The prologue sets the stage by introducing key themes and background essential for understanding the story's world. It provides context that enriches your grasp of characters' motivations and plot development. Dive into the rest of the article to uncover how this opening shapes the narrative journey ahead.
Table of Comparison
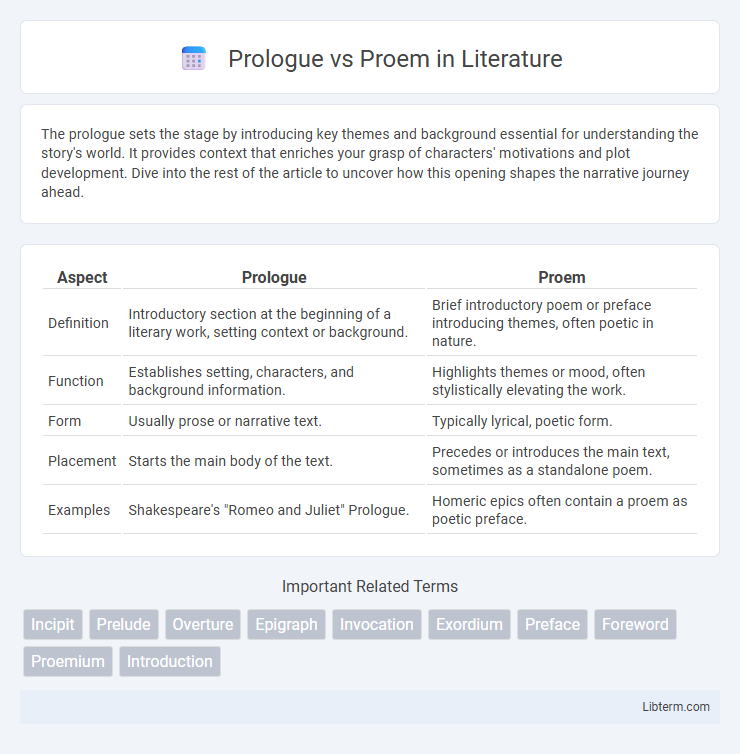
| Aspect | Prologue | Proem |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Introductory section at the beginning of a literary work, setting context or background. | Brief introductory poem or preface introducing themes, often poetic in nature. |
| Function | Establishes setting, characters, and background information. | Highlights themes or mood, often stylistically elevating the work. |
| Form | Usually prose or narrative text. | Typically lyrical, poetic form. |
| Placement | Starts the main body of the text. | Precedes or introduces the main text, sometimes as a standalone poem. |
| Examples | Shakespeare's "Romeo and Juliet" Prologue. | Homeric epics often contain a proem as poetic preface. |
Understanding Prologue and Proem: Key Definitions
A prologue serves as an introductory section in a literary work, providing background information or context that sets the stage for the main narrative. A proem, often used interchangeably but distinct in some traditions, functions as a brief preface or prelude, typically poetic, that introduces themes or tone. Understanding the key definitions reveals that a prologue aims to establish narrative foundation, while a proem emphasizes thematic or stylistic framing.
Historical Origins of Prologue and Proem
The historical origins of the prologue trace back to ancient Greek and Roman theater, where it served as an introductory speech to set the scene, provide background information, and prepare the audience for the unfolding narrative. The proem, rooted in classical epic poetry, functions as a formal preface or invocation, often found in works like Homer's "Iliad" and Virgil's "Aeneid," establishing the poem's theme and poet's purpose. Both terms originate from the Greek word "prologos," but the prologue evolved primarily within dramatic literature, whereas the proem is tied to lyrical and epic traditions.
Structural Placement in Literature
Prologues are positioned at the very beginning of a literary work, setting the stage before the main narrative unfolds, whereas proems serve as introductory passages, often found at the start of chapters or sections. The prologue functions as a standalone segment that provides background or context, while the proem integrates smoothly into the immediate text to prepare readers for upcoming content. Understanding this structural placement distinction aids in analyzing an author's approach to framing themes and guiding reader expectations.
Purpose and Function: Prologue vs Proem
A prologue serves as an introductory section in literature or drama designed to provide background information, set the scene, or introduce themes and characters essential for understanding the main narrative. A proem functions as a prefatory poem or brief introductory statement that establishes the tone or thematic focus without extensive exposition. While both introduce the work, the prologue is more narrative-driven and informative, whereas the proem emphasizes poetic atmosphere and thematic emphasis.
Usage in Different Literary Genres
A prologue typically introduces a story in novels, plays, or epic poetry, setting the stage by providing background or context essential for understanding the main narrative. Proems, often used in classical and lyrical poetry, serve as poetic preambles that establish thematic tone or philosophical reflection without advancing plot. The prologue is more common in fiction and drama, while the proem predominantly appears in poetry, highlighting their distinct roles across literary genres.
Examples of Prologues in Classic Works
Classic literary works feature prologues as introductory sections that set the stage for the narrative, such as the prologue in Shakespeare's "Romeo and Juliet," which outlines the tragic fate of the protagonists. Chaucer's "The Canterbury Tales" employs a prologue to introduce the diverse group of pilgrims and establish the storytelling framework. Similarly, the prologue in Dante's "Divine Comedy" prepares readers for the allegorical journey through Hell, Purgatory, and Paradise, illustrating its role in framing complex themes.
Examples of Proems in Notable Texts
Proems serve as introductory passages that set the tone and thematic framework of literary works, distinct from prologues that often provide background or a separate narrative. Examples of notable proems include the opening verses of Virgil's *Aeneid*, which establish epic grandeur and thematic motifs, and the preamble of Dante's *Divine Comedy*, framing the allegorical journey. Such proems function to prepare readers for the narrative's larger philosophical or poetic exploration, embedding key concepts from the outset.
Comparative Analysis: Prologue and Proem
The comparative analysis of prologue and proem reveals distinct functions and literary significance; a prologue typically serves as an introductory section in drama or narrative, providing context, background, or thematic framing, whereas a proem is a brief poetic preface or preamble that directly addresses the reader or sets the tone. Prologues often elaborate on plot elements and characters, enriching the audience's understanding, while proems emphasize stylistic and rhetorical qualities, establishing mood or purpose with concise, lyrical language. Both forms enhance the reader's engagement but differ in structure, length, and narrative impact within classical and modern literature.
Choosing Between Prologue and Proem as a Writer
Choosing between a prologue and a proem as a writer depends on the narrative purpose and stylistic goals; a prologue offers a detailed introductory scene or background essential for plot understanding, while a proem serves as a concise, poetic preface that sets tone and theme. Writers should assess if the story benefits from immersive exposition typical of a prologue or the thematic, often lyrical framing provided by a proem. Careful consideration of audience engagement and narrative clarity guides the choice, enhancing the work's overall coherence and impact.
Impact on Reader Engagement and Narrative Flow
A prologue typically sets the stage for the main story, offering background details or a glimpse into future events, which can heighten reader anticipation and engagement. A proem, often a poetic or formal preamble, creates an atmospheric tone and establishes thematic elements that influence the narrative's mood and reader immersion. The choice between a prologue and proem affects narrative flow by either directly advancing plot information or providing a stylistic introduction, shaping how seamlessly readers transition into the story.
Prologue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com