Alliteration enhances writing by repeating initial consonant sounds, creating rhythm and emphasis that engage readers. This literary device can make your message more memorable and enjoyable, especially in poetry, speeches, and advertising. Explore the rest of the article to discover techniques for mastering alliteration in your writing.
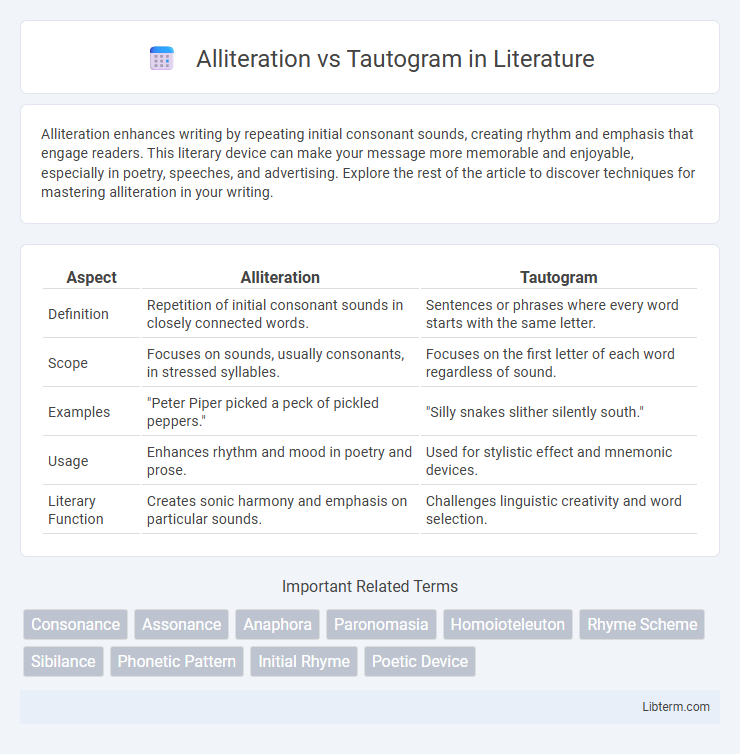
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Alliteration | Tautogram |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetition of initial consonant sounds in closely connected words. | Sentences or phrases where every word starts with the same letter. |
| Scope | Focuses on sounds, usually consonants, in stressed syllables. | Focuses on the first letter of each word regardless of sound. |
| Examples | "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers." | "Silly snakes slither silently south." |
| Usage | Enhances rhythm and mood in poetry and prose. | Used for stylistic effect and mnemonic devices. |
| Literary Function | Creates sonic harmony and emphasis on particular sounds. | Challenges linguistic creativity and word selection. |
Understanding Alliteration: Definition and Examples
Alliteration is the repetition of the same initial consonant sound in closely positioned words, enhancing rhythm and memorability in language. For example, phrases like "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers" showcase alliteration by repeating the "p" sound. This literary device is commonly used in poetry, tongue twisters, and brand names to create a pleasing auditory effect and emphasize key concepts.
What Is a Tautogram? Key Features Explained
A tautogram is a form of alliteration where every word in a sentence or phrase begins with the same letter or sound, creating a uniform phonetic pattern. Key features of a tautogram include strict adherence to the initial letter, rhythmic flow, and enhanced memorability due to repetitive consonance. Unlike general alliteration, which may only repeat consonant sounds intermittently, tautograms maintain consistent initial sounds throughout the entire text or phrase.
Alliteration vs Tautogram: Core Differences
Alliteration involves the repetition of the initial consonant sound in closely positioned words, enhancing rhythm and emphasis within a phrase or sentence. Tautogram is a type of alliteration where every word in a sentence or phrase begins with the same letter, creating a more restrictive and uniform pattern. The core difference lies in scope: alliteration focuses on sound repetition typically in a sequence, while tautogram requires every word to start with the identical letter, making it a specialized subset of alliteration.
Historical Roots of Alliteration and Tautogram
Alliteration, rooted in Old English and ancient Germanic poetry, historically served as a mnemonic device in oral traditions, emphasizing the repetition of initial consonant sounds to create rhythm and cohesion. Tautogram, a subset of alliteration dating back to classical rhetoric, focuses on entire words beginning with the same letter, often employed for stylistic emphasis in Latin and medieval manuscripts. Both devices highlight the evolution of linguistic patterns used to enhance literary aesthetics and memory through sound repetition.
Usage in Poetry: Alliteration vs Tautogram
Alliteration involves the repetition of initial consonant sounds across neighboring words to create rhythm and mood, often enhancing musicality and emphasis within a poem. Tautogram is a specific form of alliteration where every word in a line or verse starts with the same letter, intensifying the sonic effect and challenging poetic creativity. Poets use alliteration for subtle sound patterns while tautograms demand deliberate word choice, both enriching the auditory experience of poetry.
Creative Writing Applications
Alliteration emphasizes the repetition of initial consonant sounds within closely connected words, enhancing rhythm and mood in poetry and prose, making it valuable for engaging readers and creating memorable phrases. Tautograms, a specific form of alliteration where every word in a sentence or phrase begins with the same letter, challenge writers to craft inventive and cohesive sentences, often used for stylistic impact or mnemonic devices. Both techniques provide creative writers with tools to enrich language texture, emphasize key themes, and experiment with linguistic patterns.
Language and Sound Patterns
Alliteration emphasizes the repetition of consonant sounds at the beginning of closely placed words, enhancing rhythm and musicality in language. Tautogram requires every word in a phrase or sentence to start with the same letter, creating a more restrictive and visually uniform pattern. Both sound patterns influence phonetic harmony, but alliteration prioritizes auditory effect while tautograms focus on orthographic consistency.
Tips for Crafting Effective Alliterations
Effective alliterations emphasize the repetition of initial consonant sounds within closely connected words, enhancing rhythm and memorability. Choosing strong, vivid words with matching sounds, maintaining natural flow, and avoiding forced or excessive repetition are key tips for crafting impactful alliterations. Integrating alliterations seamlessly into the context ensures clarity while enriching the text's aesthetic appeal.
How to Write Compelling Tautograms
Crafting compelling tautograms involves selecting words that not only begin with the same initial letter but also create meaningful and engaging content, enhancing the alliterative effect. Focus on varying sentence structure and incorporating vivid, descriptive language to maintain reader interest while reinforcing the repeated consonant sound. Employ precise vocabulary and rhythmic flow to elevate the tautogram from mere repetition to a captivating literary device.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Alliteration and tautograms both emphasize repeated initial sounds, but common mistakes arise when they are confused: alliteration requires repetition of consonant sounds in closely connected words, while tautograms mandate every word to start with the same letter. Writers often misuse tautogram by including words with different initial letters that share the same sound, or overlook the phonetic focus required in alliteration. Clarifying the distinction and carefully selecting words based on sound versus letter can avoid these errors and ensure precise use of both literary devices.
Alliteration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com