Evolutionary analysis examines how species adapt and change through genetic variations, natural selection, and environmental pressures over time. By understanding these mechanisms, researchers can trace the lineage of organisms and predict future evolutionary trends. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your knowledge of how evolutionary analysis shapes our understanding of biodiversity.
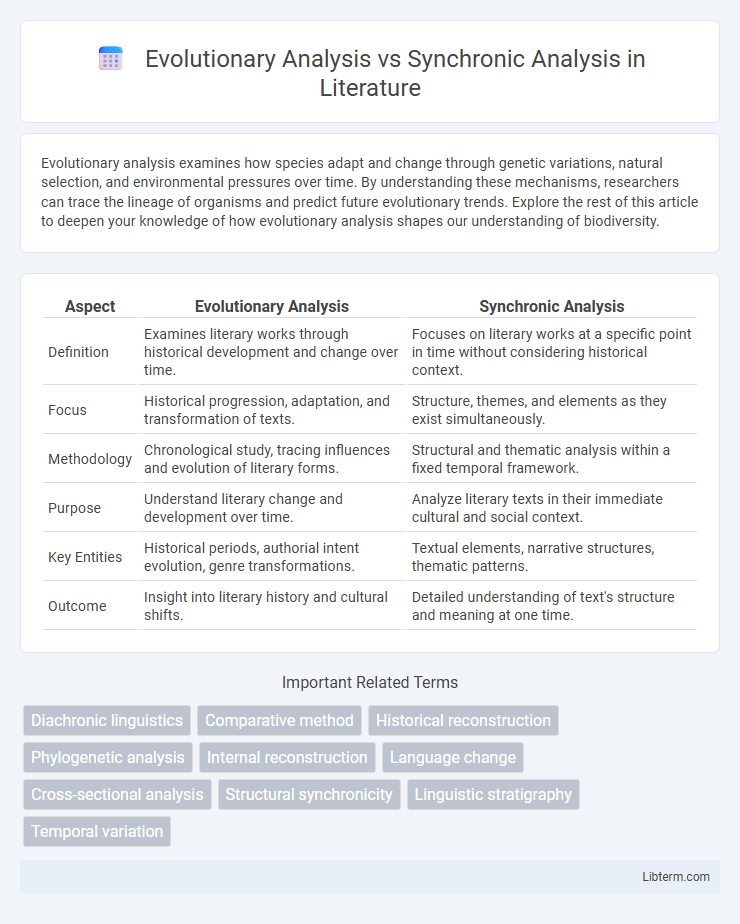
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Evolutionary Analysis | Synchronic Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Examines literary works through historical development and change over time. | Focuses on literary works at a specific point in time without considering historical context. |
| Focus | Historical progression, adaptation, and transformation of texts. | Structure, themes, and elements as they exist simultaneously. |
| Methodology | Chronological study, tracing influences and evolution of literary forms. | Structural and thematic analysis within a fixed temporal framework. |
| Purpose | Understand literary change and development over time. | Analyze literary texts in their immediate cultural and social context. |
| Key Entities | Historical periods, authorial intent evolution, genre transformations. | Textual elements, narrative structures, thematic patterns. |
| Outcome | Insight into literary history and cultural shifts. | Detailed understanding of text's structure and meaning at one time. |
Introduction to Linguistic Analysis Methods
Evolutionary analysis examines language change over time by studying historical data, tracking phonetic, morphological, and syntactic shifts. Synchronic analysis investigates language structures at a specific point, emphasizing contemporary grammar, semantics, and phonology for descriptive purposes. These linguistic analysis methods provide complementary perspectives essential for understanding language development and current usage patterns.
Defining Evolutionary Analysis
Evolutionary analysis examines language change and development over time, tracing the historical progression of phonetics, syntax, and semantics within linguistic systems. It focuses on diachronic data to understand how languages evolve through processes such as sound shifts, morphological changes, and semantic drift. This method contrasts with synchronic analysis, which studies language at a specific point without considering temporal transformations.
Understanding Synchronic Analysis
Synchronic analysis examines linguistic or cultural phenomena at a specific point in time, providing a snapshot of structure and relationships without considering historical development. This approach enables researchers to understand the internal system and functional aspects of language or culture as they exist simultaneously. Synchronic analysis complements evolutionary analysis by offering insights into current states, facilitating comparisons and highlighting patterns independent of diachronic changes.
Historical Development of Analytical Approaches
Evolutionary analysis examines changes and adaptations over time, emphasizing historical development and transformation within systems or languages. Synchronic analysis, by contrast, focuses on a specific point in time, analyzing structures without considering their historical context. Understanding the evolution of analytical approaches reveals a shift from purely synchronic methods, prevalent in early 20th-century linguistics with Ferdinand de Saussure, to integrative frameworks that incorporate diachronic perspectives, reflecting a more comprehensive understanding of dynamic processes.
Core Principles of Evolutionary Analysis
Evolutionary Analysis focuses on understanding how systems, behaviors, or languages change and develop over time by examining historical processes and the dynamics of adaptation. It prioritizes diachronic data, emphasizing temporal sequences, variation, and selective pressures that drive gradual transformation. Core principles include cumulative change, adaptation to environmental shifts, and the branching patterns of descent with modification.
Key Concepts in Synchronic Analysis
Synchronic analysis centers on examining a language at a specific point in time, emphasizing structural relationships and usage patterns without considering historical development. Key concepts include phonemes, morphosyntactic structures, and semantic roles within contemporary linguistic systems. This approach contrasts with evolutionary analysis by prioritizing systematic description over diachronic change.
Comparative Methodology: Evolutionary vs Synchronic
Evolutionary analysis in comparative methodology examines languages or cultures over time, emphasizing historical development and transformational changes to uncover genetic relationships. Synchronic analysis focuses on languages or cultures at a specific point in time, prioritizing structural and functional features without considering historical context. This contrast allows evolutionary approaches to trace lineage and origins, while synchronic studies highlight systemic patterns and contemporary interactions.
Applications in Language Studies
Evolutionary analysis examines language change over time, revealing how phonetics, grammar, and vocabulary develop across historical periods, crucial for diachronic linguistics and language reconstruction. Synchronic analysis focuses on the structure and use of language at a specific point, enhancing understanding of current linguistic systems, dialect variations, and sociolinguistic dynamics. Both approaches are essential in language studies, with evolutionary analysis informing historical language relationships while synchronic analysis supports contemporary language teaching, computational linguistics, and discourse analysis.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
Evolutionary analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of linguistic changes over time, revealing the historical development and root causes of language variation, but it may overlook current language usage and context. Synchronic analysis offers detailed insights into the structure and function of a language at a specific point, facilitating clear descriptions of grammatical rules and usage patterns, yet it lacks the ability to explain language evolution or historical influences. Each approach complements the other by balancing diachronic perspectives with contemporary linguistic states, though their limitations emphasize the need for integrated methodologies in language research.
Future Directions in Linguistic Analysis
Future directions in linguistic analysis emphasize integrating evolutionary analysis with synchronic analysis to better understand language development and current usage patterns. Advances in computational modeling and big data analytics enable researchers to trace diachronic changes while capturing synchronic variability across languages and dialects. Embracing interdisciplinary approaches, including cognitive science and sociolinguistics, enhances predictive models for language evolution and real-time linguistic shifts.
Evolutionary Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com