Syllepsis is a rhetorical device where a single word governs or modifies two or more words, though the word applies differently to each. This figure of speech creates a striking effect by blending together disparate ideas or meanings, often with humorous or clever results. Discover how syllepsis can enhance your writing and add layers of meaning by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
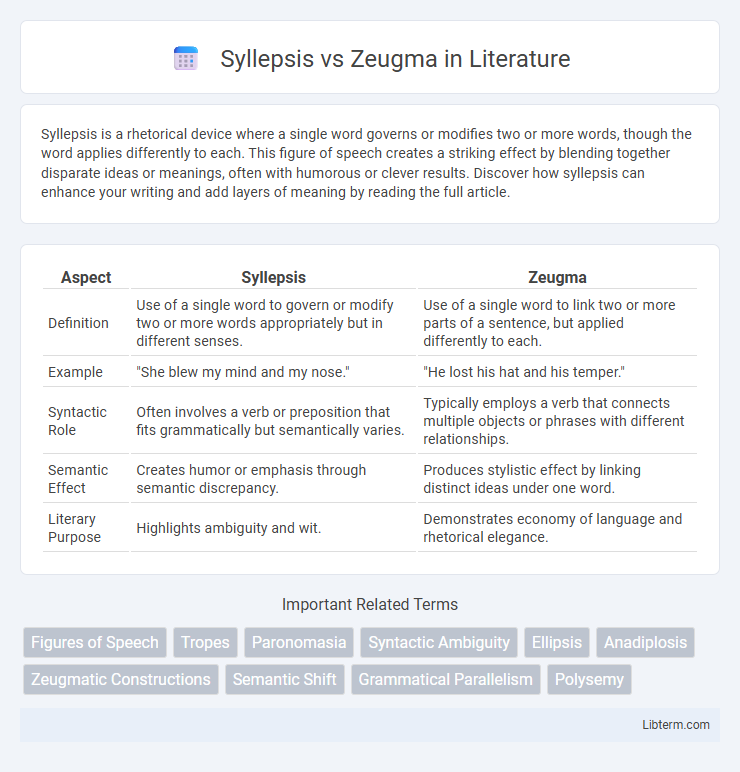
| Aspect | Syllepsis | Zeugma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of a single word to govern or modify two or more words appropriately but in different senses. | Use of a single word to link two or more parts of a sentence, but applied differently to each. |
| Example | "She blew my mind and my nose." | "He lost his hat and his temper." |
| Syntactic Role | Often involves a verb or preposition that fits grammatically but semantically varies. | Typically employs a verb that connects multiple objects or phrases with different relationships. |
| Semantic Effect | Creates humor or emphasis through semantic discrepancy. | Produces stylistic effect by linking distinct ideas under one word. |
| Literary Purpose | Highlights ambiguity and wit. | Demonstrates economy of language and rhetorical elegance. |
Understanding Syllepsis and Zeugma
Syllepsis and zeugma are rhetorical devices that involve a single word linking two parts of a sentence but differ in their semantic relationships; syllepsis connects a single word to two others in grammatically or logically different ways, often creating a witty or humorous effect, while zeugma uses one word to govern or modify two or more words, typically in the same grammatical or logical sense. Understanding syllepsis involves recognizing how one word applies differently to each connected element, often leading to a shift in meaning or interpretation. Grasping zeugma requires identifying how one word unites multiple elements under a consistent grammatical role, enhancing conciseness and stylistic impact.
Origins and Etymology
Syllepsis originates from the Greek word "syllepsis," meaning "a taking together," emphasizing the unity of the construction despite differences in governing elements. Zeugma, derived from the Greek "zeugnynai," meaning "to yoke" or "to join," highlights the linking of words in a sentence by a shared word, often creating a stylistic effect. Both terms describe rhetorical devices involving a single word governing multiple parts, but their roots reflect subtle differences in the concept of connection or binding.
Defining Syllepsis: Key Characteristics
Syllepsis is a rhetorical device where a single word, often a verb or an adjective, governs or modifies two or more different words, but the word applies in different senses to each. Key characteristics include the word's ability to create a play on meanings, producing a witty or ironic effect by simultaneously linking literal and figurative interpretations. Unlike zeugma, which typically applies one word to multiple others in a uniform or related way, syllepsis highlights the contrast in meanings governed by the single word.
Defining Zeugma: Key Characteristics
Zeugma is a literary device in which a single word, often a verb or an adjective, governs two or more words, though the word applies differently in meaning to each. Unlike syllepsis, where the governing word agrees grammatically and semantically with only one of the objects, zeugma creates a striking or humorous effect by linking disparate elements in a single phrase. Key characteristics of zeugma include the intentional play on multiple meanings of a word and the blending of different contexts within one sentence structure.
Structural Differences Between Syllepsis and Zeugma
Syllepsis involves a single word, often a verb or adjective, that governs two or more parts of a sentence, but applies differently to each, creating a shift in meaning or grammatical function. Zeugma occurs when one word governs multiple parts of a sentence in the same way, maintaining consistent meaning and grammatical relationship across elements. The key structural difference lies in Syllepsis's varied application of one word to multiple elements versus Zeugma's uniform application.
Function and Purpose in Rhetoric
Syllepsis and zeugma function as rhetorical devices that create a connection between a single word and multiple parts of a sentence, enhancing succinctness and wit. Syllepsis relies on a single word governing multiple meanings or senses, often producing a humorous or clever effect by semantic ambiguity. Zeugma links one word to multiple others in different syntactic or semantic relationships, serving to produce economy of language and emphasize relationships among ideas.
Famous Examples in Literature
Syllepsis and zeugma are rhetorical devices that link a single word to two or more words, often creating a surprising or witty effect. A famous example of zeugma is from Alexander Pope's "The Rape of the Lock": "Here Thou, Great Anna, Whom three Realms obey, Dost sometimes Counsel take--and sometimes Tea," where "take" applies differently to "counsel" and "tea." In literature, syllepsis often involves a word used both literally and figuratively, as in Mark Twain's line: "You held your breath and the door for me," combining physical and metaphorical actions.
Common Misconceptions and Overlaps
Syllepsis and zeugma are often confused due to their shared feature of linking a single word to multiple parts of a sentence, yet syllepsis specifically involves a single word grammatically or logically fitting differently with the connected elements. A common misconception is treating any instance of a word governing two phrases as zeugma, whereas zeugma typically unifies phrases in a more stylistically nuanced or unexpected way, often creating a rhetorical effect. Overlaps occur because both figures involve economy of expression and surprise, but distinguishing them requires analyzing how the governing word interacts semantically and syntactically with the connected elements.
Impact on Reader and Stylistic Effect
Syllepsis and zeugma both create a striking stylistic effect by linking multiple phrases with a single word, but they differ in their impact on the reader. Syllepsis often evokes humor or surprise by applying one word to multiple meanings, sharpening the reader's attention to language play and dual meanings. Zeugma tends to produce a more clever or concise effect, enhancing textual unity and rhythmic flow, which engages readers through stylistic sophistication and cognitive contrast.
Tips for Using Syllepsis and Zeugma in Writing
Effective use of syllepsis and zeugma requires understanding their subtle differences: syllepsis involves a single word governing two or more words with a different sense for each, while zeugma uses one word to link two others in a related, though often unexpected, way. Employ syllepsis to create witty, succinct expressions that emphasize contrast or dual meanings, ensuring clarity to avoid confusion. Employ zeugma for stylistic elegance and impact by coordinating related elements, but balance it carefully to maintain coherence and enhance the text's rhetorical effect.
Syllepsis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com