Hyperbole is a powerful literary device that employs deliberate exaggeration to emphasize a point or evoke strong emotions. It enhances storytelling by creating vivid imagery and amplifying the impact of descriptions, making your message more memorable. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how hyperbole can transform your writing effectively.
Table of Comparison
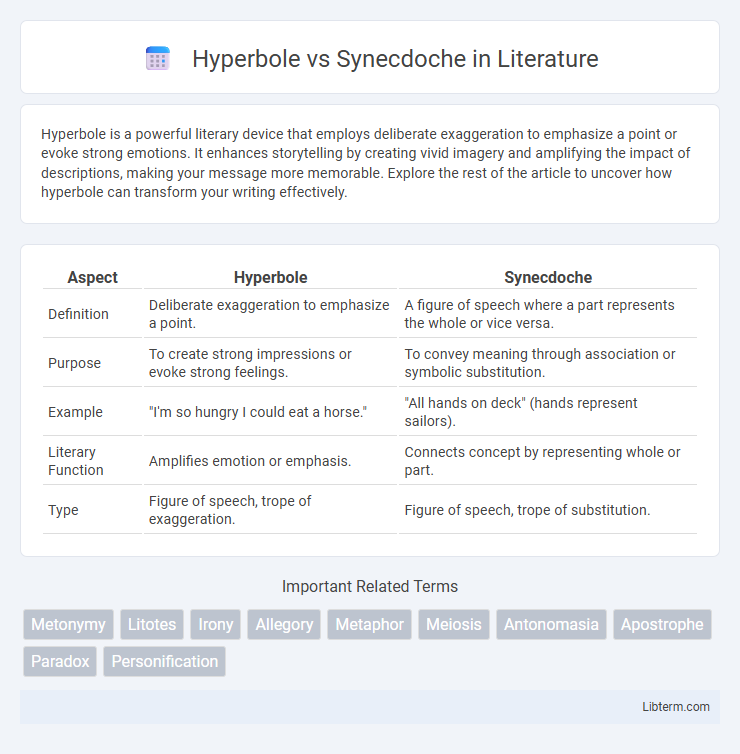
| Aspect | Hyperbole | Synecdoche |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate exaggeration to emphasize a point. | A figure of speech where a part represents the whole or vice versa. |
| Purpose | To create strong impressions or evoke strong feelings. | To convey meaning through association or symbolic substitution. |
| Example | "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse." | "All hands on deck" (hands represent sailors). |
| Literary Function | Amplifies emotion or emphasis. | Connects concept by representing whole or part. |
| Type | Figure of speech, trope of exaggeration. | Figure of speech, trope of substitution. |
Understanding Hyperbole: Definition and Purpose
Hyperbole is a rhetorical device that involves deliberate exaggeration to emphasize a point or evoke strong feelings, often enhancing storytelling or persuasive communication. It serves to create vivid imagery and emphasize emotions by overstating facts beyond literal truth, distinguishing it from more literal expressions like synecdoche. Understanding hyperbole's purpose aids in recognizing when language aims to dramatize rather than precisely describe reality.
Synecdoche Explained: Meaning and Usage
Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which a part of something is used to represent the whole, or vice versa, enhancing expressive language by creating a vivid connection between the fragment and the entire entity. For example, referring to a car as "wheels" exemplifies synecdoche by using a component to signify the complete object, which helps convey meaning succinctly and powerfully. This rhetorical device is frequently employed in literature, advertising, and everyday speech to emphasize certain attributes and evoke stronger imagery.
Key Differences Between Hyperbole and Synecdoche
Hyperbole is a figure of speech that involves deliberate exaggeration for emphasis or effect, often used to create strong impressions or evoke emotions. Synecdoche is a rhetorical device in which a part represents the whole or vice versa, commonly used to create vivid imagery or simplify complex ideas. The key difference lies in hyperbole's exaggeration versus synecdoche's substitution of a part for the whole, impacting how meaning is conveyed in language.
Historical Origins of Hyperbole and Synecdoche
Hyperbole originated in ancient Greek rhetoric, where it was used as an exaggerated expression to evoke strong emotions and emphasize a point. Synecdoche, also rooted in classical literature, emerged as a figure of speech that substitutes a part for the whole or vice versa, widely utilized in both Greek and Latin texts to convey complex ideas succinctly. Both devices have been integral to literary and rhetorical traditions, influencing various cultures and languages throughout history.
Common Examples of Hyperbole in Literature
Hyperbole, a deliberate exaggeration for emphasis or effect, frequently appears in literature through examples like "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse" and "I've told you a million times." These expressions amplify emotions or situations beyond reality, creating vivid imagery and strong impressions for readers. In contrast, synecdoche uses a part to represent the whole, such as "all hands on deck," serving distinct rhetorical purposes from hyperbole.
Classic Instances of Synecdoche in Writing
Classic instances of synecdoche in writing include expressions like "all hands on deck," where "hands" represent sailors, and "wheels" to mean a car, showcasing part-to-whole relationships. This figure of speech effectively conveys vivid imagery and nuanced meaning by substituting a part for the whole or vice versa. Hyperbole, contrastingly, relies on deliberate exaggeration for emphasis, such as saying "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse."
Effects on Reader Perception: Hyperbole vs Synecdoche
Hyperbole amplifies emotions and creates heightened intensity, making readers perceive situations as extraordinary or exaggerated, often evoking strong feelings of urgency or humor. Synecdoche fosters a deeper connection by emphasizing a part to represent the whole, encouraging readers to engage intellectually and interpret nuanced meanings. The distinct cognitive engagement elicited by hyperbole versus synecdoche shapes readers' emotional and analytical responses differently, influencing tone and impact.
Why Writers Use Hyperbole and Synecdoche
Writers use hyperbole to create emphasis and evoke strong emotions by exaggerating details beyond the literal truth, making descriptions more vivid and impactful. Synecdoche allows writers to represent a whole by mentioning a part, or vice versa, enriching the text with symbolic meaning and enhancing readers' engagement through recognizable, concrete imagery. Both devices serve to deepen meaning and convey complex ideas succinctly and memorably in literary and rhetorical contexts.
Practical Tips: Choosing the Right Figure of Speech
Selecting between hyperbole and synecdoche depends on the rhetorical goal: hyperbole exaggerates for emphasis or humor, making statements more impactful or memorable, while synecdoche uses a part to represent the whole or vice versa, creating vivid, concise imagery. Use hyperbole when you want to highlight feelings or size dramatically, especially in persuasive or informal contexts. Opt for synecdoche to deepen meaning with symbolic representation, particularly in literary or descriptive writing to connect ideas efficiently.
Hyperbole vs Synecdoche: Impact on Style and Tone
Hyperbole amplifies emotions and imagery through deliberate exaggeration, intensifying the style to evoke strong feelings or dramatic effects. Synecdoche adds depth and nuance by substituting a part for the whole or vice versa, creating a more intricate and layered tone. The use of hyperbole often results in a bold, emphatic style, while synecdoche lends subtlety and sophistication to the narrative voice.
Hyperbole Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com