Exegesis involves the critical interpretation and explanation of texts, primarily religious scriptures, to uncover their intended meanings and contextual relevance. This process requires examining linguistic, historical, and cultural factors, enabling a deeper understanding of complex passages. Discover how exegesis can enhance your grasp of sacred writings by exploring the insights detailed in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
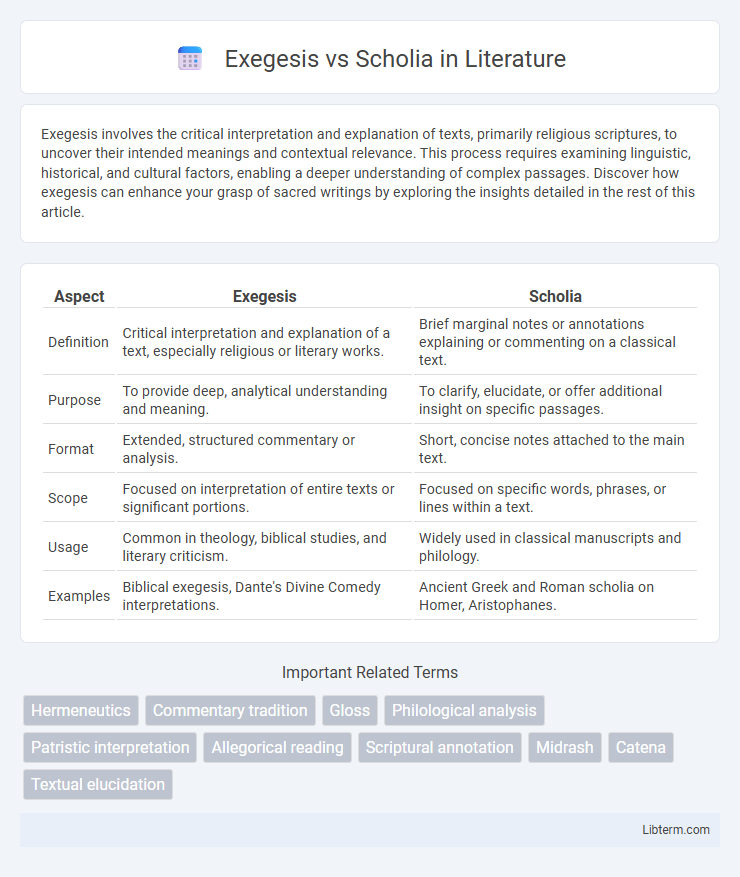
| Aspect | Exegesis | Scholia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Critical interpretation and explanation of a text, especially religious or literary works. | Brief marginal notes or annotations explaining or commenting on a classical text. |
| Purpose | To provide deep, analytical understanding and meaning. | To clarify, elucidate, or offer additional insight on specific passages. |
| Format | Extended, structured commentary or analysis. | Short, concise notes attached to the main text. |
| Scope | Focused on interpretation of entire texts or significant portions. | Focused on specific words, phrases, or lines within a text. |
| Usage | Common in theology, biblical studies, and literary criticism. | Widely used in classical manuscripts and philology. |
| Examples | Biblical exegesis, Dante's Divine Comedy interpretations. | Ancient Greek and Roman scholia on Homer, Aristophanes. |
Introduction to Exegesis and Scholia
Exegesis involves critical explanation and interpretation of religious or literary texts to uncover their intended meaning, often focusing on context, language, and historical background. Scholia are ancient or medieval marginal notes or commentary providing explanations and insights directly linked to specific passages, often clarifying difficult words or concepts. Both exegesis and scholia serve complementary roles in textual analysis, with exegesis offering comprehensive interpretation and scholia providing concise, passage-specific elucidations.
Defining Exegesis
Exegesis is the critical explanation or interpretation of a text, particularly religious scriptures, aiming to uncover the original meaning and context intended by the author. It involves rigorous analysis of language, historical background, and cultural setting to provide an accurate understanding. Unlike scholia, which are marginal notes or brief commentary, exegesis offers a systematic and in-depth exploration of the text's significance.
Understanding Scholia
Scholia are concise ancient or medieval marginal notes or explanations attached to classical texts, providing context, interpretations, or linguistic clarifications that enhance comprehension of the primary work. Unlike extensive exegesis, which offers thorough and systematic critical analysis, scholia serve as immediate, succinct annotations that illuminate specific passages for readers or students. These notes often preserve invaluable historical insights into the reception and interpretation practices of classical literature.
Historical Origins and Development
Exegesis originated in ancient religious traditions as a method for interpreting sacred texts, focusing on uncovering deeper meanings and theological insights through systematic analysis. Scholia developed in classical antiquity as marginal notes or explanatory comments added by scholars to manuscripts, aimed at clarifying language, context, and references within texts. Both exegesis and scholia played crucial roles in the transmission and preservation of knowledge, evolving through medieval and Renaissance periods alongside the growth of textual criticism and hermeneutics.
Purposes and Functions Compared
Exegesis aims to provide a detailed critical explanation and interpretation of a text, often clarifying difficult passages and uncovering deeper meanings. Scholia function as concise marginal notes or commentary that offer brief explanations, interpretations, or textual variants to assist readers in understanding specific elements of the text. While exegesis seeks comprehensive analysis to support theological or literary insights, scholia primarily serve as quick reference aids enhancing immediate comprehension.
Methodologies and Approaches
Exegesis employs a systematic methodology centered on critical analysis of texts, emphasizing historical context, linguistic nuances, and authorial intent to derive accurate interpretations. Scholia utilize a more commentary-based approach, compiling marginal notes and explanations from various ancient scholars, often blending linguistic, grammatical, and interpretive insights without extensive critical evaluation. The exegesis approach prioritizes detailed textual scrutiny and contextual relevance, whereas scholia serve as supplementary interpretive tools reflecting collective scholarly traditions.
Key Differences in Interpretation
Exegesis involves critical explanation and systematic interpretation of a text, focusing on uncovering the original meaning based on linguistic, historical, and cultural context. Scholia refer to marginal notes or explanatory comments by ancient scholars that provide brief clarifications, interpretations, or textual variants without extensive analysis. Key differences lie in the depth of analysis--exegesis delivers comprehensive interpretation and theological insight, whereas scholia offer concise annotations aimed at supporting immediate understanding.
Examples from Classical Texts
Exegesis offers detailed interpretations of classical texts like Homer's epics, explaining thematic elements and cultural contexts, such as analyzing the role of fate in the *Iliad*. Scholia provide concise marginal notes or summaries on these same works, exemplified by the Byzantine scholia on Sophocles' *Oedipus Rex*, which clarify linguistic nuances and textual variants. Together, exegesis and scholia enrich understanding by combining in-depth analysis with accessible commentary.
Impact on Modern Scholarship
Exegesis provides critical interpretation of religious or classical texts, shaping theological discourse and guiding contemporary hermeneutics. Scholia, as ancient marginal notes or commentaries, preserve historical perspectives that enrich understanding of primary texts and support philological research. The combined influence of exegesis and scholia advances modern scholarship by fostering comprehensive textual analysis and contextual interpretation.
Conclusion: Exegesis vs Scholia
Exegesis meticulously interprets ancient texts by analyzing linguistic, historical, and cultural contexts to reveal original meanings, while scholia provide brief, often explanatory or critical marginal notes that supplement the main text. Both serve essential roles in understanding classical literature, yet exegesis offers comprehensive analysis, whereas scholia function as concise interpretative aids. Integrating detailed exegesis with scholia enriches textual comprehension and scholarly insight.
Exegesis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com