Permanence signifies the enduring quality of something that remains unchanged over time, offering stability and reliability in an ever-evolving world. This concept is crucial in various fields, from architecture to personal relationships, where lasting impact and dependability are valued. Explore this article further to understand how permanence influences your life and decisions.
Table of Comparison
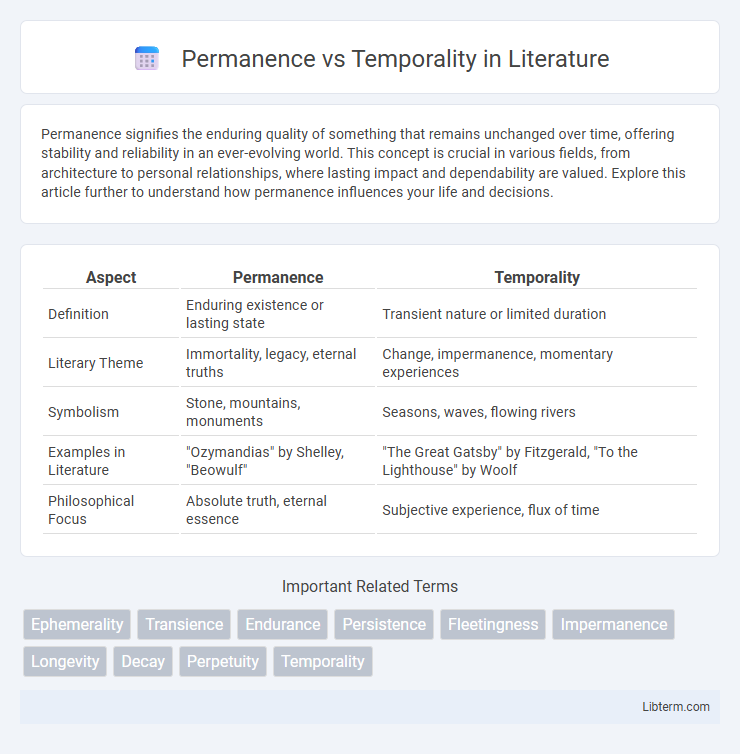
| Aspect | Permanence | Temporality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enduring existence or lasting state | Transient nature or limited duration |
| Literary Theme | Immortality, legacy, eternal truths | Change, impermanence, momentary experiences |
| Symbolism | Stone, mountains, monuments | Seasons, waves, flowing rivers |
| Examples in Literature | "Ozymandias" by Shelley, "Beowulf" | "The Great Gatsby" by Fitzgerald, "To the Lighthouse" by Woolf |
| Philosophical Focus | Absolute truth, eternal essence | Subjective experience, flux of time |
Understanding Permanence and Temporality
Understanding permanence involves recognizing concepts or states that endure over time, maintaining consistent existence or influence without significant change. Temporality refers to the transient, time-bound nature of phenomena, emphasizing change, progression, and impermanence. Analyzing permanence and temporality together clarifies how stability and change coexist in philosophical, cultural, and natural contexts.
Historical Perspectives on Lasting Change
Historical perspectives on lasting change emphasize the tension between permanence and temporality in societal structures, cultural norms, and political institutions. Scholars analyze how certain innovations, revolutions, or reforms achieve enduring impact, while others remain transient due to contextual shifts or resistance. The study of historical continuity and disruption highlights key factors such as institutional resilience, collective memory, and socio-economic dynamics influencing the durability of change.
The Psychology Behind Seeking Permanence
The psychology behind seeking permanence reveals humans' innate desire for stability and control amid life's uncertainties. This drive manifests in forming lasting relationships, creating long-term goals, and valuing traditions to establish a sense of security and identity. Studies in developmental and social psychology demonstrate that perceived permanence contributes significantly to emotional well-being and resilience.
Embracing the Beauty of Transience
Embracing the beauty of transience reveals the profound value in impermanence, highlighting that moments of change foster growth, creativity, and renewal. Temporal experiences evoke deep appreciation and mindfulness, encouraging presence in fleeting beauty rather than attachment to permanence. This perspective enriches life's texture and cultivates resilience by accepting transformation as an essential and enriching aspect of existence.
Permanence in Art and Architecture
Permanence in art and architecture emphasizes the creation of enduring structures and artworks designed to withstand the test of time, reflecting cultural values and historical legacy. Materials such as stone, bronze, and concrete are selected for their durability and resistance to environmental decay, ensuring lasting physical presence. This focus on permanence not only preserves artistic expression but also anchors collective memory across generations.
Temporal Trends in Society and Culture
Temporal trends in society and culture reflect shifting values, technological advancements, and evolving social norms that reshape collective behavior and cultural expressions. These trends emphasize temporality, highlighting transient phenomena such as fashion cycles, viral internet content, and political movements. Despite this flux, underlying cultural permanence persists through enduring traditions, language preservation, and long-established institutions, providing continuity amid ongoing temporal change.
The Role of Technology: Permanent vs. Ephemeral
Technology shapes the balance between permanence and temporality by determining how data is stored and accessed, with cloud storage enabling long-term preservation and social media platforms promoting ephemeral content like stories and snaps. Innovations in data encryption and blockchain foster enduring records, while real-time messaging apps emphasize transient communication tailored for instant connection. This dual role of technology influences cultural memory and information retention, highlighting the evolving nature of digital permanence versus ephemerality.
Personal Identity: Fixed or Ever-Changing?
Personal identity grapples with the tension between permanence and temporality, questioning whether the self remains fixed or evolves continuously. Psychological continuity theories emphasize memory and consciousness as anchors of a stable identity over time, while narrative identity perspectives highlight the fluidity of personal stories shaped by ongoing experiences. Neuroscientific research reveals that brain plasticity contributes to an ever-changing self, challenging the notion of a permanent, unalterable core identity.
Navigating Relationships: Lasting Bonds vs. Fleeting Connections
Navigating relationships involves balancing permanence and temporality, where lasting bonds foster deep trust, emotional support, and shared growth, crucial for long-term well-being. Fleeting connections, often characterized by brief interactions and limited emotional investment, offer flexibility and diverse social exposure without heavy commitments. Understanding the dynamics between enduring relationships and temporary encounters enables effective social navigation and emotional resilience.
Finding Balance Between Permanence and Temporality
Striking a balance between permanence and temporality involves integrating lasting values with adaptive flexibility to ensure resilience in an ever-changing environment. Emphasizing core principles provides stability, while embracing change allows for innovation and growth. Effective decision-making requires assessing when to uphold tradition and when to implement timely adjustments for sustainable success.
Permanence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com