accurate usage, while polysemy refers to a single word with multiple related meanings, complicating comprehension and translation due to semantic ambiguity. Effective language learning requires mastering synonym nuances to enhance vocabulary precision, whereas translators must navigate polysemous terms carefully to maintain intended meaning across languages. Misinterpretation of polysemy often leads to translation errors, emphasizing the need for contextual analysis in both linguistic education and professional translation settings.
Methods for Analyzing Synonymy and Polysemy
Methods for analyzing synonymy often involve distributional semantics, measuring word similarity through context vectors derived from large corpora, while polysemy analysis utilizes word sense disambiguation (WSD) algorithms to distinguish multiple meanings of a single word based on contextual clues. Clustering techniques and lexical databases like WordNet are instrumental in mapping synonym sets (synsets) and sense inventories, aiding in automated semantic differentiation and inference. Machine learning models, such as transformers, enhance both synonymy detection and polysemy resolution by leveraging deep contextual embeddings for nuanced semantic interpretation.
Conclusion: Importance in Semantic Studies
Synonymy and polysemy play crucial roles in semantic studies by highlighting how meaning varies within language. Understanding synonymy reveals subtle differences between words with similar meanings, while polysemy demonstrates how a single word can convey multiple related senses. These concepts are essential for accurate language processing, lexicography, and improving natural language understanding systems.
Synonymy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com