Discover the foundation of this insightful text, setting the tone for the themes and ideas explored throughout the article. This foreword provides essential context to help you fully grasp the significance of the following content. Dive into the rest of the article to unlock deeper understanding and valuable perspectives.
Table of Comparison
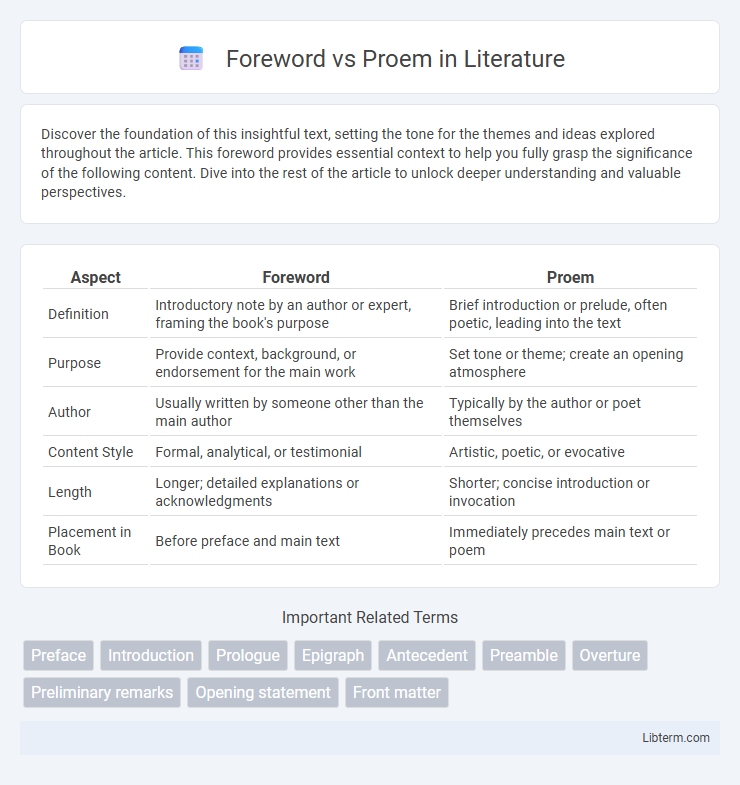
| Aspect | Foreword | Proem |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Introductory note by an author or expert, framing the book's purpose | Brief introduction or prelude, often poetic, leading into the text |
| Purpose | Provide context, background, or endorsement for the main work | Set tone or theme; create an opening atmosphere |
| Author | Usually written by someone other than the main author | Typically by the author or poet themselves |
| Content Style | Formal, analytical, or testimonial | Artistic, poetic, or evocative |
| Length | Longer; detailed explanations or acknowledgments | Shorter; concise introduction or invocation |
| Placement in Book | Before preface and main text | Immediately precedes main text or poem |
Introduction to Foreword and Proem
A foreword is an introductory section written by someone other than the author, often providing credibility, context, or endorsement of the work. A proem, derived from the Greek term "prooimion," serves as a preface or prelude, typically written by the author, introducing the themes or purpose of the text. Both foreword and proem function to prepare readers but differ in authorship and perspective within literary and academic contexts.
Defining Foreword: Purpose and Structure
A foreword serves as an introductory note written by someone other than the author, typically offering credibility, context, or endorsement for the work. Its purpose is to establish the importance and relevance of the book, often including personal anecdotes or insights about the author or subject. Structurally, a foreword is concise, positioned before the main text, and distinct from prefaces or introductions, emphasizing external perspectives rather than the author's own narrative.
What is a Proem? Meaning and Origins
A proem is an introductory section in a literary work, often a poem or speech, designed to prepare the audience for the content that follows by setting the tone or theme. Originating from the Greek word "prooimion," meaning "prelude" or "preface," proems serve as a thematic gateway, outlining the purpose or subject matter. Unlike a foreword, which is typically written by someone other than the author to provide context or endorsement, a proem is usually crafted by the author as an integral part of the text.
Historical Context of Foreword and Proem
The foreword originated in early printed books as an author or notable figure's introductory note, setting historical context and lending authority to the text, often reflecting literary and cultural norms of its era. In contrast, the proem, rooted in classical literature and ancient manuscripts, served as a formal prelude or poetic introduction, framing the narrative's thematic and rhetorical structure. Historical analysis reveals the foreword's evolution as a distinct, personalized commentary, while the proem remains a stylistic device emphasizing tradition and narrative anticipation.
Key Differences Between Foreword and Proem
A foreword is an introductory section written by someone other than the author, providing credibility and context, while a proem is a brief opening or prelude written by the author to set the tone or theme. Forewords often include endorsements or reflections on the work's significance, contrasting with proems which serve as literary or thematic preludes. The key difference lies in authorship and purpose: forewords function as external validation, whereas proems establish the author's initial narrative voice.
Functions in Literature and Publishing
A foreword serves as an introductory note by an author or expert, providing context, credibility, and background to enhance the reader's understanding of the book's significance. A proem, often poetic or lyrical, functions as an opening passage that sets the tone and themes, engaging readers through stylistic and thematic immersion. Both elements guide readers differently: the foreword frames the work's importance, while the proem establishes its literary atmosphere.
Stylistic Features of Foreword vs Proem
The foreword exhibits a formal and authoritative tone, often penned by an expert or notable figure to endorse the main text, enhancing credibility and setting a contextual framework. In contrast, the proem employs a poetic and evocative style, using metaphor, imagery, and lyrical language to capture the reader's imagination and introduce thematic elements. Forewords prioritize clarity and informative content, while proems emphasize aesthetic appeal and emotional resonance through stylistic devices like alliteration and vivid descriptions.
When to Use a Foreword or a Proem
A foreword is typically used by someone other than the author to introduce a book, providing credibility or context, making it ideal for established authors or experts endorsing the work. A proem, traditionally an introductory poem or prose passage, serves to set the tone or theme at the beginning of a literary work, best suited for artistic or thematic purposes. Choose a foreword when seeking external validation or historical framing, and a proem when aiming to evoke mood or philosophical reflection within the text.
Examples from Famous Works
The foreword in famous works, such as George Orwell's "1984," often provides context or author insights written by someone other than the author. In contrast, a proem, seen in classical texts like Homer's "Iliad," serves as an introductory poem or prelude written by the author, setting the thematic tone. Examples highlight how forewords perform external framing while proems offer intrinsic literary commencement.
Conclusion: Choosing the Appropriate Prefatory Element
The conclusion in selecting between a foreword and a proem hinges on their distinct purposes: a foreword provides credibility through endorsement or context from an expert, while a proem introduces the thematic essence of the work creatively. Authors and publishers should assess whether external validation or thematic framing best serves the reader's engagement. Optimal use of each prefatory element enhances the book's reception and aligns with its narrative goals.
Foreword Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com